This Python-based tool is designed for transcribing YouTube videos and playlists into text. It integrates various technologies like faster-whisper for transcription, SpaCy for natural language processing, and CUDA for GPU acceleration, aimed at processing video content efficiently. The script is capable of handling both individual videos and entire playlists, outputting accurate transcripts along with metadata.
 |
|---|
| Bulk Transcripts Have Never Been This Easy! |
- YouTube Downloading: Uses
pytubeto download the audio from YouTube videos or playlists. - Audio Transcription:
- Local Inference: Leverages
faster_whisper.WhisperModelfor converting audio to text. This model is a variant of OpenAI's Whisper designed for speed and accuracy. - OpenAI API: Optionally uses the OpenAI API for transcription, though this uses an older and less accurate version of the Whisper model.
- Local Inference: Leverages
- NLP Processing: Optionally, integrates SpaCy for sophisticated sentence splitting, enhancing the readability and structure of the transcript.
- CUDA Acceleration: Implements CUDA support for GPU utilization, enhancing processing speed for compatible hardware.
- Progress Tracking: Utilizes
tqdmfor displaying progress bars during transcription.
-
Initialization:
- The script starts by determining whether to process a single video or a playlist based on the
convert_single_videoflag. - It sets up necessary directories for storing downloaded audio, transcripts, and metadata.
- The script starts by determining whether to process a single video or a playlist based on the
-
Environment Configuration:
- Adds CUDA Toolkit path to the system environment for GPU utilization.
- Configures the number of workers for transcription based on the CPU core count.
-
Video Processing:
- For each video in the playlist or the single video, the script downloads the audio.
- It ensures unique naming for each audio file to avoid overwrites.
-
Transcription:
- The audio files are passed to either the local WhisperModel or the OpenAI API for transcription.
- The script handles GPU acceleration if available, defaulting to CPU otherwise for local inference.
- Transcription results are split into sentences, either using SpaCy or a custom regex-based splitter.
-
Metadata Generation:
- Along with the transcript, the script generates metadata including timestamps and confidence scores for each segment.
-
Output:
- The transcripts are saved in plain text, CSV, and JSON formats, providing both the raw transcript and structured metadata.
-
Display/Read:
- To make the transcripts easier to read, an html file is provided,
transcript_reader.html, which does further clean up and offers a "Reader Mode" where you can choose the font, text size, text width, and toggle dark mode. Simply open this html file in your browser and paste in the transcript text from one of the generated files in thegenerated_transcript_combined_textsfolder.
- To make the transcripts easier to read, an html file is provided,
 |
|---|
| Screenshot of it in Action |
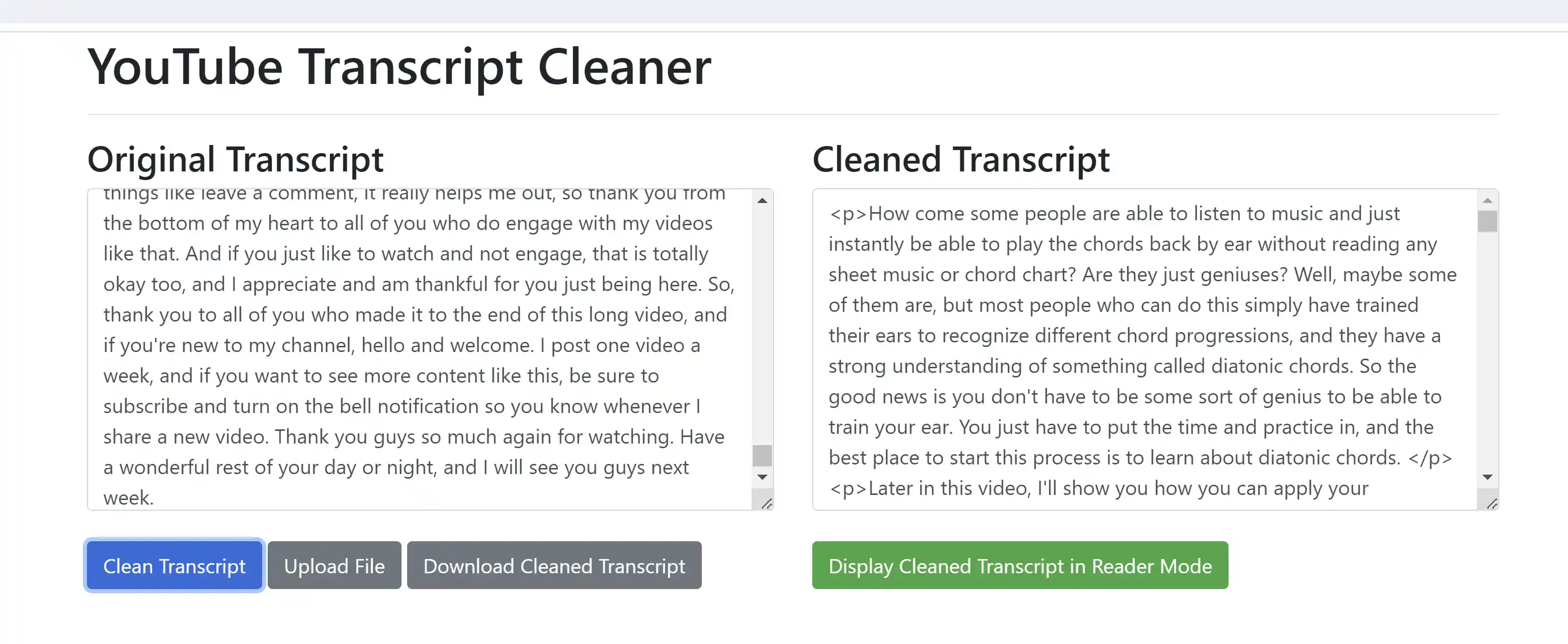 |
 |
|---|---|
| Paste Transcript Text into the Transcript Reader HTML File | Reader using Dark Mode and Cambria Font |
- Content Analysis: Useful for researchers and analysts working with video content.
- Accessibility: Assists in creating subtitles and closed captions for videos.
- Educational Purposes: Helps in creating study materials from educational videos.
- Archival: Transcribes and archives video content for long-term storage and retrieval.
git clone https://github.com/Dicklesworthstone/bulk_transcribe_youtube_videos_from_playlist.git
cd bulk_transcribe_youtube_videos_from_playlistIf you prefer to use pyenv for managing Python versions, follow these steps:
# Install pyenv if not already installed
if ! command -v pyenv &> /dev/null; then
git clone https://github.com/pyenv/pyenv.git ~/.pyenv
echo 'export PYENV_ROOT="$HOME/.pyenv"' >> ~/.bashrc
echo 'export PATH="$PYENV_ROOT/bin:$PATH"' >> ~/.bashrc
echo 'eval "$(pyenv init --path)"' >> ~/.bashrc
source ~/.bashrc
fi
# Update pyenv and install Python 3.12
cd ~/.pyenv && git pull && cd -
pyenv install 3.12
# Set local Python version for the project
pyenv local 3.12Choose one of the following methods:
# Create a virtual environment
python3 -m venv venv
# Activate the virtual environment
source venv/bin/activate
# Upgrade pip and install wheel
python3 -m pip install --upgrade pip
python3 -m pip install wheel
# Install dependencies
pip install -r requirements.txt# Create a virtual environment
python -m venv venv
# Activate the virtual environment
source venv/bin/activate
# Upgrade pip and install wheel
python -m pip install --upgrade pip
python -m pip install wheel
# Install dependencies
pip install -r requirements.txtOpen the bulk_transcribe_youtube_videos_from_playlist.py file and set the following variables according to your preferences:
convert_single_video: Set to1for a single video,0for a playlistuse_spacy_for_sentence_splitting: Set to1to use SpaCy,0for regex-based splittinguse_openai_api_for_transcription: Set to1to use OpenAI API,0for local Whisper modelopenai_api_key: If using OpenAI API, replace with your API keysingle_video_url: URL of the single video (ifconvert_single_videois1)playlist_url: URL of the playlist (ifconvert_single_videois0)
Execute the script with Python:
python bulk_transcribe_youtube_videos_from_playlist.py- If you're using the OpenAI API for transcription, make sure you have a valid API key and sufficient credits.
- The script will create necessary directories for storing downloaded audio and generated transcripts.
- Progress bars will display the transcription progress for each video.
- Remember that local inference using the Whisper model provides higher accuracy compared to the OpenAI API version.
If you encounter any issues during setup or execution, please check the project's issue tracker on GitHub or create a new issue with details about the problem.
- Video Mode Selection: Determines whether to process a single video or a playlist based on the
convert_single_videoflag. This choice dictates which URL (eithersingle_video_urlorplaylist_url) will be used for downloading content. - System Path Modification:
add_to_system_pathfunction adds new paths to the system environment, ensuring that dependencies like CUDA Toolkit are accessible. For Windows systems, it also handles the case where the new path contains spaces, enclosing it in quotes. - CUDA Toolkit Path Detection:
get_cuda_toolkit_pathlocates the CUDA Toolkit directory, crucial for GPU acceleration. It checks the Anaconda packages directory for the toolkit's installation path. - Directory Setup: Creates necessary directories for storing downloaded audio files, combined transcript texts, and metadata tables.
- Video Downloading:
download_audioasynchronously downloads audio from YouTube videos. It ensures unique naming for each audio file by appending a counter if a file with the same name already exists. This function returns the path to the downloaded audio file and the filename. - Audio Stream Handling: The function selects the first available audio stream from the video. If no audio stream is found, it raises an error.
- Transcription Setup:
compute_transcript_with_whisper_from_audio_funcconfigures either the local WhisperModel or the OpenAI API for transcription. For local inference, it checks CUDA availability and sets the device and compute type accordingly. - Transcript Computation: This function performs the actual transcription, processing the audio file through the chosen method. It captures segments of transcribed text along with their metadata (start and end times, average log probability).
- Sentence Splitting: Depending on the
use_spacy_for_sentence_splittingflag, the script either uses SpaCy or a custom regex-based method for sentence splitting. This is important for structuring the transcript into readable sentences.
- Metadata Handling: The script generates detailed metadata for each transcribed segment, including timestamps and a measure of transcription confidence (normalized log probability).
- Output Generation: Transcripts are saved in text format, while metadata is stored in both CSV and JSON formats, providing structured data for further analysis or processing.
- Filename Cleaning:
clean_filenamesanitizes video titles for use as filenames, removing special characters and replacing spaces with underscores. - Pagination Break Removal:
remove_pagination_breakscleans up the transcript text by removing hyphens at line breaks and correcting line break issues, improving readability. - Log Probability Normalization:
normalize_logprobsnormalizes the log probabilities of transcription segments, useful for assessing the model's confidence in its transcription.
- The script's main execution starts in the
__main__block, where it selects the URL to process (single video or playlist) and initiates theprocess_video_or_playlistcoroutine. - Concurrent Downloads and Transcription:
process_video_or_playlisthandles the asynchronous downloading and transcription of videos. It creates a semaphore to limit the number of simultaneous downloads based onmax_simultaneous_youtube_downloads.
- Model Initialization: Initializes the WhisperModel with the specified device and compute type. The "large-v3" model variant is chosen, balancing between performance and accuracy.
- Request Time Tracking: The function records the UTC datetime when the transcription request starts. This can be used for performance metrics or logging purposes.
- API Initialization: Sets up the OpenAI API client with the provided API key.
- Model Selection: Uses the "whisper-1" model for transcription.
Important Note: The OpenAI API version of Whisper uses an older and less accurate version of the Whisper model. Users will achieve significantly higher transcription accuracy using local inference with the latest Whisper model.
- Transcription Execution: For local inference, calls
model.transcribeon a separate thread usingasyncio.to_threadto maintain the asynchronous nature of the script. For the OpenAI API, sends a request to the transcription endpoint. - Transcription Settings: For local inference, the transcription uses a
beam_sizeof 10 and activates thevad_filter. Thebeam_sizeparameter affects the trade-off between accuracy and speed during transcription - a higher value can lead to more accurate results but requires more computational resources. Thevad_filter(Voice Activity Detection filter) helps in ignoring non-speech segments in the audio, focusing the transcription process on relevant audio parts.
- Segment Processing: Each segment returned by the transcription process contains the transcribed text, its start and end times in the audio, and (for local inference) an average log probability (a measure of confidence). The function iterates over these segments, compiling the full transcript and generating a list of sentences using
sophisticated_sentence_splitter. - Metadata Generation: For each segment, it rounds off the start and end times and the average log probability (where applicable) to two decimal places and stores this data in a list of dictionaries. This metadata includes timing and confidence information for each transcribed segment.
- Text File: Writes the combined transcript to a text file, named after the audio file and stored in 'generated_transcript_combined_texts'.
- CSV and JSON: Converts the metadata list into a DataFrame and then exports it to both CSV and JSON formats, allowing for structured access to the transcription metadata.
- The function returns the combined transcript text, the list of metadata dictionaries, and the list of transcript sentences. These outputs can be used for further processing or analysis.
- Optional Integration: The tool optionally uses SpaCy, an advanced natural language processing library, for sentence splitting. This integration is controlled by the
use_spacy_for_sentence_splittingflag. - Model Downloading: If SpaCy is not installed, the script downloads the specified model (default is
en_core_web_sm) usingdownload_spacy_model. This model is optimized for English language processing, focusing on tasks like tokenization, lemmatization, and sentence boundary detection. - Sentence Splitter Functionality: The function
sophisticated_sentence_splitter, when using SpaCy, processes the transcript text to extract sentences. This process involves removing pagination breaks, tokenizing the text into sentences using SpaCy's model, and trimming whitespaces. - Regex-based Alternative: If SpaCy is not used, a custom regex-based method for sentence splitting is employed. This method uses a pattern to identify sentence boundaries, considering various punctuation marks and linguistic nuances.
- Video Queue Management: The script uses an
asyncio.Semaphoreto control the number of simultaneous downloads, ensuring that the system resources are not overwhelmed. - Asynchronous Downloads: Utilizes asynchronous programming to download and process multiple videos concurrently, significantly improving efficiency, especially for playlists with numerous videos.
- Error Handling: In the event of a download error or if no audio stream is found, the script logs the error and proceeds with the next video, ensuring that the process is not halted.
- Robustness: The script is designed to handle various errors gracefully, such as issues in downloading audio, absence of audio streams, or failures in transcription.
- Logging: Throughout the process, the script logs important information, such as the status of downloads, transcription progress, and any errors encountered. This logging is crucial for monitoring the script's performance and troubleshooting potential issues.
- TQDM Integration: The script now uses
tqdmto display progress bars during the transcription process, providing visual feedback on the progress of each video being processed.
This tool represents a comprehensive solution for transcribing YouTube videos and playlists. By leveraging state-of-the-art technologies in machine learning, natural language processing, and asynchronous programming, it offers an efficient and reliable way to convert audio content into structured text data. Whether for accessibility, content analysis, educational purposes, or archival, this script provides a robust framework to meet a wide range of transcription needs.
We welcome contributions to this project! Whether you're interested in fixing bugs, adding new features, or improving documentation, your help is greatly appreciated. To contribute:
- Fork the Repository: Start by forking the repository to your GitHub account.
- Create a Branch: Create a branch in your fork for your modifications.
- Make Your Changes: Implement your changes or improvements in your branch.
- Test Your Changes: Ensure your changes don't break existing functionality.
- Submit a Pull Request: Once you're satisfied with your changes, submit a pull request for review.
Please adhere to the existing coding style and add unit tests for any new functionality. If you have any questions or need assistance, feel free to open an issue in the repository.
MIT License
Copyright (c) 2023 by Jeffrey Emanuel
Permission is hereby granted, free of charge, to any person obtaining a copy of this software and associated documentation files (the "Software"), to deal in the Software without restriction, including without limitation the rights to use, copy, modify, merge, publish, distribute, sublicense, and/or sell copies of the Software, and to permit persons to whom the Software is furnished to do so, subject to the following conditions:
The above copyright notice and this permission notice shall be included in all copies or substantial portions of the Software.
THE SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED "AS IS", WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO THE WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY, FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND NONINFRINGEMENT. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE AUTHORS OR COPYRIGHT HOLDERS BE LIABLE FOR ANY CLAIM, DAMAGES OR OTHER LIABILITY, WHETHER IN AN ACTION OF CONTRACT, TORT OR OTHERWISE, ARISING FROM, OUT OF OR IN CONNECTION WITH THE SOFTWARE OR THE USE OR OTHER DEALINGS IN THE SOFTWARE.
See my other open-source projects at https://github.com/Dicklesworthstone, including:
- Swiss Army Llama
- Automatic Log Collector and Analyzer
- Fast Vector Similarity
- Cloud Benchmarker
- Prepare Project for LLM Prompt
- SQLAlchemy Data Model Visualizer
- Llama2 Aided Tesseract OCR
 |
|---|
| Take Your YouTube Transcript Addiction to the Next Level! |