┏━━━┓━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━┏┓━┏━━━┓━━━━━━━━━━┏┓━┏┓━━
┃┏━┓┃━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━┏┛┗┓┃┏━┓┃━━━━━━━━━┏┛┗┓┃┃━━
┃┗━━┓┏━━┓┏━━┓┏━┓┏━━┓┗┓┏┛┃┗━━┓┏┓━┏┓┏━┓━┗┓┏┛┃┗━┓
┗━━┓┃┃┏┓┃┃┏━┛┃┏┛┃┏┓┃━┃┃━┗━━┓┃┃┃━┃┃┃┏┓┓━┃┃━┃┏┓┃
┃┗━┛┃┃┃━┫┃┗━┓┃┃━┃┃━┫━┃┗┓┃┗━┛┃┃┗━┛┃┃┃┃┃━┃┗┓┃┃┃┃
┗━━━┛┗━━┛┗━━┛┗┛━┗━━┛━┗━┛┗━━━┛┗━┓┏┛┗┛┗┛━┗━┛┗┛┗┛
━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━┏━┛┃━━━━━━━━━━━━━
━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━┗━━┛━━━━━━━━━━━━━
A python-based tool for discovering secrets with multiple secret scanning solutions across multiple orgs, and repositories. Secret Synth leverages the following secret scanning tools:
- gitleaks
- trufflehog
- Github Advanced Security
- Nosey Parker
Only pulls from GitHub are currently supported.
In short, to help you:
- Identify what secrets scanning solution(s) and strategy you may want to deploy.
- Know how many secrets may be discovered in your repositories (like a dry run).
- Identify classes of secrets that are being identified in your source code.
- Identify true positives and remediate them before rolling out a secrets alerting solution.
- Identify false positives and tune your alerting system to eliminate noisy alerts (which decreases developer productivity).
This project is licensed under the MIT License. See the LICENSE file for details. As such, the software is provided "as-is" and without warranty. The authors are not responsible for any damages or liabilities that may arise from the use of the software.
- Python 3.6+
- A Github account with sufficient permissions to access the target repositories
- A Github access token with sufficient permissions get a listing of repositories from the Github REST API
gitinstalled and in your PATHgitleaksinstalled and in your PATHtrufflehoginstalled and in your PATHnoseyparkerinstalled and in your PATH
The following versions were used during development:
- noseyparker, v0.16.0.
- gitleaks, v8.18.1
- trufflehog, v3.66.2
- GitHub REST API, API Version 2022-11-28
- Clone this repository:
git clone https://github.com/yourusername/yourrepository.git
- Install the required Python packages:
pip install -r requirements.txt
- Install the other required secrets scanners.
Here's the command-line help:
usage: secretsynth.py [-h] [--clean] [--dry-run] [--keep-secrets-in-reports] [--repos-internal-type]
[--org-type {users,orgs}] [--owners OWNERS] [--skip-noseyparker] [--skip-trufflehog]
[--skip-ghas] [--skip-gitleaks] [--open-report-in-browser]
optional arguments:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
--clean delete the directories ./checkouts and ./reports. When --clean is present all other commands are
ignored.
--dry-run run the script in dry run mode, don't execute any commands
--keep-secrets-in-reports
Keep plain text secrets in the aggregated reports. By default the tool will hash secrets for final reports if this flag is missing.
--repos-internal-type
If your repositories are internal, this flag will be added when fetching repositories from Github.
--open-report-in-browser
Open the report in a browser after it's generated
--org-type {users,orgs}
set the organization type
--owners OWNERS comma-delimited list of owners
--skip-noseyparker Skip the Noseyparker scan
--skip-trufflehog Skip the TruffleHog scan
--skip-ghas Skip the GitHub Advanced Security scan
--skip-gitleaks Skip the Gitleaks scan
--open-report-in-browser
Open the report in a browser after it's generated
- Set your GitHub access token as an environment variable:
export GITHUB_ACCESS_TOKEN=youraccesstoken
See Managing your personal access tokens for more information. You will only need the ability to list repositories so the script will know what to checkout via git checkout
- Review .gitleaks.toml for path and file exclusions. Modify as necessary.
Gitleaks can generate a lot of false positives out of the box. So review results carefully and add exclusions as necessary to minimize false positives.
- Run the
secretsynthscript from theorg-scandirectory:
Here are some examples of use cases for running the script:
Example: Running on a personal owner account:
🚀🚀 This example uses some small open source repos with secrets in them. Hence, this is a good test for you to quickly evaluate the setup is correct for your environment. 🚀🚀
python3 secretsynth.py --org-type users --owners swell-consulting --skip-ghas --open-report-in-browser
Example: Running on a personal owner account and keeping plain text secrets in the output, but omit trufflehog from the execution:
python3 secretsynth.py --org-type users --owners austimkelly --keep-secrets-in-reports --skip-trufflehog
Example: Running on multiple organizations:
python3 secretsynth.py --org-type orgs --owners org1,org2,org3
Note: Multiple Github Personal Access Tokens are not supported yet.
Example: Cleaning up source and scanning artifacts:
python3 secretsynth.py --clean
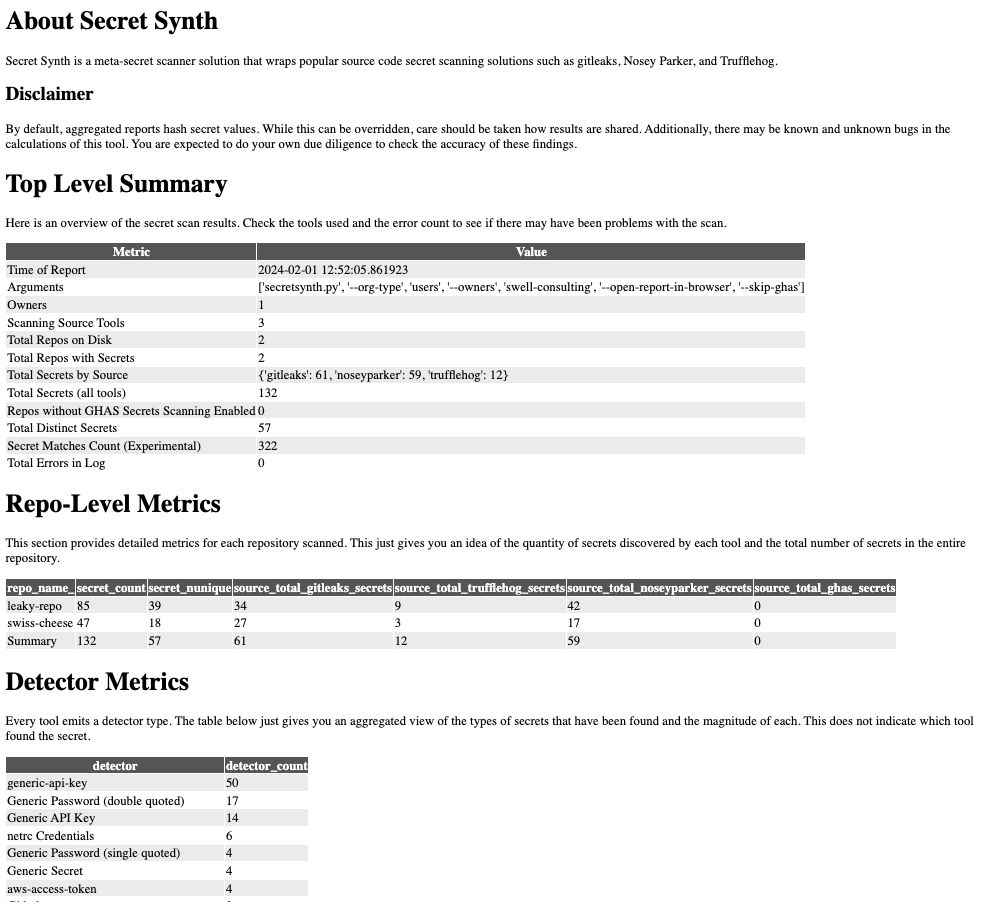
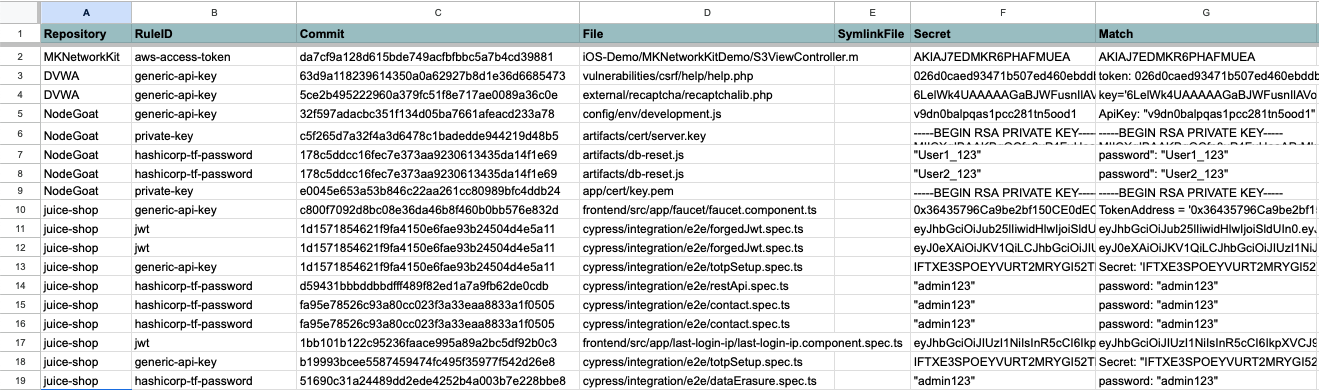
After the script has finished running, you can find the consolidated reports in the ./org-scan/reports/reports_<YYYYMMDDHHMM> directory. An HTML file in that directory contains a short summary of the results, CSV artifacts with merged alerts, and an error log for any tool failures you want to investigate.
Here's an example of the output:
You can further analyze the data in your favorite spreadsheet or data warehouse:
sequenceDiagram
participant User
participant Script as secretsynth.py
participant GitHub
participant FileSystem as Local File System
User->>Script: Run script
loop for each organization
Script->>GitHub: Request list of repositories for organization
GitHub-->>Script: Return list of repositories
loop for each repository
Script->>GitHub: Clone repository
Script->>FileSystem: Save repository to local file system
Script->>Script: Run gitleaks on cloned repository
Script->>FileSystem: Save gitleaks report to local file system
Script->>Script: Run TruffleHog on cloned repository
Script->>FileSystem: Save TruffleHog report to local file system
Script->>Script: Run Nosey Parker on cloned repository
Script->>FileSystem: Save Nosey Parker report to local file system
Script->>GitHub: Fetch GHAS secret alerts for repository
GitHub-->>Script: Return GHAS secret alerts
Script->>FileSystem: Save GHAS secret alerts to local file system
end
end
This repository also contains a Github Action that can be used to scan a repository for secrets using Gitleaks. The action is located in the .github/actions/gitleaks directory.
NOTE: That running gitleaks against a repo owned by a user is free. A repository owned by an organization will require a free API key. See Obtaining a Gitleaks License
- Gitleaks
- TruffleHog
- Github Advanced Security
- A Comparative Study of Software Secrets Reporting by Secret Detection Tools
- SecretBench - Reference data set used by the comparative paper above.
- secrets-magpie - A similar tool to this one with more source scanning options.
- Meet Nosey Parker — An Artificial Intelligence Based Scanner That Sniffs Out Secrets - Some really good data science work here on the precision of Nosey Parker.
- The script does not support multiple Github Personal Access Tokens yet. When pulling GHAS Secert Alerts for multiple orgs, this will only use one token.
- Internal repositories are treated with a separate flag. If you have a mix of internal, private, and public repositories in an org, you will have incomplete results.
- Matching does not happen with GHAS Secret Alerts. The API does not return secrets, line or file numbers in the alerts. As such
- Only clones from Github are supported. Adding filesystem and other repos could be done upon request.
- Git fetch depth or custom scan depths on tools is not supported.