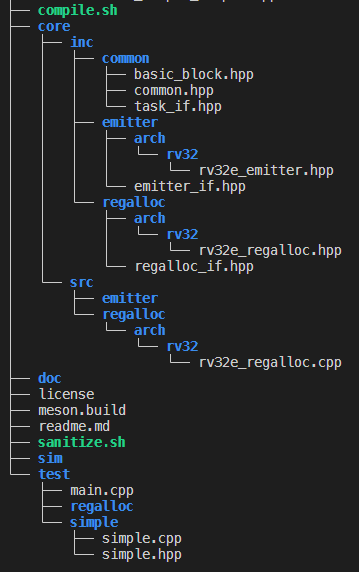
RVEmitter is a playground space for a primitive instruction emitter targetting Risc5 ISA.
The following dependencies must be installed on the build instance depending on the build configuration.
- meson
- fmt
- clang
- clang-tools
On top of the lite build requirements include:
- verilator
- any riscv softcore rtl
Wip
Wip
To compile the code simply issue the following commands:
chmod +x compile.sh(required first time)./compile.sh
You may also run sanitize.sh if you'd like to use clang-address-sanitizer.
To generate code 3 components are required:
- A basic block that holds the generated instructions and data.
- A register allocator to allocate registers on demand (or fallback to stack if there are no available registers).
- An emitter that emits instructions within basic block's memory space.
The example below performing a simple addition demonstrates the intended use of the framework by a JIT/AOT compiler:
const int32_t SimpleTest::Run(const int argc, const char** argv) {
fmt::print("Simple test start..\n");
// Create a basic block to emit instructions & Define label and offset.
constexpr const std::string_view bb_label = "main";
constexpr const size_t bb_offset = 0;
std::unique_ptr< BasicBlock > bb { std::make_unique<BasicBlock>(bb_label, bb_offset) };
// Create a register allocator
std::unique_ptr< RegisterAllocatorInterface > ralloc { std::make_unique<RV32E_SimpleRegisterAllocator>() };
// Create an emitter and pass in the block & reg allocator
std::unique_ptr< EmitterInterface > emitter { std::make_unique<RV32E_Emitter>( bb.get(), ralloc.get()) };
// Get 2 available registers to work
const auto lhs = ralloc->GetNextGPR(rcls_temp);
const auto rhs = ralloc->GetNextGPR(rcls_temp);
assert ((lhs != k_invalid_reg_index) && (rhs != k_invalid_reg_index) );
// Move data
emitter->LoadImmediate(lhs, 64);
emitter->LoadImmediate(rhs, 32);
// Perform lhs(rd) = lhs(rs1) + rhs(rs2)
emitter->AddRmRn(lhs, lhs, rhs);
// Free registers
ralloc->FreeGPR(lhs);
ralloc->FreeGPR(rhs);
// Code is now stored in bb->GetCode()
fmt::print("Simple test end..\n");
// Done
return 0;
}Currently all tests run from within the main entry point of the application. No dedicated TestBench or automated testing flow is set.