This repo contains a library for running a .NET Core application as windows service, without the need for a wrapper assembly or the full (desktop) .NET Framework. It is built using P/Invoke calls into native windows assemblies.
Usage scenarios include:
- Running on Windows Nano Server (no full framework but can run windows services)
- Shipping a modern service application using the latest .NET core version to systems where you cannot upgrade to new versions of .NET, but you want to use new framework features.
- Build truly portable applications that can for example run as service on windows and as daemon on linux, just using runtime checks / switches
Prerequisites:
- .NET Core SDK 2.0.3 or higher (
.csprojbased tooling) - Windows machine
- Elevated command prompt: Run cmd as administrator.
> cd samples\TestService
> dotnet restore
> dotnet run --register-service --urls http://*:5080
...
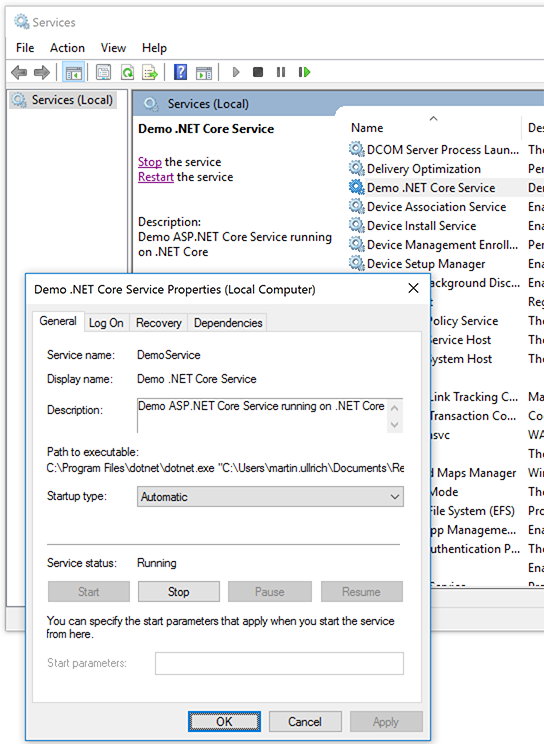
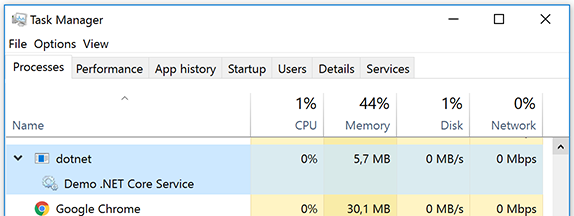
Successfully registered and started service "Demo .NET Core Service" ("Demo ASP.NET Core Service running on .NET Core")Open http://localhost:5080 in a browser. You should see Hello world.
The "Services" administrative tool should show the service:
> dotnet run --unregister-service
...
Successfully unregistered service "Demo .NET Core Service" ("Demo ASP.NET Core Service running on .NET Core")Note that the service may show up as disabled for some time until all tools accessing the windows services apis have been closed.
See this Stackoverflow question.
Add a NuGet package reference to DasMulli.Win32.ServiceUtils.
Write a windows service using:
using DasMulli.Win32.ServiceUtils;
class Program
{
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
var myService = new MyService();
var serviceHost = new Win32ServiceHost(myService);
serviceHost.Run();
}
}
class MyService : IWin32Service
{
public string ServiceName => "Test Service";
public void Start(string[] startupArguments, ServiceStoppedCallback serviceStoppedCallback)
{
// Start coolness and return
}
public void Stop()
{
// shut it down again
}
}You can then register your service via sc.exe (run cmd / powershell as administrator!):
sc.exe create MyService DisplayName= "My Service" binpath= "C:\Program Files\dotnet\dotnet.exe C:\path\to\MyService.dll --run-as-service"
Now go the services console / task manager and start your service.
Not that sc will install your service as SYSTEM user which has way to many access rights to run things like web apps.
See it's reference for more options.
If you want to get rid of it again, use:
sc.exe delete MyService
You can also create a service that registers itself like the example provided by taking a look at the sample source.
Also take a look at the ASP.NET Core MVC sample, which has additional logic to set the correct working directory.
When running it in development and not from the published output, be sure to pass --preserve-working-directory to it when registering
so that it will run from the project directory (e.g. run dotnet run --register-service --preserve-working-directory from and administrative
command prompt).
- No custom exceptions / error codes. Everything will throw a
Win32Exceptionif something goes wrong (It's message should be interpretable on windows). - All exceptions thrown by the service implementation will cause the service host to report exit code -1 / 0xffffffff to the service control manager.
- Currently, no direct support for services supporting pause and continue commands as well as other commands (power event, system shutdown)
- However, consumers can now use
IWin32ServiceStateMachineto implement custom behavior. CopySimpleServiceStateMachineas a starting point to implement extended services.
- However, consumers can now use