Dedalus is a flexible framework for solving partial differential equations using modern spectral methods. The code is open-source and developed by a team of researchers studying astrophysical, geophysical, and biological fluid dynamics.
Dedalus is written primarily in Python and features an easy-to-use interface with symbolic vectorial equation specification. For example, to simulate incompressible hydrodynamics in a ball, you can symbolically enter the equations, including gauge conditions and boundary conditions enforced with the tau method, as:
problem.add_equation("div(u) + tau_p = 0")
problem.add_equation("dt(u) - nu*lap(u) + grad(p) + lift(tau_u) = - u@grad(u)")
problem.add_equation("u(r=1) = 0")
problem.add_equation("integ(p) = 0")Our numerical algorithms produce sparse and spectrally accurate discretizations of PDEs on simple domains, including Cartesian domains of any dimension, disks, annuli, spheres, spherical shells, and balls:
The resulting systems are efficiently solved using compiled libraries and are automatically parallelized using MPI. See the documentation for tutorials and additional examples.
- Project homepage: http://dedalus-project.org
- Code repository: https://github.com/DedalusProject/dedalus
- Documentation: http://dedalus-project.readthedocs.org
- Mailing list: https://groups.google.com/forum/#!forum/dedalus-users





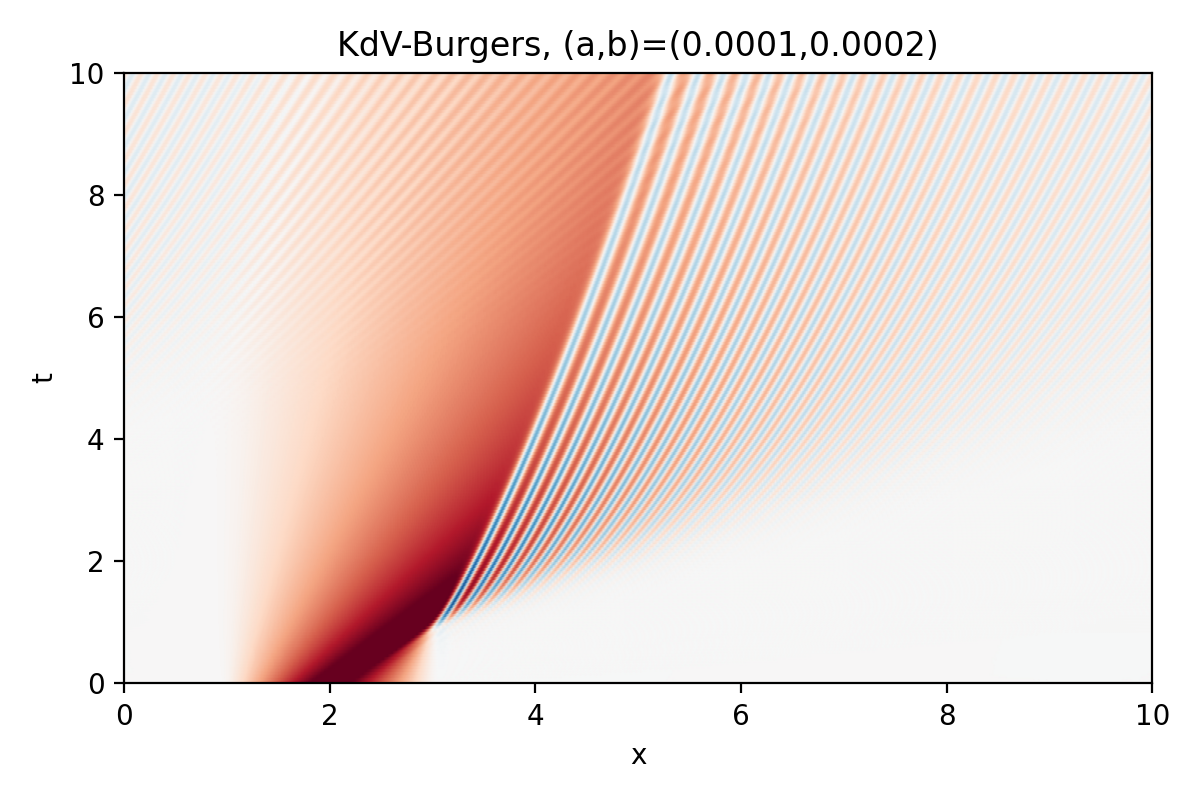 KdV-Burgers equation (1D IVP)
KdV-Burgers equation (1D IVP)
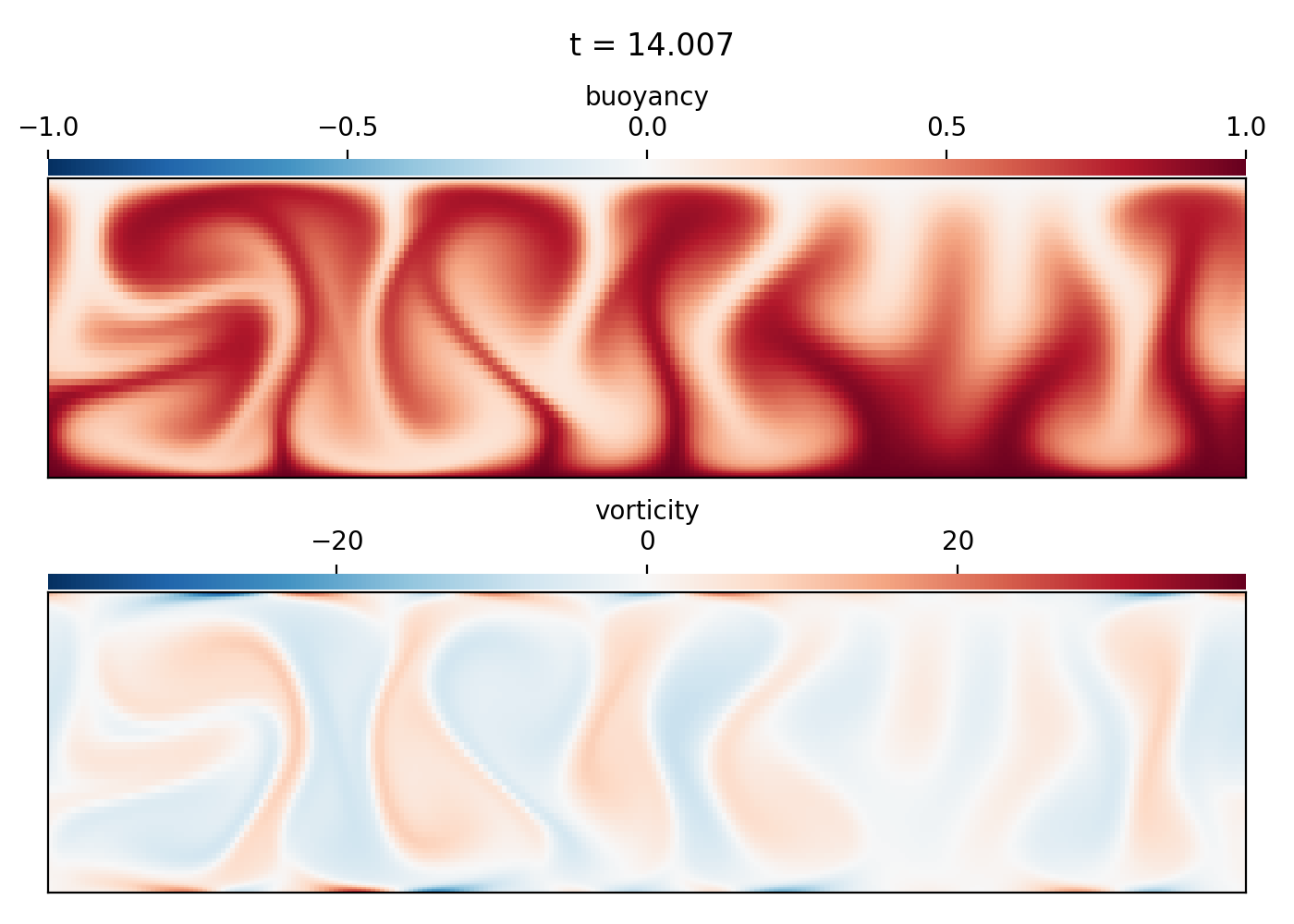 Rayleigh-Benard convection (2D IVP)
Rayleigh-Benard convection (2D IVP)
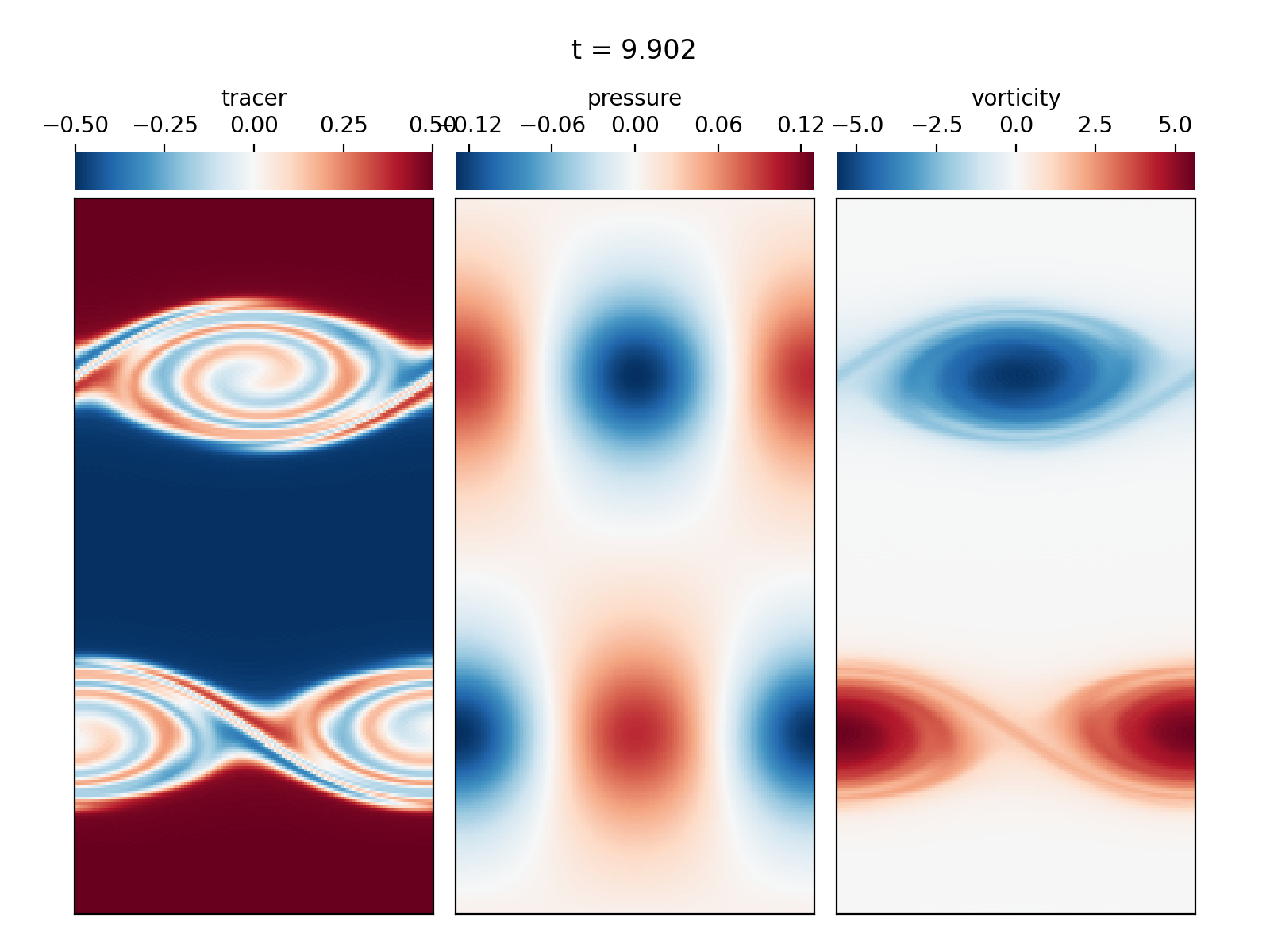 Periodic shear flow (2D IVP)
Periodic shear flow (2D IVP)
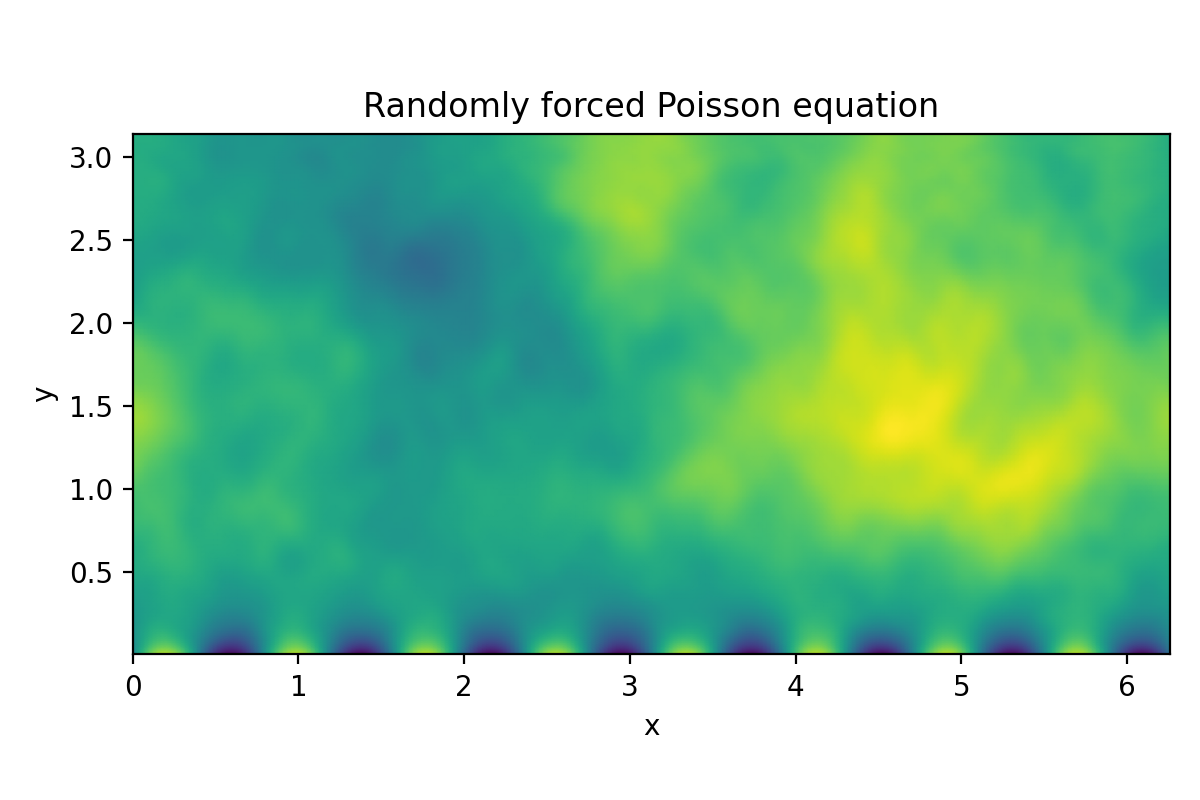 Poisson equation (2D LBVP)
Poisson equation (2D LBVP)
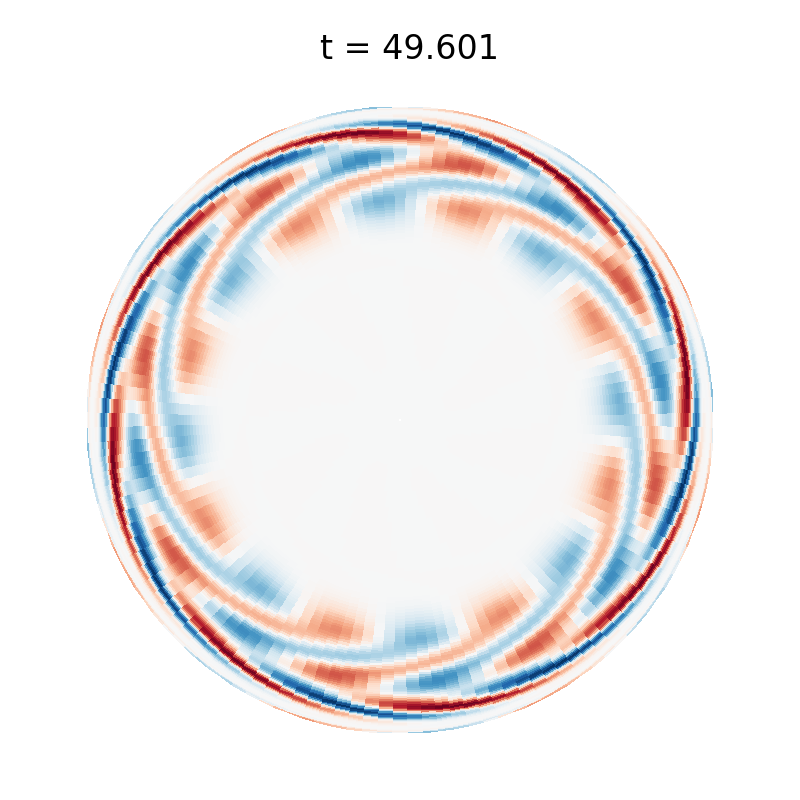 Librational instability (disk IVP)
Librational instability (disk IVP)
 Spherical shallow water (sphere IVP)
Spherical shallow water (sphere IVP)
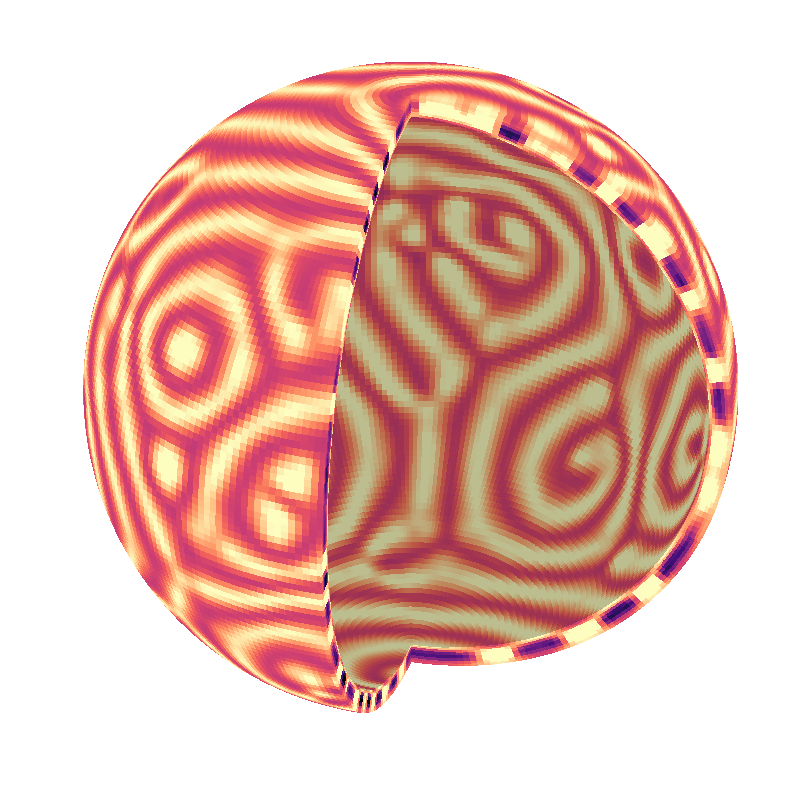 Spherical shell convection (shell IVP)
Spherical shell convection (shell IVP)
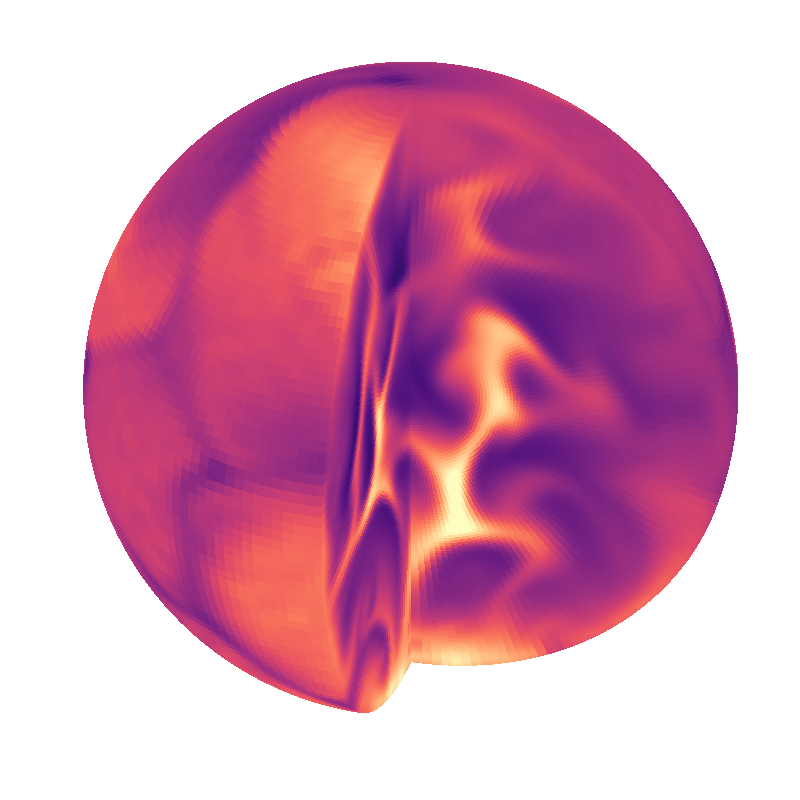 Internally heated convection (ball IVP)
Internally heated convection (ball IVP)