Table of Contents
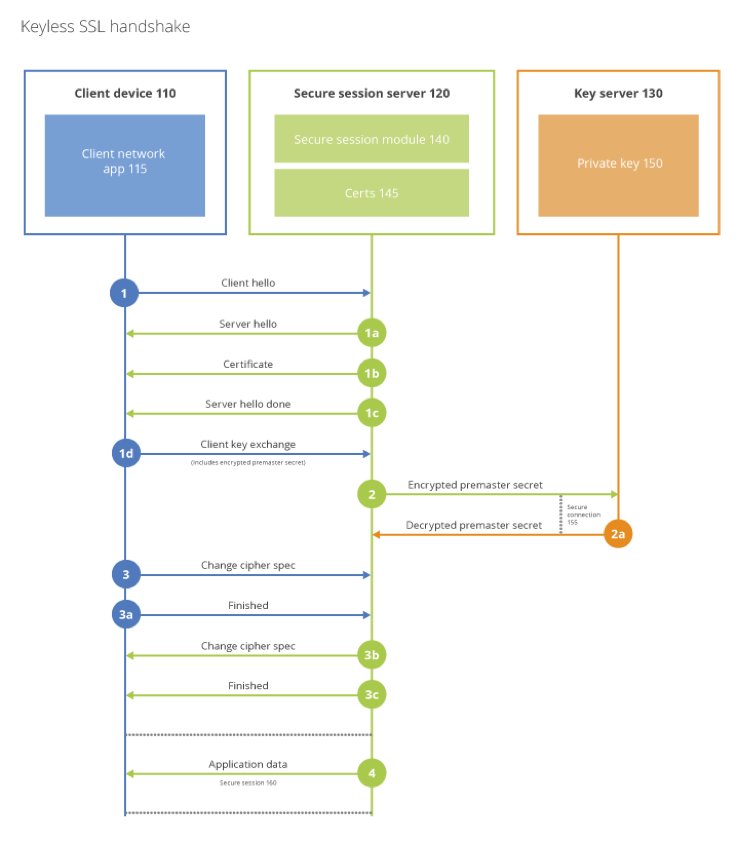
Go Keyless is an implementation Cloudflare's Keyless SSL Protocol in Go. It is provided as an upgrade to the previous C implementation.
The Cloudflare Keyless SSL client communicates to the server via a binary protocol over a mutually authenticated TLS 1.2 tunnel. Messages are in binary format and identified by a unique ID.
Messages consist of a fixed length header, and a variable length body. The body of the message consists of a sequence of items in TLV (tag, length, value) messages.
All messages with major version 1 will conform to the following format. The minor version is currently set to 0 and is reserved for communicating policy information.
Header:
0 - - 1 - - 2 - - 3 - - 4 - - 5 - - 6 - - 7 - - 8
| Maj | Min | Length | ID |
| Body |
| Body | <- 8 + Length
Item:
0 - - 1 - - 2 - - 3 - - 4 - - 5 - - 6 - - 7 - - 8
| Tag | Length | Data |
| Data | <- 3 + Length
All numbers are in network byte order (big endian).
The following tag values are possible for items:
0x01 - Certificate Digest,
0x02 - Server Name Indication,
0x03 - Client's IP address,
0x11 - Opcode,
0x12 - Payload,
0x13 - CustomFuncName, (for use with opcode 0x24)
A requests contains a header and the following items:
0x01 - length: 32 bytes, data: SHA256 of RSA modulus
0x02 - length: variable, data: SNI string
0x03 - length: 4 or 16 bytes, data: IPv4/6 address
0x11 - length: 1, data: opcode describing operation
0x12 - length: variable, data: payload to sign or encrypt
The following opcodes are supported in the opcode item:
0x01 - operation: RSA decrypt payload
0x02 - operation: RSA sign MD5SHA1
0x03 - operation: RSA sign SHA1
0x04 - operation: RSA sign SHA224
0x05 - operation: RSA sign SHA256
0x06 - operation: RSA sign SHA384
0x07 - operation: RSA sign SHA512
0x08 - operation: RSA raw decrypt payload
0x12 - operation: ECDSA sign MD5SHA1
0x13 - operation: ECDSA sign SHA1
0x14 - operation: ECDSA sign SHA224
0x15 - operation: ECDSA sign SHA256
0x16 - operation: ECDSA sign SHA384
0x17 - operation: ECDSA sign SHA512
0x23 - operation: RPC
0x24 - operation: Custom Function
0x35 - operation: RSASSA-PSS sign SHA256
0x36 - operation: RSASSA-PSS sign SHA384
0x36 - operation: RSASSA-PSS sign SHA512
Responses contain a header with a matching ID and only two items:
0x11 - length: 1, data: opcode describing operation status
0x12 - length: variable, data: payload response
The following opcodes are supported in the opcode item:
0xF0 - operation: success, payload: modified payload
0xFF - operation: RSA decrypt payload, payload:
On an error, these are the possible 1-byte payloads:
0x01 - cryptography failure
0x02 - key not found - no matching certificate ID
0x03 - read error - I/O read failure
0x04 - version mismatch - unsupported version incorrect
0x05 - bad opcode - use of unknown opcode in request
0x06 - unexpected opcode - use of response opcode in request
0x07 - format error - malformed message
0x08 - internal error - memory or other internal error
Defines and further details of the protocol can be found in kssl.h from the C implementation.
The Keyless SSL server is a TLS server and therefore requires cryptographic keys. All requests are mutually authenticated, so both the client and the server need a TLS 1.2 compatible key pair. The client must present a client certificate that can be verified against the CA that the keyless server is configured to use.
The server will need a valid key and certificate pair in PEM format that the Cloudflare Keyless SSL clients will trust (the server will automatically generate the pair using the Cloudflare API). The following options are required and take a path to these files. These two parameters set up the certificate (and associated private key) that will be presented by the server when a client connects.
--auth-cert
--auth-key
In order for this server to authenticate the Cloudflare client's certificate, a custom CA file is required. This CA certificate is provided by Cloudflare and specified with:
--cloudflare-ca-cert
The private keys that this server is able to use must be stored with a .key extension in either PEM or DER format, in one or more comma-separated directories denoted by the option:
--private-key-dirs
Note that the configuration file is the recommended way to specify these options; see below for more information.
Private keys can also be stored on a Hardware Security Module. Keyless can access such a key using a PKCS #11 URI in the configuration file. Here are some examples of URIs for keys stored on various HSM providers:
private_key_stores:
- uri: pkcs11:token=SoftHSM2%20RSA%20Token;id=%03?module-path=/usr/lib64/libsofthsm2.so&pin-value=1234
- uri: pkcs11:token=accelerator;object=thaleskey?module-path=/opt/nfast/toolkits/pkcs11/libcknfast.so
- uri: pkcs11:token=YubiKey%20PIV;id=%00?module-path=/usr/lib64/libykcs11.so&pin-value=123456&max-sessions=1
- uri: pkcs11:token=SoftHSM2%20RSA%20Token;id=%03?module-path=/usr/lib64/libsofthsm2.so&pin-value=1234
- uri: pkcs11:token=elab2parN;id=%04?module-path=/usr/lib/libCryptoki2_64.so&pin-value=crypto1
Note you must provide exactly one of the token, serial, or slot-id attributes to identify the token.
Full instructions: https://developers.cloudflare.com/ssl/keyless-ssl/hardware-security-modules#communicating-using-pkcs11
note: support added in v1.6.4
Private keys can also be stored in Azure's key management offerings.
private_key_stores:
- uri: https://keyless-hsm-1.managedhsm.azure.net/keys/keyless-a/256400ae07e74327b5d233c15aea837
- uri: https://keyless-vault-1.vault.azure.net/keys/keyless-b/d791e7f42b3a4f3ea8acc65014ea6a95
If gokeyless is running in a VM with Managed Services enabled, auth works out of the box. Otherwise, credentials can also be specified with an env var containing the path to a file. (env vars are defined here)
The required roles are /keys/read/action and /keys/sign/action
Full instructions: https://developers.cloudflare.com/ssl/keyless-ssl/hardware-security-modules/azure-managed-hsm
note: support added in v1.6.4
Private keys can also be stored in Google Cloud's key management offerings
private_key_stores:
- uri: projects/abc/locations/us-west1/keyRings/xyz/cryptoKeys/example-key/cryptoKeyVersions/3
Application Default Credentials are supported, the required IAM role is roles/cloudkms.signerVerifier
Full instructions: https://developers.cloudflare.com/ssl/keyless-ssl/hardware-security-modules/google-cloud-hsm
Instructions for installing Go Keyless from .deb and .rpm packages can be found at https://pkg.cloudflare.com.
Compiling Go Keyless requires Go 1.11. Binary distributions can be found at golang.org/dl.
Installing the appropriate package for your operating system should leave you with a working Go installation and a properly set GOPATH.
PKCS#11 support also requires cgo, which needs a working toolchain. Install the build-essential and libltdl-dev packages on debian, or their equivalents for your OS.
Then install the gokeyless binary:
$ go get -u github.com/cloudflare/gokeyless/...
$ go install github.com/cloudflare/gokeyless/cmd/gokeyless/...
The the keyserver for Keyless SSL consists of a single binary file, gokeyless. When you run the binary, it will first check for a gokeyless.yaml file in the current working directory, falling back to the system wide file located at /etc/keyless/gokeyless.yaml (the default configuration file will be placed there if you install via one of the .deb or .rpm packages).
You should add your Cloudflare account details to the configuration file, and optionally customize the location of the private key directory. Most users should not need to modify the remaining defaults.
Each option can optionally be overridden via environment variables or command-line arguments. Run gokeyless -h to see the full list of available options.
Unit tests and benchmarks have been implemented for various parts of Go Keyless via go test. Most of the tests run out of the box, but some setup is necessary to run the HSM-related tests:
-
Follow https://wiki.opendnssec.org/display/SoftHSMDOCS/SoftHSM+Documentation+v2 to install SoftHSM2
-
Copy the test tokens to the location of your SoftHSM2 token directory (commonly
/var/lib/softhsm/tokens, but may vary):$ cp -r tests/testdata/tokens/* /path/to/token/directory/ -
The tests currently assume the SoftHSM2 library will be installed at
/usr/local/lib/softhsm/libsofthsm2.so. If your system differs, you must create a symlink (sudo may be required):$ mkdir -p /usr/local/lib/softhsm $ ln -s /path/to/libsofthsm2.so /usr/local/lib/softhsm/libsofthsm2.so
Then simply run make test to execute the test suite.
Note that if you need to run the tests without first configuring SoftHSM2 for some reason, you can use the test-nohsm target.
See the LICENSE file for details. Note: the license for this project is not 'open source' as described in the Open Source Definition.