This repository contains the Proof of Concept (PoC) implementation of the paper titled "Moving Object 3D Detection and Segmentation Using Optical Flow Clustering" authored by Dmitriy Zhuravlev. The implementation provides a method for 3D object detection and instance segmentation using classical computer vision techniques, with a focus on monocular camera setups. It aims to offer an alternative approach to deep learning-based methods, emphasizing efficiency and applicability to resource-constrained devices.
Deep learning methods have recently improved the performance and accuracy of prediction using big data and abundant computing resources. However, many complex problems in Computer Vision, including 3D detection, motion estimation, and image segmentation, cannot be easily solved. All the same, it is still possible to benefit from using 'traditional' methods.
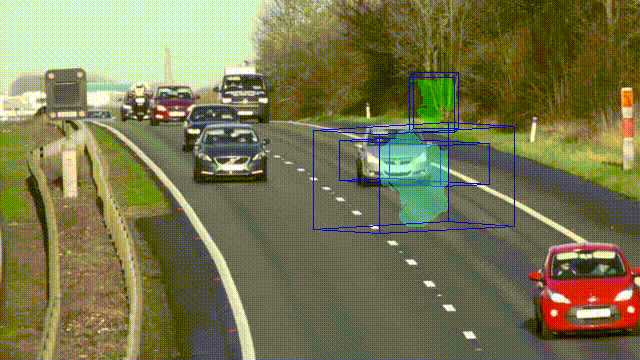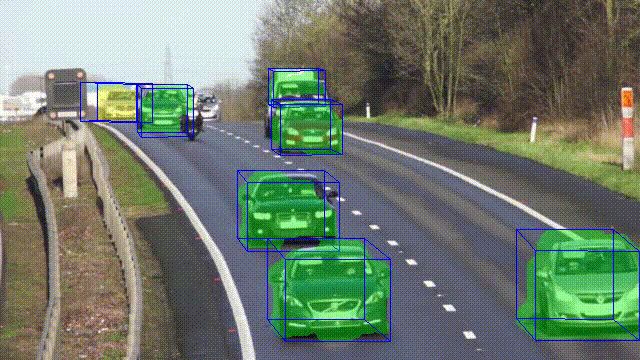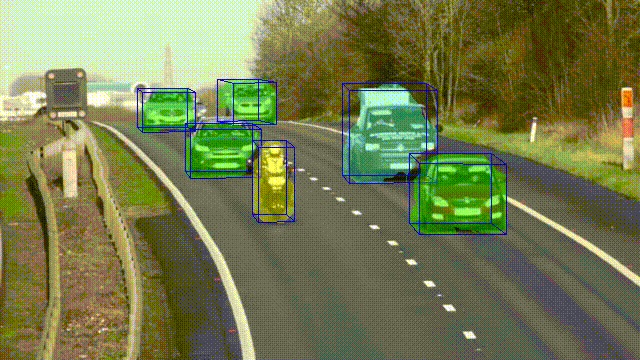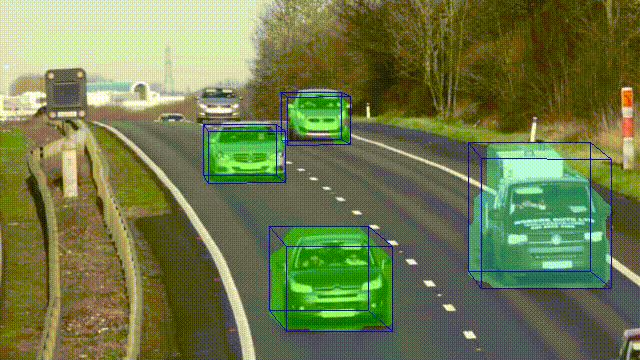
This article analyzes the relationship between optical flow and object localization. The proposed algorithm works with moving objects and performs not only instance segmentation but also determines the type of objects and estimates 3D bounding boxes using geometric constraints. Since the method is based only on an algorithmic understanding of three-dimensional data, it does not require data and time for the training process and can be deployed on constrained devices.
- Estimation of object orientation using Optical Flow clustering.
- Determination of object type from instance segmentation.
- Construction of 3D bounding boxes based on object orientation and type.
- Algorithm for instance segmentation based on 3D localization.
- End-to-end baseline architecture for high performance and accuracy.
- Open-sourced PoC implementation.
- Title: Moving Object 3D Detection and Segmentation Using Optical Flow Clustering
- Author: Dmitriy Zhuravlev
- Affiliation: T. Shevchenko National University, Kiev, Ukraine
- Email: dzhuravlev@ukr.net
- LinkedIn: Dmitriy Zhuravlev's LinkedIn Profile
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-35314-7_38
To use this PoC implementation, follow the instructions in the provided codebase. You can clone this repository and explore the code and associated documentation for more details on how to apply the 3D object detection and segmentation method.
In this paper, a novel approach for joint monocular 3D object detection and instance segmentation is introduced. Despite the fact that it is based exclusively on classical methods of computer vision, it shows promising performance results. The method is efficient, requires less time and computational resources than deep learning-based algorithms, and can handle overlapping objects in the image plane.
The proposed method not only provides a solution to complex modern problems but is also well-suited for tasks under conditions of limited time and resources. It does not require training data and time, and its prediction error of 3D localization is fully described mathematically.
Future studies may consider the non-static case with a moving camera to provide a 3D view for a moving vehicle.
This project is licensed under the MIT License.
We would like to acknowledge the contributions of Dmitriy Zhuravlev and the research team at T. Shevchenko National University for their work on this project.
Feel free to reach out to Dmitriy Zhuravlev via LinkedIn for any questions or collaborations related to this research.