Paper |
Pretrained Models |
Datasets
Official PyTorch Implementation
Tal Ridnik, Gilad Sharir, Avi Ben-Cohen, Emanuel Ben-Baruch, Asaf Noy
DAMO Academy, Alibaba Group
Abstract
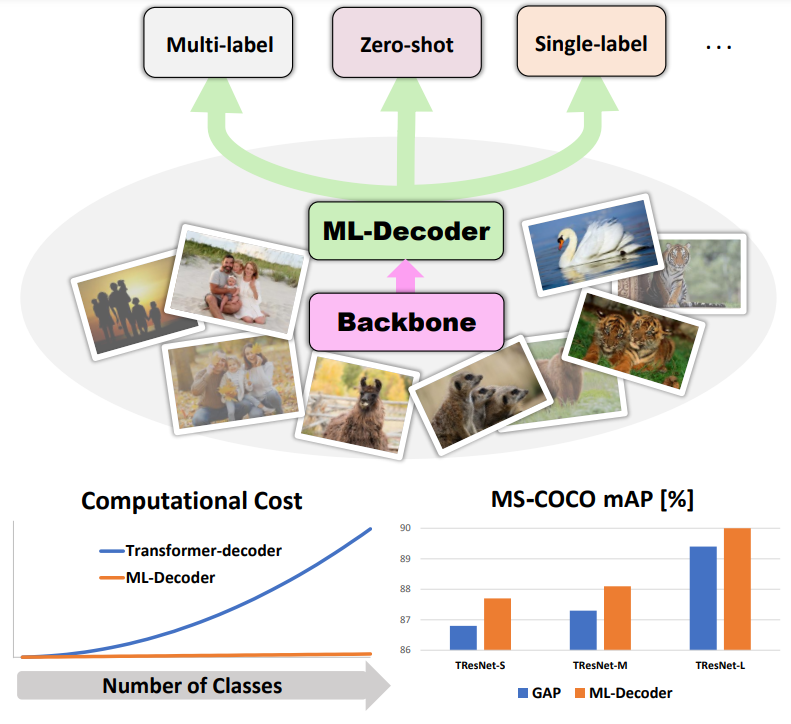
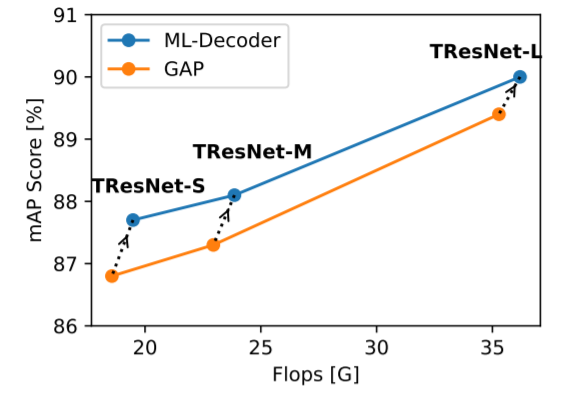
In this paper, we introduce ML-Decoder, a new attention-based classification head. ML-Decoder predicts the existence of class labels via queries, and enables better utilization of spatial data compared to global average pooling. By redesigning the decoder architecture, and using a novel group-decoding scheme, ML-Decoder is highly efficient, and can scale well to thousands of classes. Compared to using a larger backbone, ML-Decoder consistently provides a better speed-accuracy trade-off. ML-Decoder is also versatile - it can be used as a drop-in replacement for various classification heads, and generalize to unseen classes when operated with word queries. Novel query augmentations further improve its generalization ability. Using ML-Decoder, we achieve state-of-the-art results on several classification tasks: on MS-COCO multi-label, we reach 91.4% mAP; on NUS-WIDE zero-shot, we reach 31.1% ZSL mAP; and on ImageNet single-label, we reach with vanilla ResNet50 backbone a new top score of 80.7%, without extra data or distillation.
 |
 |
ML-Decoder implementation is available here. It can be easily integrated into any backbone using this example code:
ml_decoder_head = MLDecoder(num_classes) # initilization
spatial_embeddings = self.backbone(input_image) # backbone generates spatial embeddings
logits = ml_decoder_head(spatial_embeddings) # transfrom spatial embeddings to logits
See Model Zoo
 |
We share a full reproduction code for the article results.
A reproduction code for MS-COCO multi-label:
python train.py \
--data=/home/datasets/coco2014/ \
--model_name=tresnet_l \
--image_size=448
Our single-label training code uses the excellent timm repo. Reproduction code is currently from a fork, we will work toward a full merge to the main repo.
git clone https://github.com/mrT23/pytorch-image-models.git
This is the code for A2 configuration training, with ML-Decoder (--use-ml-decoder-head=1):
python -u -m torch.distributed.launch --nproc_per_node=8 \
--nnodes=1 \
--node_rank=0 \
./train.py \
/data/imagenet/ \
--amp \
-b=256 \
--epochs=300 \
--drop-path=0.05 \
--opt=lamb \
--weight-decay=0.02 \
--sched='cosine' \
--lr=4e-3 \
--warmup-epochs=5 \
--model=resnet50 \
--aa=rand-m7-mstd0.5-inc1 \
--reprob=0.0 \
--remode='pixel' \
--mixup=0.1 \
--cutmix=1.0 \
--aug-repeats 3 \
--bce-target-thresh 0.2 \
--smoothing=0 \
--bce-loss \
--train-interpolation=bicubic \
--use-ml-decoder-head=1
First download the following files to the root path of the dataset:
benchmark_81_v0.json
wordvec_array.pth
data.csv
Training code for NUS-WIDE ZSL:
python train_zsl_nus.py \
--data=/home/datasets/nus_wide/ \
--image_size=224
Using ML-Decoder classification head, we reached a top result of 96.41% on Stanford-Cars dataset, and 95.1% on CIFAR-100 dataset. We will add this result to a future version of the paper.
@misc{ridnik2021mldecoder,
title={ML-Decoder: Scalable and Versatile Classification Head},
author={Tal Ridnik and Gilad Sharir and Avi Ben-Cohen and Emanuel Ben-Baruch and Asaf Noy},
year={2021},
eprint={2111.12933},
archivePrefix={arXiv},
primaryClass={cs.CV}
}




