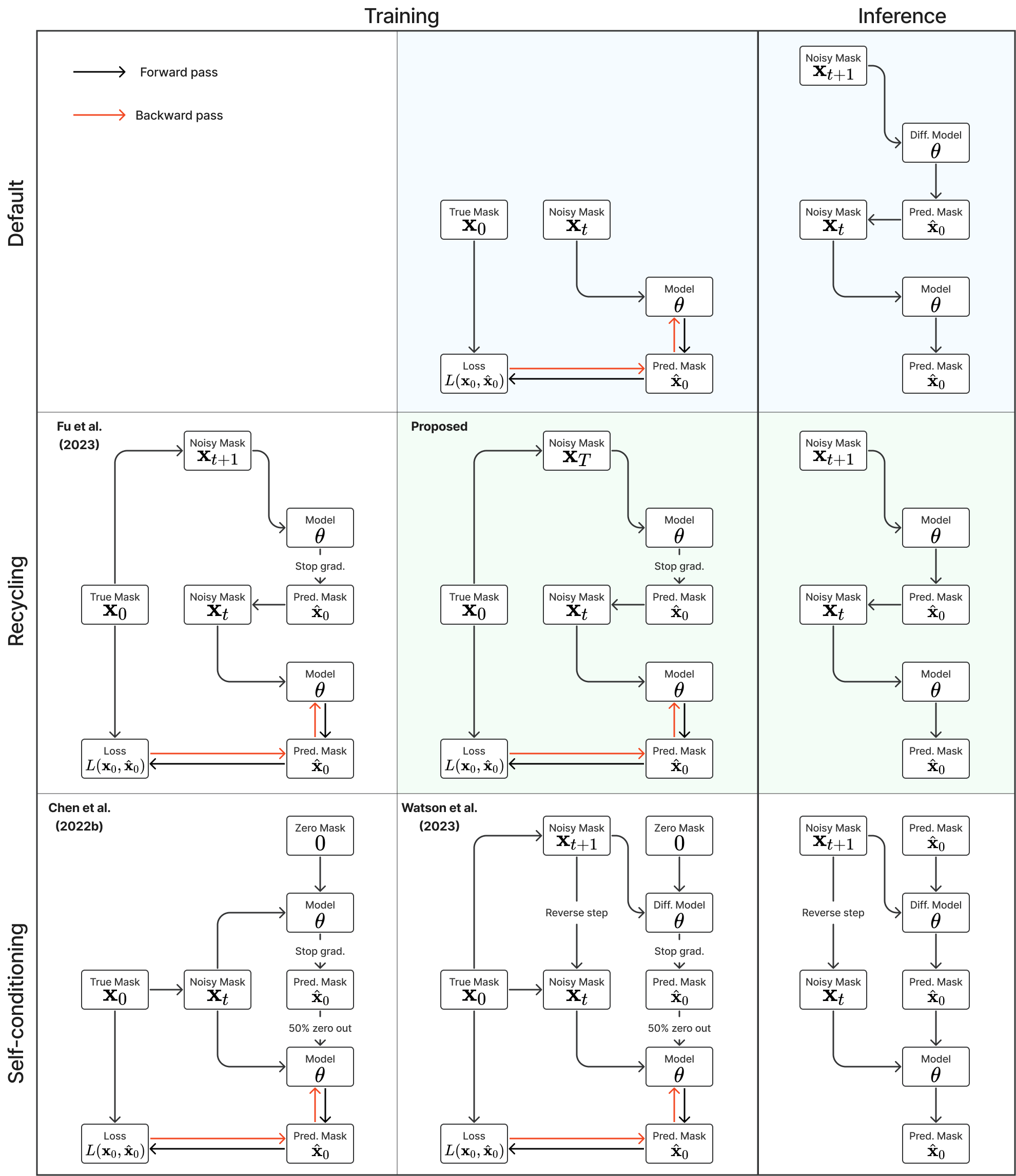
🎉 This is a follow-up work of Importance of Aligning Training Strategy with Evaluation for Diffusion Models in 3D Multiclass Segmentation (paper, code), with better recycling method, better network, more baseline training methods (including self-conditioning) on four data sets (muscle ultrasound, male pelvic MR, abdominal CT, brain MR).
📑 The preprint is available on arXiv.
ImgX is a Jax-based deep learning toolkit for biomedical image segmentations.
Current supported functionalities are summarized as follows.
Data sets
See the readme for details on training, validation, and test splits.
- Muscle ultrasound from Marzola et al. 2021.
- Male pelvic MR from Li et al. 2022.
- AMOS CT from Ji et al. 2022.
- Brain MR from Baid et al. 2021.
Algorithms
- Supervised segmentation.
- Diffusion-based segmentation.
- Gaussian noise based diffusion.
- Prediction of noise or ground truth.
- Training with recycling or self-conditioning.
Models
- U-Net with Transformers supporting 2D and 3D images.
Training
- Patch-based training.
- Multi-device training (one model per device).
- Mixed precision training.
- Gradient clipping and accumulation.
The following instructions have been tested only for TPU-v3-8. The docker container uses root user.
-
Build the docker image inside the repository.
sudo docker build --build-arg USER_ID=$(id -u) --build-arg GROUP_ID=$(id -g) -f docker/Dockerfile.tpu -t imgx .
where
--build-argprovides argument values.-fprovides the docker file.-ttag the docker image.
-
Run the Docker container.
mkdir -p $(cd ../ && pwd)/tensorflow_datasets sudo docker run -it --rm --privileged --network host \ -v "$(pwd)":/app/ImgX \ -v "$(cd ../ && pwd)"/tensorflow_datasets:/root/tensorflow_datasets \ imgx bash
-
Install the package inside container.
make pip
TPU often has limited disk space. RAM disk can be used to help.
sudo mkdir /tmp/ramdisk
sudo chmod 777 /tmp/ramdisk
sudo mount -t tmpfs -o size=256G imgxramdisk /tmp/ramdisk
cd /tmp/ramdisk/The following instructions have been tested only for CUDA == 11.4.1 and CUDNN == 8.2.0. The docker container uses non-root user. Docker image used may be removed.
-
Build the docker image inside the repository.
docker build --build-arg HOST_UID=$(id -u) --build-arg HOST_GID=$(id -g) -f docker/Dockerfile -t imgx .
where
--build-argprovides argument values.-fprovides the docker file.-ttag the docker image.
-
Run the Docker container.
mkdir -p $(cd ../ && pwd)/tensorflow_datasets docker run -it --rm --gpus all \ -v "$(pwd)":/app/ImgX \ -v "$(cd ../ && pwd)"/tensorflow_datasets:/home/app/tensorflow_datasets \ imgx bash
where
--rmremoves the container once exit it.-vmaps theImgXfolder into container.
-
Install the package inside container.
make pip
Download Miniforge from GitHub and install it.
conda install -y -n base conda-libmamba-solver
conda config --set solver libmamba
conda env update -f docker/environment_mac_m1.ymlInstall Conda and then create the environment.
conda install -y -n base conda-libmamba-solver
conda config --set solver libmamba
conda env update -f docker/environment.ymlActivate the environment and install the package.
conda activate imgx
make pipUse the following commands to (re)build all data sets. Check the README of imgx_datasets for details. Especially, manual downloading is required for the BraTS 2021 dataset.
make build_dataset
make rebuild_datasetExample command to use two GPUs for training, validation and testing. The
outputs are stored under wandb/latest-run/files/, where
ckptstores the model checkpoints and corresponding validation metrics.test_evaluationstores the prediction on test set and corresponding metrics.
# limit to two GPUs if using NVIDIA GPUs
export CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES="0,1"
# select data set to use
export DATASET_NAME="male_pelvic_mr"
export DATASET_NAME="amos_ct"
export DATASET_NAME="muscle_us"
export DATASET_NAME="brats2021_mr"
# Vanilla segmentation
imgx_train data=${DATASET_NAME} task=seg
imgx_valid --log_dir wandb/latest-run/
imgx_test --log_dir wandb/latest-run/
# Diffusion-based segmentation
imgx_train data=${DATASET_NAME} task=gaussian_diff_seg
imgx_valid --log_dir wandb/latest-run/ --num_timesteps 5 --sampler DDPM
imgx_test --log_dir wandb/latest-run/ --num_timesteps 5 --sampler DDPM
imgx_valid --log_dir wandb/latest-run/ --num_timesteps 5 --sampler DDIM
imgx_test --log_dir wandb/latest-run/ --num_timesteps 5 --sampler DDIMimgx_test --log_dir wandb/latest-run/ --num_timesteps 5 --num_seeds 3Optionally, for debug purposes, use flag debug=True to run the experiment with
a small dataset and smaller models.
imgx_train --config-name config_${DATASET_NAME}_seg debug=True
imgx_train --config-name config_${DATASET_NAME}_diff_seg debug=TrueInstall pre-commit hooks:
pre-commit install
wily build .Update hooks, and re-verify all files.
pre-commit autoupdate
pre-commit run --all-filesRun the command below to test and get coverage report. As JAX tests requires two
CPUs, -n 4 uses 4 threads, therefore requires 8 CPUs in total.
pytest --cov=imgx -n 4 tests- Segment Anything (PyTorch)
- MONAI (PyTorch)
- Cross Institution Few Shot Segmentation (PyTorch)
- MegSegDiff (PyTorch)
- MegSegDiff (PyTorch, lucidrains)
- DeepReg (Tensorflow)
- Scenic (JAX)
- DeepMind Research (JAX)
- Haiku (JAX)
This work was supported by the EPSRC grant (EP/T029404/1), the Wellcome/EPSRC Centre for Interventional and Surgical Sciences (203145Z/16/Z), the International Alliance for Cancer Early Detection, an alliance between Cancer Research UK (C28070/A30912, C73666/A31378), Canary Center at Stanford University, the University of Cambridge, OHSU Knight Cancer Institute, University College London and the University of Manchester, and Cloud TPUs from Google's TPU Research Cloud (TRC).
If you find the code base and method useful in your research, please cite the relevant paper:
@article{fu2023recycling,
title={A Recycling Training Strategy for Medical Image Segmentation with Diffusion Denoising Models},
author={Fu, Yunguan and Li, Yiwen and Saeed, Shaheer U and Clarkson, Matthew J and Hu, Yipeng},
journal={arXiv preprint arXiv:2308.16355},
year={2023},
doi={10.48550/arXiv.2308.16355},
url={https://arxiv.org/abs/2308.16355},
}
@article{fu2023importance,
title={Importance of Aligning Training Strategy with Evaluation for Diffusion Models in 3D Multiclass Segmentation},
author={Fu, Yunguan and Li, Yiwen and Saeed, Shaheer U and Clarkson, Matthew J and Hu, Yipeng},
journal={arXiv preprint arXiv:2303.06040},
year={2023},
doi={10.48550/arXiv.2303.06040},
url={https://arxiv.org/abs/2303.06040},
}