I use Python and SQLAlchemy to do basic climate analysis and data exploration of my climate database. All of the following analysis was completed using SQLAlchemy ORM queries, Pandas, and Matplotlib.
-
I choose a start date and end date for my trip. I make sure that my vacation range was approximately 3-15 days total.
-
I used SQLAlchemy
create_engineto connect to my sqlite database as well as, SQLAlchemyautomap_base()to reflect my tables into classes and save a reference to those classes calledStationandMeasurement.
-
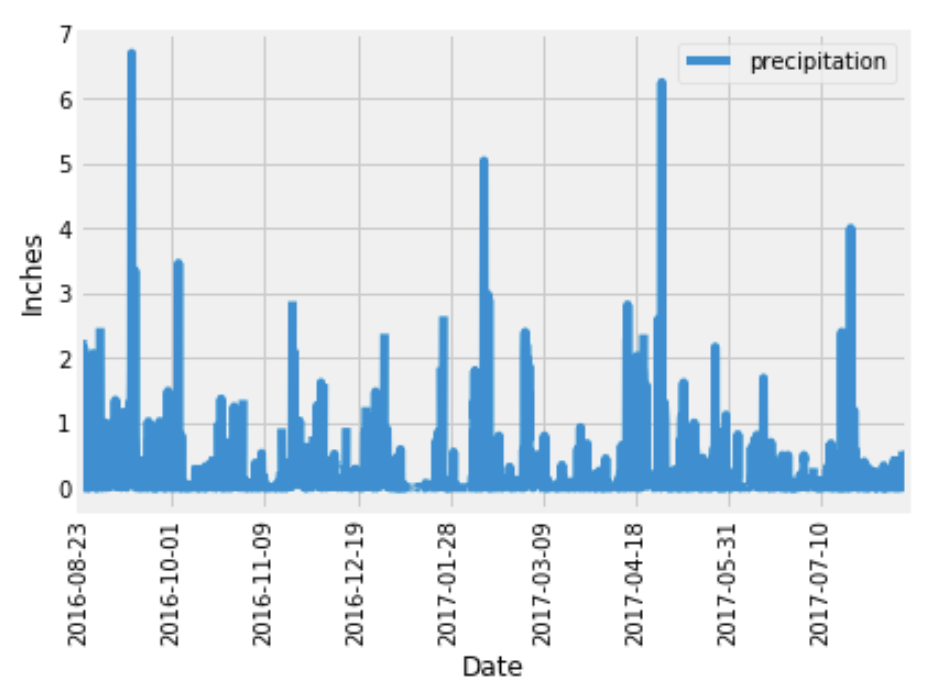
Designed a query to retrieve the last 12 months of precipitation data.
-
Selected only the
dateandprcpvalues. -
Loaded the query results into a Pandas DataFrame and set the index to the date column.
-
Sorted the DataFrame values by
date. -
Ploted the results using the DataFrame
plotmethod. -
Used Pandas to print the summary statistics for the precipitation data.
-
Designed a query to calculate the total number of stations.
-
Designed a query to find the most active stations.
-
Listed the stations and observation counts in descending order.
-
Showed which station has the highest number of observations?
-
-
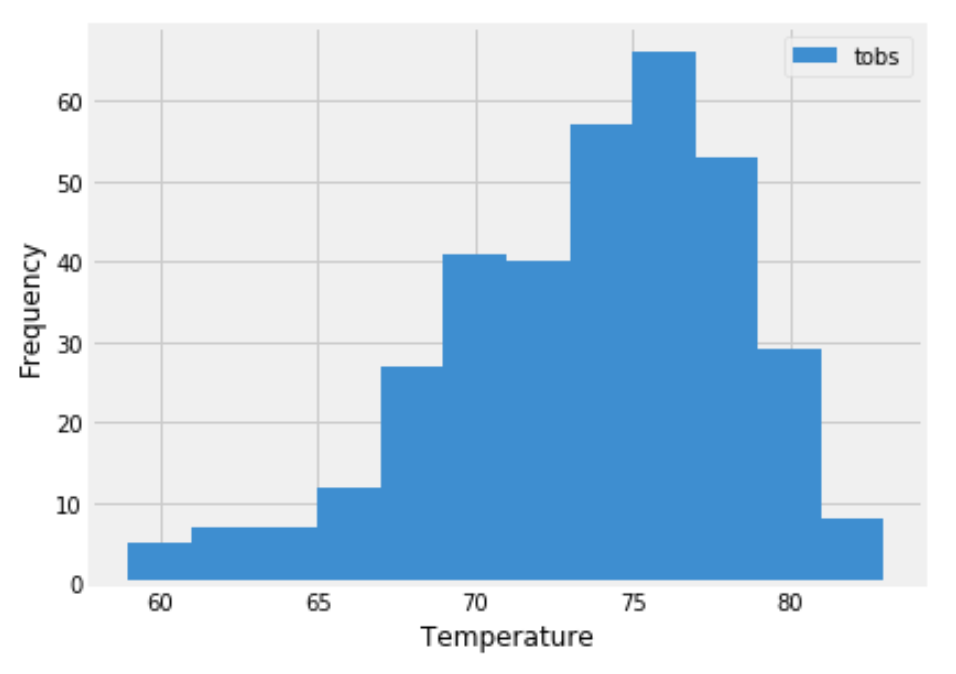
Designed a query to retrieve the last 12 months of temperature observation data (TOBS).
After having completed my initial analysis, I design a Flask API based on the queries that I have just developed.
- Used Flask to create my routes.
-
/-
Home page.
-
Listed all routes that are available.
-
-
/api/v1.0/precipitation-
Converted the query results to a dictionary using
dateas the key andprcpas the value. -
Returned the JSON representation of your dictionary.
-
-
/api/v1.0/stations- Returned a JSON list of stations from the dataset.
-
/api/v1.0/tobs-
Queryd the dates and temperature observations of the most active station for the last year of data.
-
Returned a JSON list of temperature observations (TOBS) for the previous year.
-
-
/api/v1.0/<start>and/api/v1.0/<start>/<end>-
Returned a JSON list of the minimum temperature, the average temperature, and the max temperature for a given start or start-end range.
-
When given the start only, calculated
TMIN,TAVG, andTMAXfor all dates greater than and equal to the start date. -
When given the start and the end date, calculated the
TMIN,TAVG, andTMAXfor dates between the start and end date inclusive.
-
-
Hawaii is reputed to enjoy mild weather all year. Is there a meaningful difference between the temperature in, for example, June and December?
-
Identified the average temperature in June at all stations across all available years in the dataset. Did the same for December temperature.
-
Used the t-test to determine whether the difference in the means, if any, is statistically significant. Will I use a paired t-test, or an unpaired t-test? Why?
-
The started notebook contains a function called
calc_tempsthat will accept a start date and end date in the format%Y-%m-%d. The function will return the minimum, average, and maximum temperatures for that range of dates. -
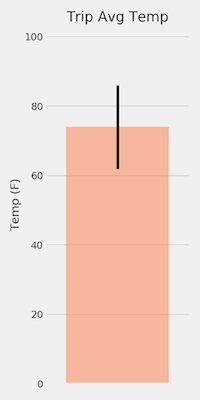
Used the
calc_tempsfunction to calculate the min, avg, and max temperatures for your trip using the matching dates from the previous year (i.e., use "2017-01-01" if your trip start date was "2018-01-01"). -
Ploted the min, avg, and max temperature from your previous query as a bar chart.
-
Calculated the rainfall per weather station using the previous year's matching dates.
-
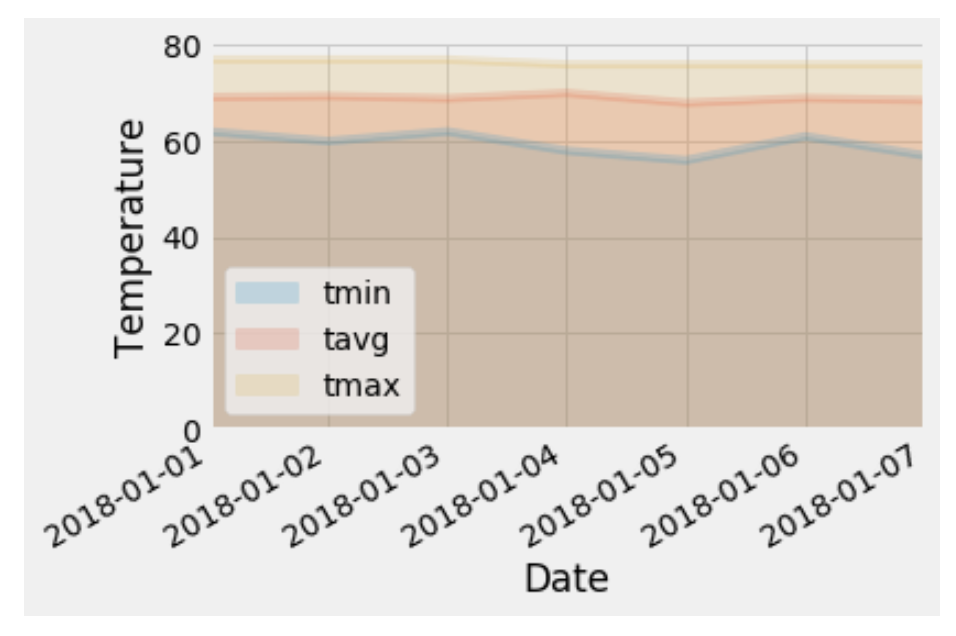
Calculated the daily normals. Normals are the averages for the min, avg, and max temperatures.
-
I was provided with a function called
daily_normalsthat will calculate the daily normals for a specific date. This date string will be in the format%m-%d. I was sure to use all historic TOBS that match that date string. -
Created a list of dates for my trip in the format
%m-%d. Used thedaily_normalsfunction to calculate the normals for each date string and append the results to a list. -
Loaded the list of daily normals into a Pandas DataFrame and set the index equal to the date.
-
Used Pandas to plot an area plot (
stacked=False) for the daily normals.