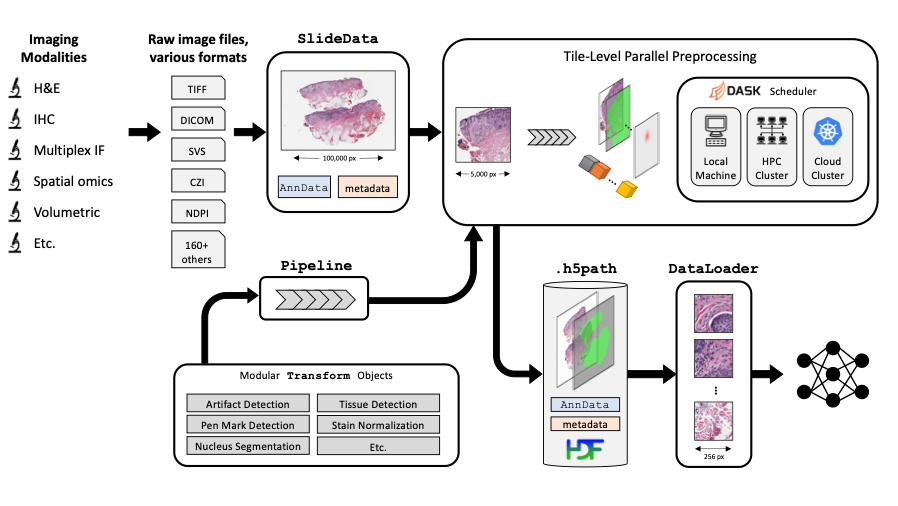
🤖🔬 PathML: Tools for computational pathology
⭐ PathML objective is to lower the barrier to entry to digital pathology
Imaging datasets in cancer research are growing exponentially in both quantity and information density. These massive datasets may enable derivation of insights for cancer research and clinical care, but only if researchers are equipped with the tools to leverage advanced computational analysis approaches such as machine learning and artificial intelligence. In this work, we highlight three themes to guide development of such computational tools: scalability, standardization, and ease of use. We then apply these principles to develop PathML, a general-purpose research toolkit for computational pathology. We describe the design of the PathML framework and demonstrate applications in diverse use cases.
🚀 The fastest way to get started?
docker pull pathml/pathml && docker run -it -p 8888:8888 pathml/pathml
Done, what analyses can I write now? 👉 
 |
This AI will:
|
📖 Official PathML Documentation
View the official PathML Documentation on readthedocs
🔥 Examples! Examples! Examples!
↴ Jump to the gallery of examples below
PathML is an advanced tool for pathology image analysis. Below are simplified instructions to help you install PathML on your system. Whether you're a user or a developer, follow these steps to get started.
We recommend using Micromamba for managing your environments. We provide instructions on how to install PathML via Micromamba below. In addition, we also provide instructions on how to install via Miniconda should you have a license.
If you don't have Miniconda installed, you can download Miniconda here.
Make sure you have the recent version of Micromamba by using the following command:
micromamba update
If you are using Micromamba, you can skip to the next section.
We recommend that Anaconda/Microconda users complete the following steps to update your Conda version and use libmamba to resolve dependency conflicts.
Recent versions of Conda have integrated libmamba, a faster dependency solver. To benefit from this improvement, first ensure your Conda is updated:
conda update -n base conda
Then, to install and set the new libmamba solver, run:
conda install -n base conda-libmamba-solver
conda config --set solver libmamba
Note: these instructions are for Linux. Commands may be different for other platforms.
For installation methods 1) and 2), you will need to install the following platform-specific packages.
- Linux: Install external dependencies with Apt:
sudo apt-get install openslide-tools g++ gcc libblas-dev liblapack-dev
- MacOS: Install external dependencies with Brew:
brew install openslide
- Windows:
- Option A: Install with vcpkg:
vcpkg install openslide
- Option B: Using Pre-built OpenSlide Binaries (Alternative)
For Windows users, an alternative to using
vcpkgis to download and use pre-built OpenSlide binaries. This method is recommended if you prefer a quicker setup.
- Download the OpenSlide Windows binaries from the OpenSlide Downloads page.
- Extract the archive to your desired location, e.g.,
C:\OpenSlide\.
micromamba create -n pathml 'openjdk<=18.0' -c conda-forge python=3.9
micromamba activate pathml
pip install pathml
conda create --name pathml python=3.9
conda activate pathml
conda install -c conda-forge 'openjdk<=18.0'
pip install pathml
git clone https://github.com/Dana-Farber-AIOS/pathml.git
cd pathml
- Linux and Windows:
conda env create -f environment.yml
conda activate pathml
To use GPU acceleration for model training or other tasks, you must install CUDA. The default CUDA version in our environment file is 11.6. To install a different CUDA version, refer to the instructions here).
- MacOS:
conda env create -f requirements/environment_mac.yml
conda activate pathml
pip install -e .
First, download or build the PathML Docker container:
-
Option A: download PathML container from Docker Hub
docker pull pathml/pathml:latestOptionally specify a tag for a particular version, e.g.
docker pull pathml/pathml:2.0.2. To view possible tags, please refer to the PathML DockerHub page. -
Option B: build docker container from source
git clone https://github.com/Dana-Farber-AIOS/pathml.git cd pathml docker build -t pathml/pathml .
Then connect to the container:
docker run -it -p 8888:8888 pathml/pathml
The above command runs the container, which is configured to spin up a jupyter lab session and expose it on port 8888.
The terminal should display a URL to the jupyter lab session starting with http://127.0.0.1:8888/lab?token=<.....>.
Navigate to that page and you should connect to the jupyter lab session running on the container with the pathml
environment fully configured. If a password is requested, copy the string of characters following the token= in the
url.
Note that the docker container requires extra configurations to use with GPU.
Note that these instructions assume that there are no other processes using port 8888.
Please refer to the Docker run documentation for further instructions
on accessing the container, e.g. for mounting volumes to access files on a local machine from within the container.
To get PathML running in a Colab environment:
import os
!pip install openslide-python
!apt-get install openslide-tools
!apt-get install openjdk-17-jdk-headless -qq > /dev/null
os.environ["JAVA_HOME"] = "/usr/lib/jvm/java-17-openjdk-amd64"
!update-alternatives --set java /usr/lib/jvm/java-17-openjdk-amd64/bin/java
!java -version
!pip install pathml
Thanks to all of our open-source collaborators for helping maintain these installation instructions!
Please open an issue for any bugs or other problems during installation process.
After you have installed all necessary dependencies and PathML itself, import it using the following command:
import pathml
For Windows users, insert the following code snippet at the beginning of your Python script or Jupyter notebook before importing PathML. This code sets up the DLL directory for OpenSlide, ensuring that the library is properly loaded:
# The path can also be read from a config file, etc.
OPENSLIDE_PATH = r'c:\path\to\openslide-win64\bin'
import os
if hasattr(os, 'add_dll_directory'):
# Windows-specific setup
with os.add_dll_directory(OPENSLIDE_PATH):
import openslide
else:
# For other OSes, this step is not needed
import openslide
# Now you can proceed with using PathML
import pathmlThis code snippet ensures that the OpenSlide DLLs are correctly found by Python on Windows systems. Replace c:\path\to\openslide-win64\bin with the actual path where you extracted the OpenSlide binaries.
If you encounter any DLL load failures, verify that the OpenSlide bin directory is correctly added to your PATH.
To use GPU acceleration for model training or other tasks, you must install CUDA. This guide should work, but for the most up-to-date instructions, refer to the official PyTorch installation instructions.
Check the version of CUDA:
nvidia-smi
Replace both instances of 'cu116' in requirements/requirements_torch.txt with the CUDA version you see. For example, for CUDA 11.7, 'cu116' becomes 'cu117'.
Then create the environment:
conda env create -f environment.yml
conda activate pathml
After installing PyTorch, optionally verify successful PyTorch installation with CUDA support:
python -c "import torch; print(torch.cuda.is_available())"
Jupyter notebooks are a convenient way to work interactively. To use PathML in Jupyter notebooks:
PathML relies on Java to enable support for reading a wide range of file formats.
Before using PathML in Jupyter, you may need to manually set the JAVA_HOME environment variable
specifying the path to Java. To do so:
- Get the path to Java by running
echo $JAVA_HOMEin the terminal in your pathml conda environment (outside of Jupyter) - Set that path as the
JAVA_HOMEenvironment variable in Jupyter:import os os.environ["JAVA_HOME"] = "/opt/conda/envs/pathml" # change path as needed
conda activate pathml
conda install ipykernel
python -m ipykernel install --user --name=pathml
This makes the pathml environment available as a kernel in jupyter lab or notebook.
Now that you are all set with PathML installation, let's get started with some analyses you can easily replicate:
If you use PathML please cite:
So far, PathML was referenced in 20+ manuscripts:
- H. Pakula et al. Nature Communications, 2024
- B. Ricciuti et al. Journal of Clinical Oncology, 2024
- A. Song et al. Nature Reviews Bioengineering, 2023
- I. Virshup et al. Nature Bioengineering, 2023
- A. Karargyris et al. Nature Machine Intelligence, 2023
- S. Pati et al. Nature Communications Engineering, 2023
- C. Gorman et al. Nature Communications, 2023
- J. Nyman et al. Cell Reports Medicine, 2023
- A. Shmatko et al. Nature Cancer, 2022
- J. Pocock et al. Nature Communications Medicine, 2022
- S. Orsulic et al. Frontiers in Oncology, 2022
- J. Linares et al. Molecular Cell, 2021
- the list continues here 🔗
This is where in the world our most enthusiastic supporters are located:

|
and this is where they work:

|
Source: https://ossinsight.io/analyze/Dana-Farber-AIOS/pathml#people
PathML is an open source project. Consider contributing to benefit the entire community!
There are many ways to contribute to PathML, including:
- Submitting bug reports
- Submitting feature requests
- Writing documentation and examples
- Fixing bugs
- Writing code for new features
- Sharing workflows
- Sharing trained model parameters
- Sharing
PathMLwith colleagues, students, etc.
See contributing for more details.
The GNU GPL v2 version of PathML is made available via Open Source licensing. The user is free to use, modify, and distribute under the terms of the GNU General Public License version 2.
Commercial license options are available also.
Questions? Comments? Suggestions? Get in touch!