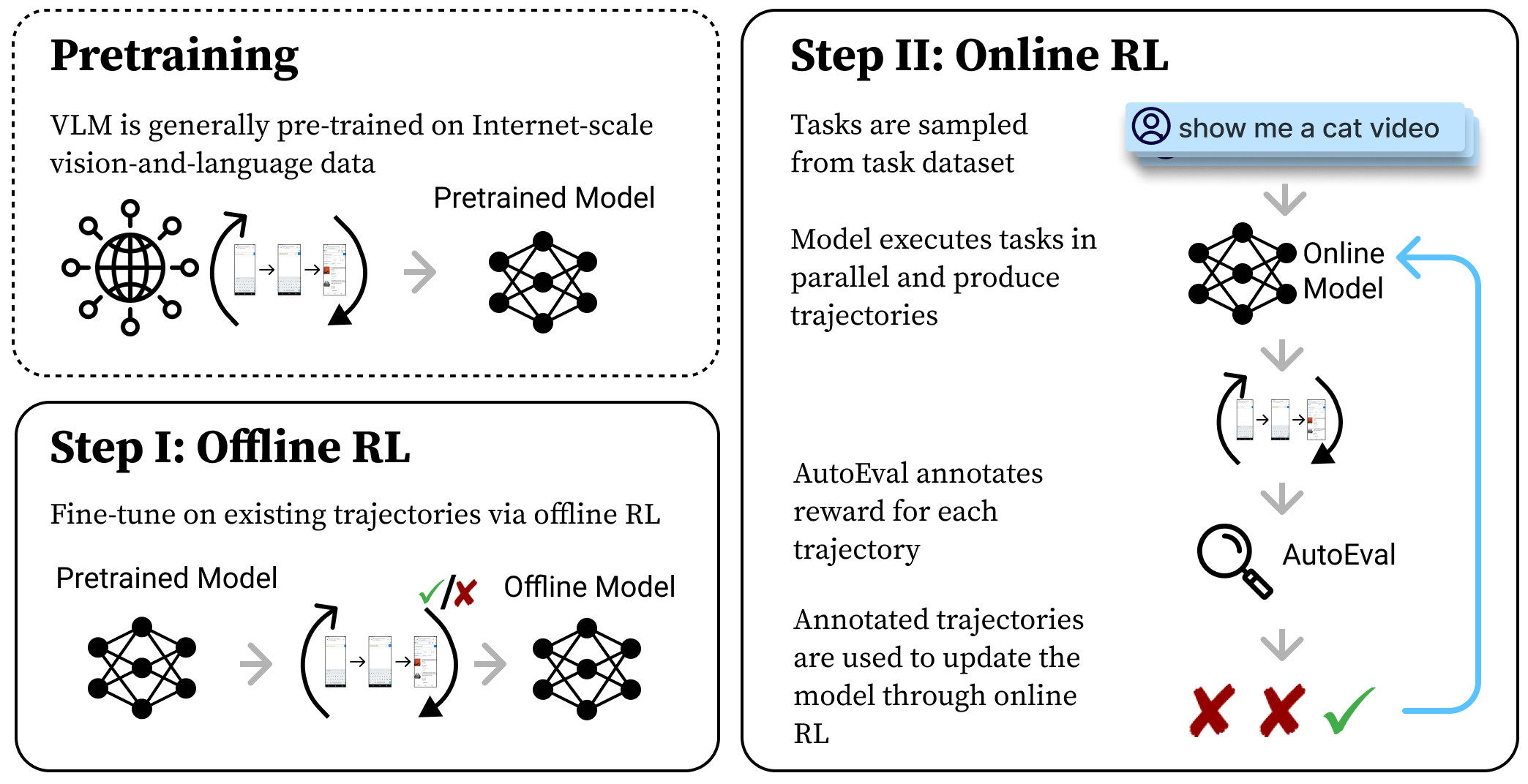
DigiRL: Training In-The-Wild Device-Control Agents with Autonomous Reinforcement Learning
Oral @ FM Wild, ICML
Neurips 2024
| Website | Demo | Results | Paper | Checkpoints | Data |
Research Code for preprint "DigiRL: Training In-The-Wild Device-Control Agents with Autonomous Reinforcement Learning".
Hao Bai*, Yifei Zhou*, Mert Cemri, Jiayi Pan, Alane Suhr, Sergey Levine, Aviral Kumar
UC Berkeley, UIUC, Google DeepMind
*Equal contribution, alphabetic order; work done at UC Berkeley
- Auto-adaptive error handling support.
- Multi-machine emulation parallel support.
- Checkpoint resuming support.
- Trajectory video recording support.
-
Two training algorithms proposed in the paper
- DigiRL (automatic curriculum + doubly robust estimator filtering).
- Filtered Behavior Cloning (reward-based filtering).
-
Three training modes:
- Offline-only training: baseline apporach - use the AutoUI checkpoint to collect data (we have this data ready for you), then train with these pre-collected sub-optimal trajectories. This mode only allows evaluation using the checkpoint.
- Online-only training: traditional RL approach - the AutoUI checkpoint simultaneously interacts with the environment learns online. This mode allows interactive training.
- Offline-to-online training: the most powerful approach as evaluated in paper - the AutoUI checkpoint first learns the pre-collected data, then simultanesouly interacts with the environment and do online learning starting from this checkpoint. This mode allows interactive training
-
Two agents:
-
Two Android-in-the-Wild task sets:
- AitW General: general browsing, opening apps.
- AitW Web Shopping: shopping on popular shopping websites.
- It'll also be interesting to explore the other AitW subsets or other task sets if you have good candidates, please propose one in the issue.
-
DDP Multi-GPU training:
- We support
acceleratefor multi-GPU training. You can turn off this feature if you only have 1 GPU. It only takes 12GB of GPU memory for AutoUI running the DigiRL algorithm, but we provide this feature in case you want to play with something larger.
- We support
First, create a conda environment and install all pip package requirements.
conda create -n digirl python==3.10
conda activate digirl
git clone https://github.com/DigiRL-agent/digirl.git
cd digirl
pip install -e .To set up the Android environment for the DigiRL/filtered BC to interact with, refer to the environment README. Before moving on, you should be able to view this screenshot by running this script.
The SFT checkpoint of the AutoUI model was released here and we use it:
Simply download Auto-UI-Base.zip, then unzip to a directory.
cd <path_to_autoui_dir>
wget https://huggingface.co/cooelf/Auto-UI/resolve/main/Auto-UI-Base.zip
unzip Auto-UI-Base.zip
# wait...
ls Auto-UI-Base
# config.json pytorch_model.bin tokenizer.json training_args.bin
# generation_config.json special_tokens_map.json tokenizer_config.jsonWe provide the pre-collected trajectories using this SFT checkpoint:
The Google Drive folder contains 4 files, with stats below (you can use gdown to download the checkpoint you want):
| File Name | #Trajectories | Horizon | File Size |
|---|---|---|---|
general-off2on-zeroshot-trajectories.pt |
608 | 10 | 95.5M |
general-offline-zeroshot-trajectories.pt |
1552 | 10 | 243.9M |
webshop-off2on-zeroshot-trajectories.pt |
528 | 20 | 115.2M |
webshop-offline-zeroshot-trajectories.pt |
1296 | 20 | 297.5M |
where general/webshop mean the AitW General/Web Shopping subset, off2on/offline means whether the data is used for offline learning or offline-to-online learning. To make a fair comparison, offline learning should use the similar amount of data that offline-to-online learning finally uses.
Store these files into a directory:
mkdir ~/data && cd ~/data
# copy the .pt file hereIf you want to use our final offline-to-online checkpoints to reproduce scores in the paper, you can also download from Google Drive. We release the first offline-to-online checkpoint (run1 in paper) for each algorithm in each environment:
The Google Drive folder also contains 4 files:
| File Name | Index in Paper | Test Set Score | File Size |
|---|---|---|---|
general-off2on-digirl.zip |
run1 |
70.8 | 1.9G |
general-off2on-filteredbc.zip |
run1 |
59.4 | 1.9G |
webshop-off2on-digirl.zip |
run1 |
75.0 | 1.9G |
webshop-off2on-filteredbc.zip |
run1 |
55.2 | 1.9G |
You can also access through Huggingface.
Note that these checkpoints only allows evaluation because we only release the AutoUI checkpoint, not the optimizer states.
Then change the huggingface_token, wandb_token, gemini_token, etc. in scripts/config/main/default.yaml, note that you need to specify all entries left blank or <username> for you in this file. This config is the default configuration - you also need to specify the subconfiguration - for example, if you want to run the online algorithm, you should also examine what to modify in scripts/config/main/digirl_online. Feel free to DIY your configs and play with the code!
Note: to load existing checkpoints, modify save_path instead of policy_lm. That is, policy_lm should still be the path to the AutoUI checkpoint.
After modifying the config to what you like, you can now run experiments with the following commands:
cd scripts
python run.py --config-path config/main --config-name digirl_onlineThe file run.py is the entrance of the program, and you can pass the config name to run different experiments. The config file is in scripts/config/ directory.
To reproduce the results in Table 1 of our paper, first download the corresponding checkpoints as described above. As the results in the training set are obtained by randomly sampling tasks, we recommend reproducing the test results (which are obtained by sequentially sampling the first 96 trajectories).
To do this, modify the eval_only.yaml config file and its parent 'default.yaml' config file to experiment settings. For instance, you can modify these configs for reproduction:
default.yaml- Set
task_split: "test"andeval_sample_mode: "sequential" - Don't forget to increase
max_stepsto20iftask_setis set towebshop(as the webshop tasks usually need more steps than the general tasks to complete).
- Set
eval_only.yaml- Make sure
rollout_size(indefault.yaml) *eval_iterations(ineval_only.yaml) = 96. For example,rollout_size (16) * eval_iterations (6) = 96.
- Make sure
The way we set CogAgent up is using a Gradio-based API approach, which means that you need to setup CogAgent inference service on a server, then use our code to query that API. To set up CogAgent, refer to the GitHub Page of project AutoEval by Jiayi Pan.
Grab the link and modify that in scripts/config/cogagent/default.yaml file. You need at least one GPU with 48GB memory to host CogAgent for inference.
If you want to launch large scale emulation (say more than 32 emulators running at the same time), you'll need multiple machines that collects trajectories at the same time. Refer to the multimachine-training README for details.
We use accelerate for multi-GPU DDP training. To enable, you need to identify the number of GPUs on your machine in the accelerate config. If you model is extremely large, it's also possible to do multi-machine DDP training but we currently don't support it.
To enable this, the only thing you need to do is to replace python run.py with accelerate launch --config_file <config_file> run.py. An example below:
accelerate launch --config_file config/accelerate_config/default_config.yaml run.py --config-path config/main --config-name digirl_off2on
You should be able to see a much faster learning speed if you've successfully set this up.
- If you frequently get the
Error in environment reseterror, you can try increasing the timeout at this line. - If you frequently get the
409 resource exhaustederror, try adding asleep()function within thecall_gemini()function here. FYI, a free-tier Gemini API fitssleep(2)very well. - If you see AVD copying errors (started with
shutil.error), you can safely ignore it unless the location copying to is empty.
We welcome the open-source community to contribute to this project. If you invented an algorithm, or you support other types of base models, please propose a PR or issue. Example topics:
- Other algorithms like PPO or any algorithm you invented.
- Other base models like LLaVA.
- Other task sets like WebArena.
- Potential sub-optimal implementations.
All content of this work is under Apache License v2.0, including codebase, data, and model checkpoints.
Consider citing our paper!
@article{bai2024digirl,
title={DigiRL: Training In-The-Wild Device-Control Agents with Autonomous Reinforcement Learning},
author={Bai, Hao and Zhou, Yifei and Cemri, Mert and Pan, Jiayi and Suhr, Alane and Levine, Sergey and Kumar, Aviral},
journal={arXiv preprint arXiv:2406.11896},
year={2024}
}