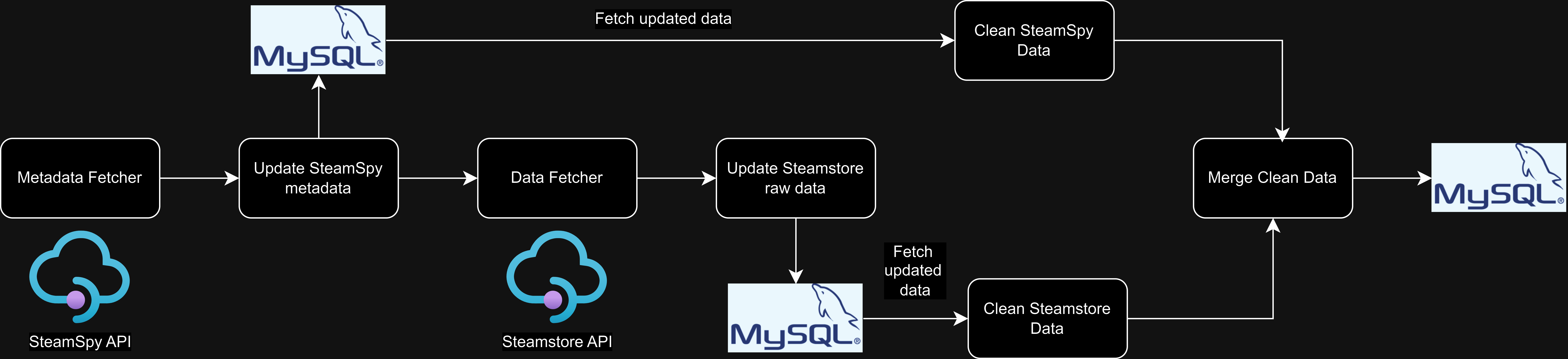
Welcome to Steam Sales Analysis – an innovative project designed to harness the power of data for insights into the gaming world. We have meticulously crafted an ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) pipeline that covers every essential step: data retrieval, processing, validation, and ingestion. By leveraging the robust Steamspy and Steam APIs, we collect comprehensive game-related metadata, details, and sales figures.
But we don’t stop there. The culmination of this data journey sees the information elegantly loaded into a MySQL database hosted on Aiven Cloud. From this solid foundation, we take it a step further: the data is analyzed and visualized through dynamic and interactive Tableau dashboards. This transforms raw numbers into actionable insights, offering a clear window into gaming trends and sales performance. Join us as we dive deep into the data and bring the world of gaming to life!
For general use, setting up the environment and dependencies is straightforward:
# Install the python distribution from PyPI
pip install steamstore-etl- Create an
.envfile in a directory.
# Database configuration
MYSQL_USERNAME=<your_mysql_username>
MYSQL_PASSWORD=<your_mysql_password>
MYSQL_HOST=<your_mysql_host>
MYSQL_PORT=<your_mysql_port>
MYSQL_DB_NAME=<your_mysql_db_name>-
Open a terminal at the specified location
-
Load
.envVariables into the TerminalTo load the variables from the
.envfile into your current terminal session, you can use theexportcommand along with thedotenvcommand if you have thedotenvutility installed.Using
exportdirectly (manual method):export $(grep -v '^#' .env | xargs)
grep -v '^#' .envremoves any comments from the file.xargsconverts the output into environment variable export commands.
Using
dotenv(requires installation):If you prefer a tool, you can use
dotenv:- Install
dotenvif you don't have it:
sudo apt-get install python3-dotenv
- Then, use the following command to load the
.envfile:
dotenv
Using
source(not typical for.envbut useful for.shfiles):If your
.envfile is simple, you can usesourcedirectly (this method assumes no special parsing is needed):source .envNote that
sourceworks well if your.envfile only contains simpleKEY=VALUEpairs. -
Verify the Variables
After loading, you can check that the environment variables are set:
echo $MYSQL_USERNAME
-
Load
.envVariables into PowerShellYou can use a PowerShell script to load the variables from the
.envfile.Create a PowerShell script (e.g.,
load_env.ps1):Get-Content .env | ForEach-Object { if ($_ -match "^(.*?)=(.*)$") { [System.Environment]::SetEnvironmentVariable($matches[1], $matches[2], [System.EnvironmentVariableTarget]::Process) } }
- This script reads each line from the
.envfile and sets it as an environment variable for the current PowerShell session.
Run the script:
.\load_env.ps1
Verify the Variables:
echo $env:MYSQL_USERNAME - This script reads each line from the
-
Load
.envVariables into Command PromptThe Command Prompt does not have built-in support for
.envfiles. You can use a batch script to achieve this.Create a batch script (e.g.,
load_env.bat):@echo off for /f "tokens=1,2 delims==" %%A in (.env) do set %%A=%%B
Run the batch script:
load_env.bat
Verify the Variables:
echo %MYSQL_USERNAME%
-
Usage:
$ steamstore [OPTIONS] COMMAND [ARGS]...Options:
--install-completion: Install completion for the current shell.--show-completion: Show completion for the current shell, to copy it or customize the installation.--help: Show this message and exit.
Commands:
clean_steam_data: Clean the Steam Data and ingest into the Custom Databasefetch_steamspy_data: Fetch from SteamSpy Database and ingest data into Custom Databasefetch_steamspy_metadata: Fetch metadata from SteamSpy Database and ingest metadata into Custom Databasefetch_steamstore_data: Fetch from Steam Store Database and ingest data into Custom Database
Clean the Steam Data and ingest into the Custom Database
Usage:
$ steamstore clean_steam_data [OPTIONS]Options:
--batch-size INTEGER: Number of records to process in each batch. [default: 1000]--help: Show this message and exit.
Fetch from SteamSpy Database and ingest data into Custom Database
Usage:
$ steamstore fetch_steamspy_data [OPTIONS]Options:
--batch-size INTEGER: Number of records to process in each batch. [default: 1000]--help: Show this message and exit.
Fetch metadata from SteamSpy Database and ingest metadata into Custom Database
Usage:
$ steamstore fetch_steamspy_metadata [OPTIONS]Options:
--max-pages INTEGER: Number of pages to fetch from. [default: 100]--help: Show this message and exit.
Fetch from Steam Store Database and ingest data into Custom Database
Usage:
$ steamstore fetch_steamstore_data [OPTIONS]Options:
--batch-size INTEGER: Number of app IDs to process in each batch. [default: 5]--bulk-factor INTEGER: Factor to determine when to perform a bulk insert (batch_size * bulk_factor). [default: 10]--reverse / --no-reverse: Process app IDs in reverse order. [default: no-reverse]--help: Show this message and exit.
For development purposes, you might need to have additional dependencies and tools:
-
Clone the repository:
git clone https://github.com/DataForgeOpenAIHub/Steam-Sales-Analysis.git cd steam-sales-analysis -
Create a virtual environment:
- Using
venv:python -m venv game source game/bin/activate # On Windows use `game\Scripts\activate`
- Using
conda:conda env create -f environment.yml conda activate game
- Using
-
Install dependencies:
- Install general dependencies:
pip install -r requirements.txt
- Install development dependencies:
pip install -r dev-requirements.txt
- Install general dependencies:
-
Configuration:
- Create an
.envfile in the root directory of the repository. - Add the following variables to the
.envfile:# Database configuration MYSQL_USERNAME=<your_mysql_username> MYSQL_PASSWORD=<your_mysql_password> MYSQL_HOST=<your_mysql_host> MYSQL_PORT=<your_mysql_port> MYSQL_DB_NAME=<your_mysql_db_name>
- Create an
The project connects to a MySQL database hosted on Aiven Cloud using the credentials provided in the .env file. Ensure that the database is properly set up and accessible with the provided credentials.
To execute the ETL pipeline, use the following commands:
-
To collect metadata:
steamstore fetch_steamspy_metadata
-
To collect SteamSpy data:
steamstore fetch_steamspy_data --batch-size 1000
-
To collect Steam data:
steamstore fetch_steamstore_data --batch-size 5 --bulk-factor 10
-
To clean Steam data:
steamstore clean_steam_data --batch-size 1000
This will start the process of retrieving data from the Steamspy and Steam APIs, processing and validating it, and then loading it into the MySQL database.
- Explore the interactive Tableau dashboard.
- Kayvan Shah |
MS in Applied Data Science|USC - Sudarshana S Rao |
MS in Electrical Engineering (Machine Learning & Data Science)|USC - Rohit Veeradhi |
MS in Electrical Engineering (Machine Learning & Data Science)|USC
- Steamspy API
- Steam Store API - InternalSteamWebAPI
- Steam Web API Documentation
- RJackson/StorefrontAPI Documentation
- Steamworks Web API Reference
This repository is licensed under the MIT License. See the LICENSE file for details.