The agrirouter is a universal data exchange platform for farmers and agricultural contractors that makes it possible to connect machinery and agricultural software, regardless of vendor or manufacturer. Agrirouter does not save data; it transfers data. As a universal data exchange platform, agrirouter fills a gap on the way to Farming 4.0. Its underlying concept unites cross-vendor and discrimination-free data transfer. You retain full control over your data. Even data exchange with service providers, (e.g., agricultural contractors) and other partners is uncomplicated: Data is very rapidly transferred via the online connection, and if you wish, is intelligently connected to other datasets.
The LMIS AG is a recognised german IT service company, certified according to DIN EN ISO 9001:2015 and based in Osnabrück, Berlin, Friedland and Wuppertal. Our core competence is the individual development, optimization and support of IT solutions. We also provide professional IT consulting services and training courses. We have been supporting the whole project during the development in the field of test management and are currently responsible for the development support of the platform.
We are active maintainers of the SDK and are using the SDK for internal testing as well. Therefore, we have a high interest in a stable and usable interface to connect to the agrirouter.
Feel free to get in touch by visiting our website or contacting us via GitHub.
This project contains the SDK for the communication with the agrirouter. Everything you need for the onboarding process, secure communication, and much more.
The release workflow follows the Microsoft DevOps Release Model where a release shows up as a branch in the repository.
The update for the new release includes some breaking changes. To have a rough overview of what has to be done to have the new features from 2.x in your application, please see the following migration / update guide when updating.
The first step is to update the coordinates of the dependencies. With the release 2.x, the coordinates changed to a new name and a new version.
<dependency>
<groupId>com.agrirouter.api</groupId>
<artifactId>agrirouter-sdk-java-api</artifactId>
<version>2.0.0</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.agrirouter.api</groupId>
<artifactId>agrirouter-sdk-java-impl</artifactId>
<version>2.0.0</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.agrirouter.api</groupId>
<artifactId>agrirouter-sdk-java-convenience</artifactId>
<version>2.0.0</version>
</dependency>
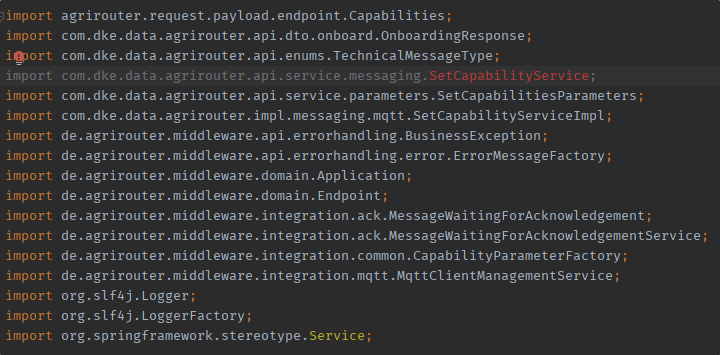
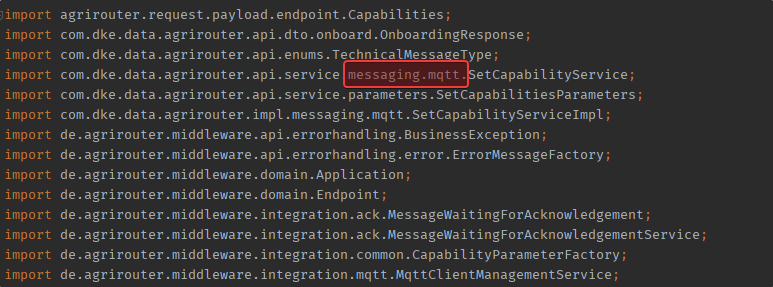
Since the package declaration was updated along with the coordinates, there will be compiler errors that should be fixed. Some classes have moved to a more meaningful package.
The new package declaration added the protocol part (http or in this case the mqtt).
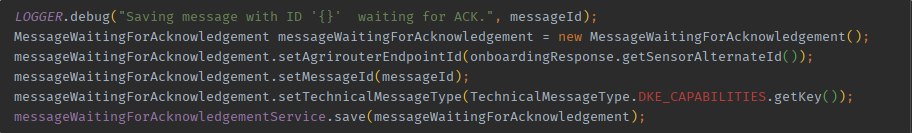
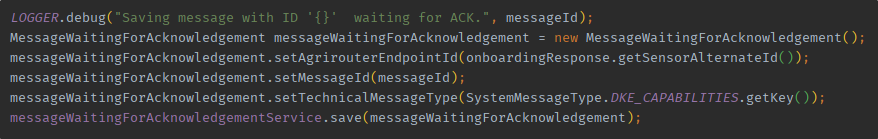
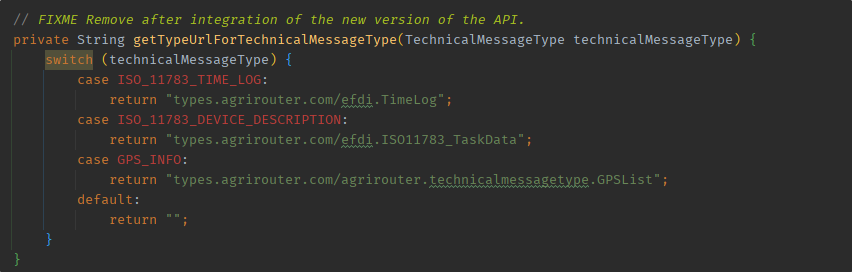
To have a better understanding about system message types and content message types, the declaration for the different types has changed.
There are two new classes, the ContentMessageType for content messages and the SystemMessageType for system messages.
The former technical message type will cause a compiler error since it was replaced.
The new declaration uses the system message type.
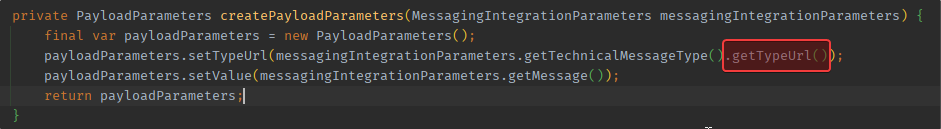
With the new release, the URLs can be fetched from the content message types and there is no need to put them into a helper method any longer.
With the new release, fetch, the URLs are way more comfortable.
The agrirouter middleware has been updated after the release of version 2.x and can be an indicator regarding the workload for the migration. Have a look at the following PR #12 to see the necessary adaptions.
The api module contains interfaces, common helper classes and DTOs as well as exceptions.
The convenience module contains common implementations for different problems which are not located within the SDK.
Those could be capability setting, MQTT client creation or other common problems that are normally not part of the SDK.
The test module contains integration tests not only for the SDK, but also for different scenarios.
If you want to add a dependency, feel free to fetch the latest release from GitHub Packages. Please find the documentation right here.
If you want to add the packages, you need to define the settings within your pom or the settings.xml otherwise.
If you need an example, you can either have a look at the ci/settings.xml for general purpose or check out the snippet below for a custom settings.xml.
<settings xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/SETTINGS/1.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/SETTINGS/1.0.0
http://maven.apache.org/xsd/settings-1.0.0.xsd">
<activeProfiles>
<activeProfile>github</activeProfile>
</activeProfiles>
<profiles>
<profile>
<id>github</id>
<repositories>
<repository>
<id>dke-data</id>
<name>GitHub DKE-Data Apache Maven Packages</name>
<url>https://maven.pkg.github.com/DKE-Data/*</url>
</repository>
</repositories>
</profile>
</profiles>
<servers>
<server>
<id>dke-data</id>
<username>{{YOUR.GITHUB.USERNAME}}</username>
<password>{{YOUR.GITHUB.ACCESS.TOKEN}}</password>
</server>
</servers>
</settings>
You can use this settings.xml and include it during the build process in a specific way.
Just use mvn clean verify -s your_path_to_the_file/settings.xml to use the settings if they are set in a local file.
We do no longer maintain the certificates within the SDK. Maintaining them in the SDK would mean that we have to release the SDK with every change of the certificate. Therefore, feel free to add the root certificates to a Java Key Store add reference it within your application.
The certificates are PEM files that can be added directly to the keystore using the following command.
keytool -importcert -file certificate.pem -keystore my_agrirouter_key_store.jksIf you try to add the command, please be aware that the containing PEM file has to fulfill the following requirements:
-
The header and footer are included enclosed between five dashes.
-
There are no trailing spaces on each line.
-
The certificate is saved as a .p7b.
If the files do not meet those requirements, the import will not be possible. The certificates are part of the integration guide which can be found in the external resources.
Here are some external resources for the development: