This is the skeleton app for deploying RDS Aurora PostgreSQL datbase using Serverless Framework.
Additionally, this simple project is demonstration of multiple modern technologies/methodologies/principles:
- Python programming language
- cloud-based app deployed to Amazon Web Services (AWS)
- Serverless (Serverless Framework) - AWS Lambda, RDS Aurora
- Infrastracture as a Code (IaaC) (Serverless framework - serverless.yml defines infrastructure resources)
- DevOps-based workflow (common code base with Makefile commands spanning Developers and Operations Teams together)
- RESTful API - simple implementation of REST API based on Python in api directory
- Fully automated CI/CD pipeline based on GitHub Actions CI/CD Server
- code syntax verification (pylint) (
make lint) - security verification (bandit) (
make security) - unit tests (unittest) (
make unittest) - code coverage (coverage python module) (
make coverage) - deploy infrastructure (AWS, Serverless framework) (
make deploy) - End-To-End tests (cucumber, pytest-bdd, selenium) (NOT IMPLEMENTED YET) (
make e2e-tests) - load/performance tests (locust) (
make load-tests) - destroy infrastructure (AWS, Serverless framework) (
make destroy)
- code syntax verification (pylint) (
- deploying from Command Line or from CI/CD
- single Makefile to control all deployment and code checkings commands
- available to deploy to multiple stages /environments (ex. DEV, SIT, PROD) using the same command (ex.
make deploy ENV=SIT) - available to deploy single lambda function (ex.
make deploy FUNC=lambdaFunctionName)
This framework is based on a Serverless Application Framework
- Set up AWS credentials for your terminal
- Install Serverless Application Framework and dependencies - Instruction. You can use
make serverlesscommand from root directory of this project (orsudo make serverlessif you seeEACCES: permission denied). - Export ENV=dev to deploy to
devstage/environment (by default ENV value is get based on feature branch name created according togit flowrules or it is HEAD if branch name is too short):
export ENV=dev
- Deploy default app
make deploy-all
- Run app and get logs (logs should contain:
Received message: test_message)
make run
sleep 20 #wait 20 seconds until logs stream is created in AWS
make logs
- Destroy app and RDS database - delete all AWS resources of your app
make destroy-all
You can work with app on specified stage (environment) ex. dev, uat, prd by passing ENV variable into the
make commands ex.:
make deploy ENV=dev
make deploy ENV=uat
make deploy ENV=prd
or export ENV variable in your terminal and use default commands ex.
export ENV=dev
make deploy run
The default stage for the app is equal to current branch name ex. master.
make deploy will build and deploy infrastructure and code as defined in serverless.yml file:
By default resources are deployed to the default
stage
(environment) based on current branch name ex. master. Thanks to that multiple users working on separate branches can deploy to
separate AWS resources to avoid resources conflicts.
After triggering the above command on master branch following resources will be created in your
AWS account:
- AWS Lambda:
myapp-master-lambda_function2 - AWS Lambda:
myapp-master-lambda_function1 - AWS SQS queue:
myapp-master-sqs-lambda_function1
The resources for different stages will be deployed with different names to be
possible to test different versions of app separately.
For example, if you trigger make deploy ENV=dev following resources will be
deployed:
myapp-dev-lambda_function1myapp-dev-lambda_function2myapp-dev-sqs-lambda_function1
We have following level of tests in the application:
make code-checks- checks code syntax usingpylintand security usingbanditmake unittest coverage- trigger all unit tests of the code and show code coveragemake e2e-tests(NOT IMPLEMETED YET) - selenium-based tests runned after deploymentmake load-tests(NOT IMPLEMENTED YET)
The CI/CD is based on Makefile targets and is integrated with GitHub Actions to trigger (however it could be easly integrated with any other CI/CD tool ex. Jenkins, BitBucket pipelines, GitLab, TravisCI, Bamboo or any other)
It consists of following steps:
You can run all the below steps/commands using one make ci command
make lint=> check code syntax usingpylinttoolmake security=> check code security breaches usingbandittoolmake unittest=> trigger unit tests and show reportmake coverage=> show unit tests code coverage
You can run all the below steps/commands using one make cd command:
make deploy=> deploys app to AWSmake e2e-tests=> run End to End tests on deployed appmake destroy=> (optional: works only on feature branches) destroy AWS resources after finishing e2e-tests
Currently CI/CD is integrated with GitHub Actions. However you can set it up quickly with any other CI/CD tool and see pipelines and actions similar to the ones below.
To run CI/CD pipelines you need to export AWS_KEY and AWS_SECRET to the
Secrets section of your GitHub project:

You can see CI/CD pipelines of project here
Pipelines of GitHub Actions looks like on this picture:
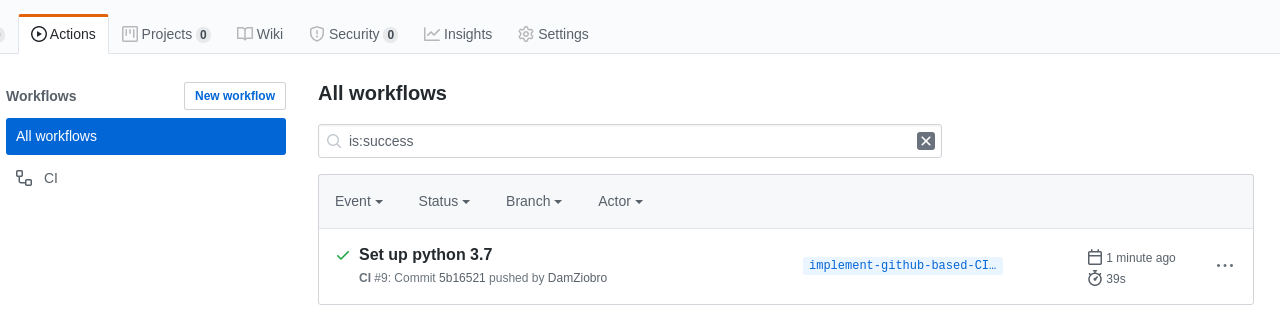
Pipeline steps are configured in pipeline config file
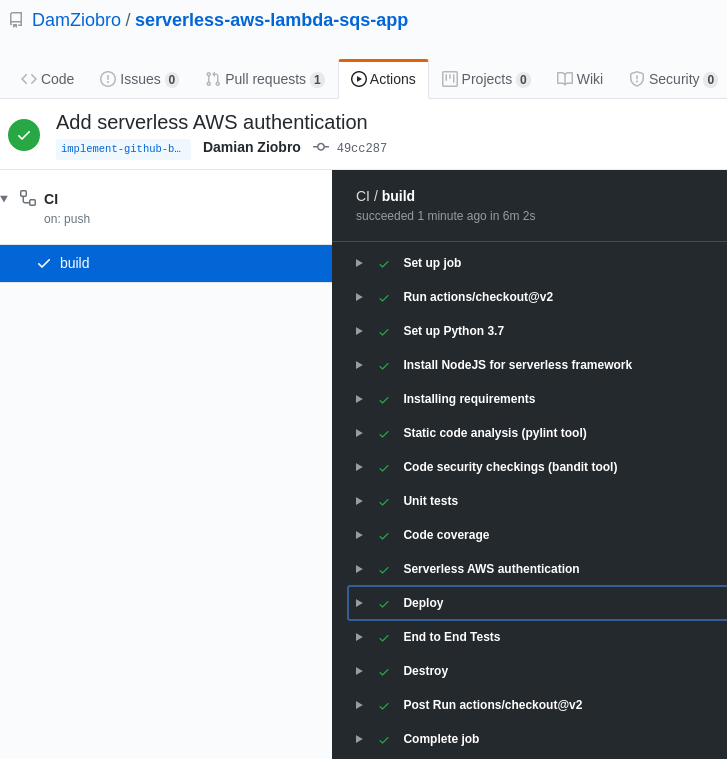
Sample pipeline processing with details of each step can be found when you click on some of the pipelines in Actions tab.
It should look like on this picture:
To create Pull Request, go to Pull Requests and fo following steps:
- Click 'New pull request'
- Select your branch and click on it.
- Make sure you selected your PR to be merged into
develop(NOTmaster) (we will use GitFlow for releases later) - Click create Pull Request
When you follow above actions, the CI/CD pipeline will be triggered automatically and perform all checkings described in CI/CD section above.
When everything will be finished you should see results like here and if everything is green you can ask your colleague for Code Review.
If something is not green, you should fix it before asking Code Review.
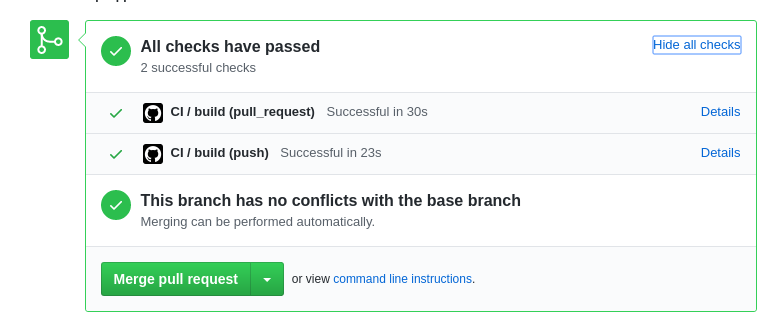
When you Code is reviewed you can click 'Merge pull request' and merge it into
develop branch.
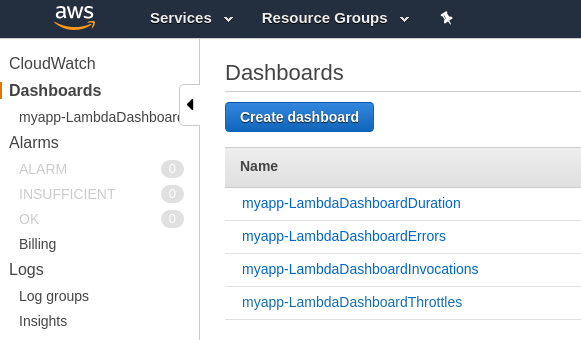
This application has integrated basic monitoring based on CloudWatch Dashboards. It is based on serverless-plugin-cloudwatch-dashboard Serverless framework plugin.
Deployment of serverless.yml creates 4 CloudWatch Dashboardss for AWS
Lambda monitoring as on the picture: