- 📣 Updates
- 📖 Introduction
- ✨ Features
- 🌐 WebUI Demo
- 🛠️ Installation
- 🚀 Quick Start
- ⚙️ Configuration
⚠️ Troubleshooting- 📋 Changelog
- 💬 Feedback and Support
- 📍 Acknowledgement
- 📚 Citation
- 2025-01.09: Add API support. Now you can use XRAG as a backend service.
- 2025-01.06: Add ollama LLM support.
- 2025-01.05: Add generate command. Now you can generate your own QA pairs from a folder which contains your documents.
- 2024-12.23: XRAG Documentation is released🌈.
- 2024-12.20: XRAG is released🎉.
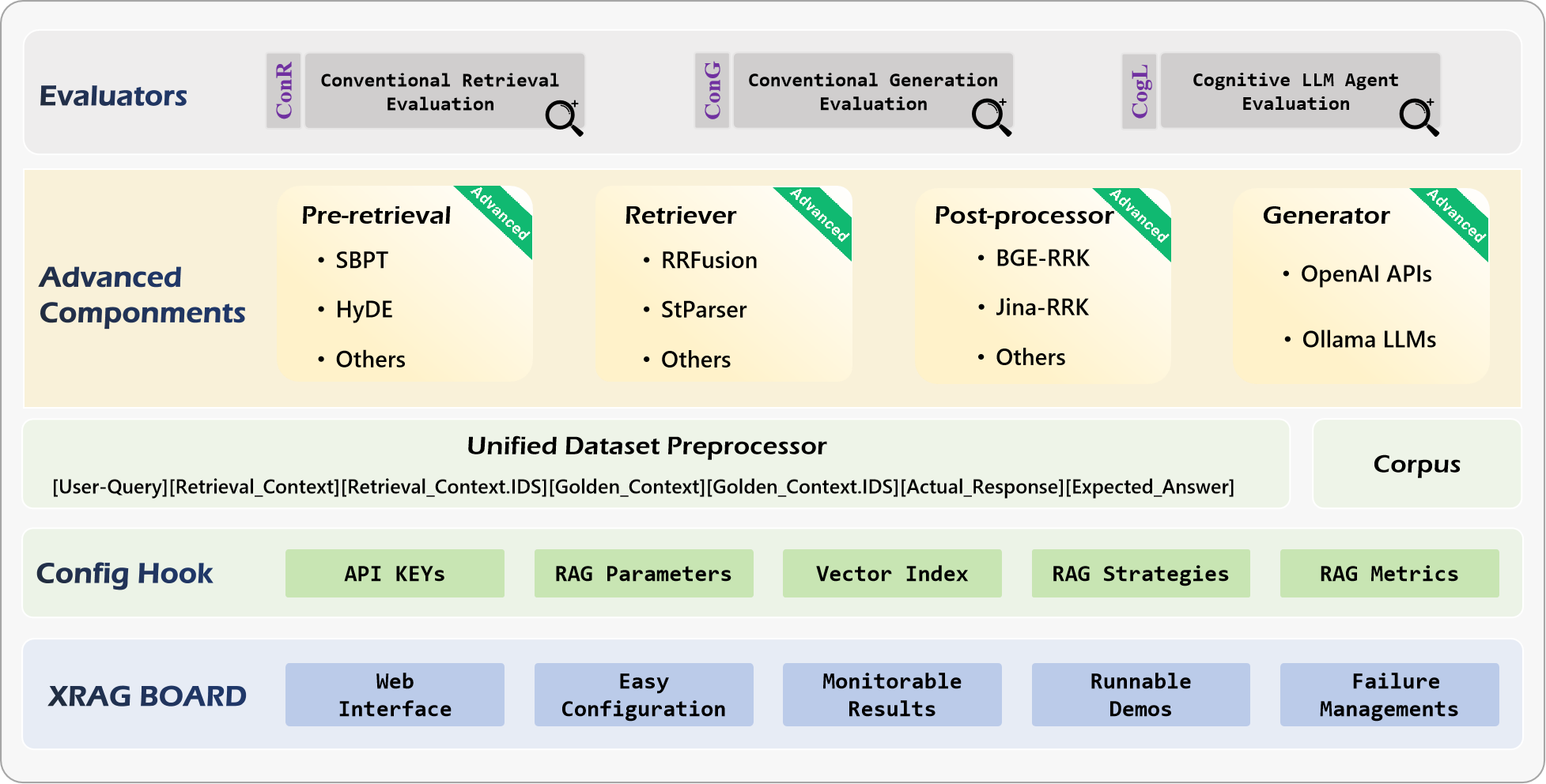
XRAG is a benchmarking framework designed to evaluate the foundational components of advanced Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) systems. By dissecting and analyzing each core module, XRAG provides insights into how different configurations and components impact the overall performance of RAG systems.
-
🔍 Comprehensive Evaluation Framework:
- Multiple evaluation dimensions: LLM-based evaluation, Deep evaluation, and traditional metrics
- Support for evaluating retrieval quality, response faithfulness, and answer correctness
- Built-in evaluation models including LlamaIndex, DeepEval, and custom metrics
-
⚙️ Flexible Architecture:
- Modular design with pluggable components for retrievers, embeddings, and LLMs
- Support for various retrieval methods: Vector, BM25, Hybrid, and Tree-based
- Easy integration with custom retrieval and evaluation strategies
-
🤖 Multiple LLM Support:
- Seamless integration with OpenAI models
- Support for local models (Qwen, LLaMA, etc.)
- Configurable model parameters and API settings
-
📊 Rich Evaluation Metrics:
- Traditional metrics: F1, EM, MRR, Hit@K, MAP, NDCG
- LLM-based metrics: Faithfulness, Relevancy, Correctness
- Deep evaluation metrics: Contextual Precision/Recall, Hallucination, Bias
-
🎯 Advanced Retrieval Methods:
- BM25-based retrieval
- Vector-based semantic search
- Tree-structured retrieval
- Keyword-based retrieval
- Document summary retrieval
- Custom retrieval strategies
-
💻 User-Friendly Interface:
- Command-line interface with rich options
- Web UI for interactive evaluation
- Detailed evaluation reports and visualizations
XRAG provides an intuitive web interface for interactive evaluation and visualization. Launch it with:
xrag-cli webuiThe WebUI guides you through the following workflow:
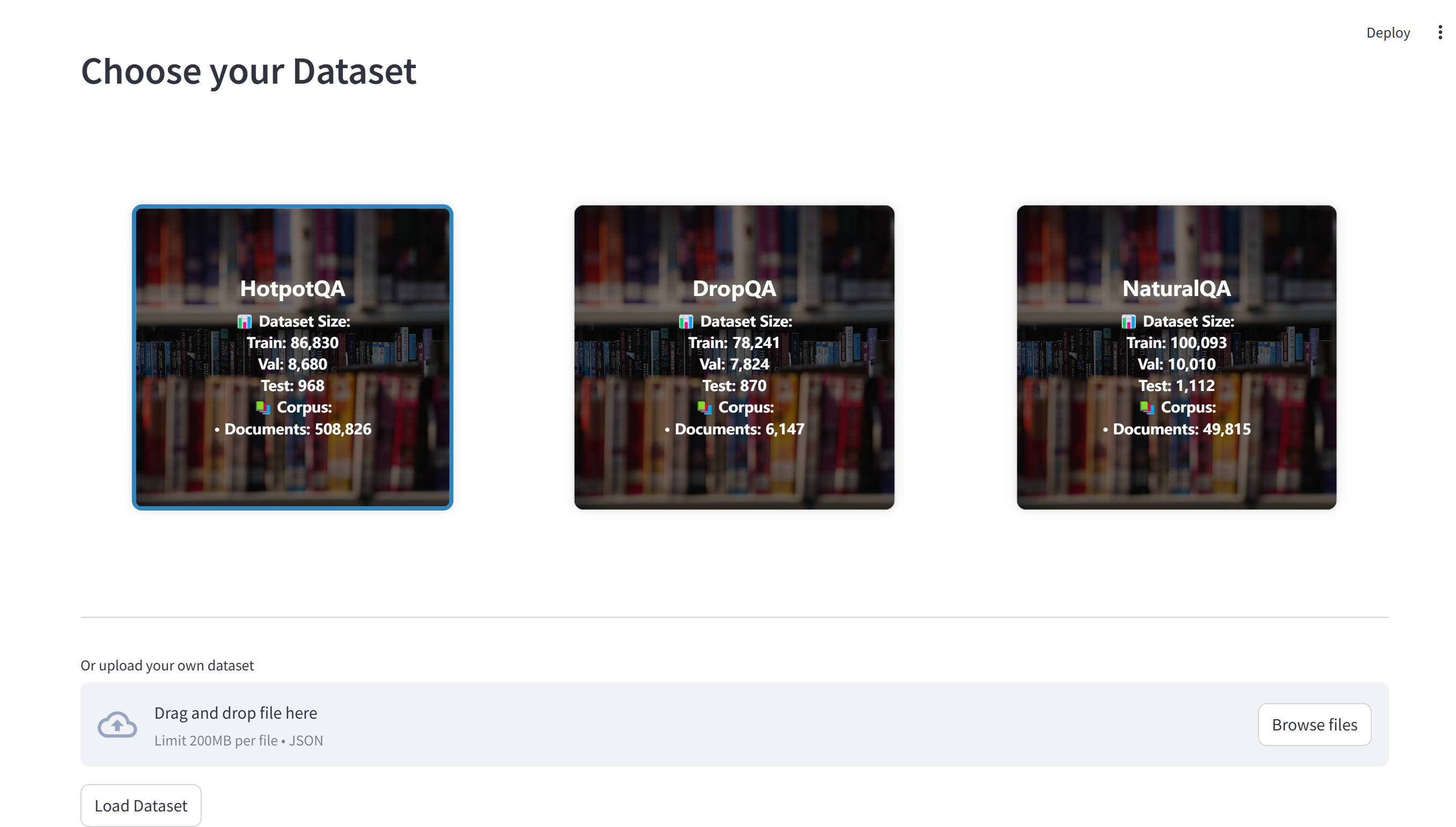
Upload and configure your datasets:
- Support for benchmark datasets (HotpotQA, DropQA, NaturalQA)
- Custom dataset integration
- Automatic format conversion and preprocessing
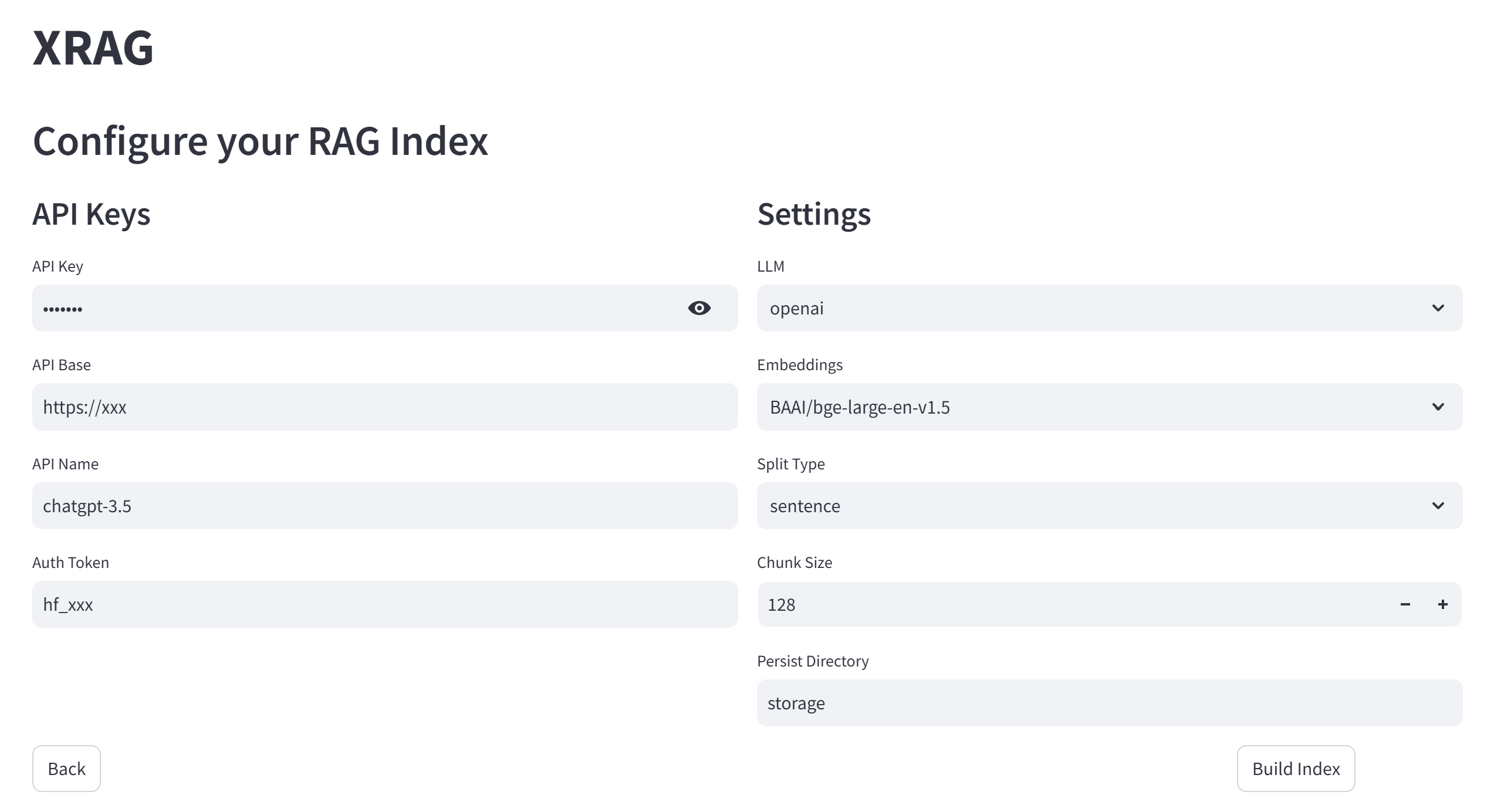
Configure system parameters and build indices:
- API key configuration
- Parameter settings
- Vector database index construction
- Chunk size optimization
Define your RAG pipeline components:
- Pre-retrieval methods
- Retriever selection
- Post-processor configuration
- Custom prompt template creation
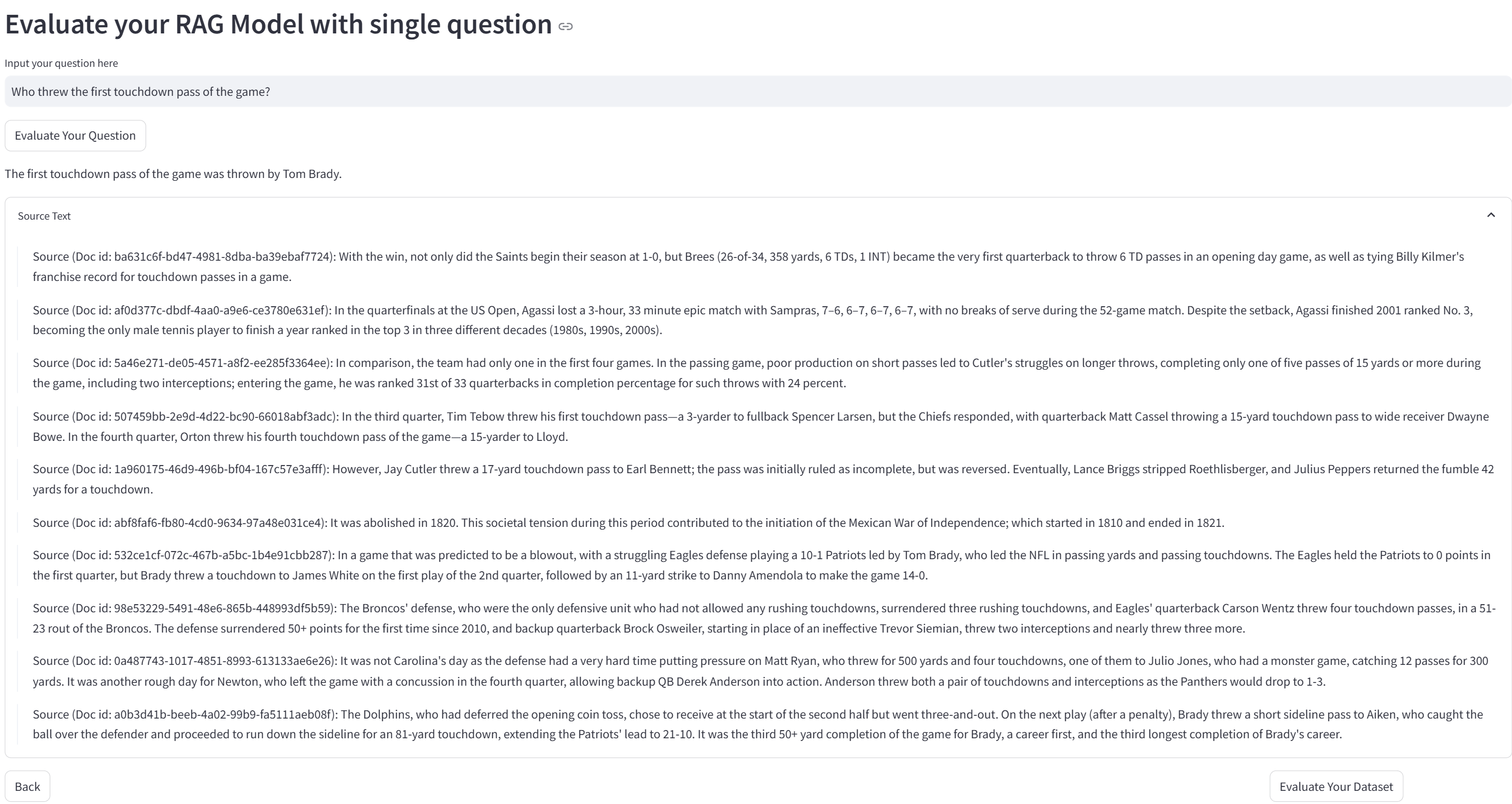
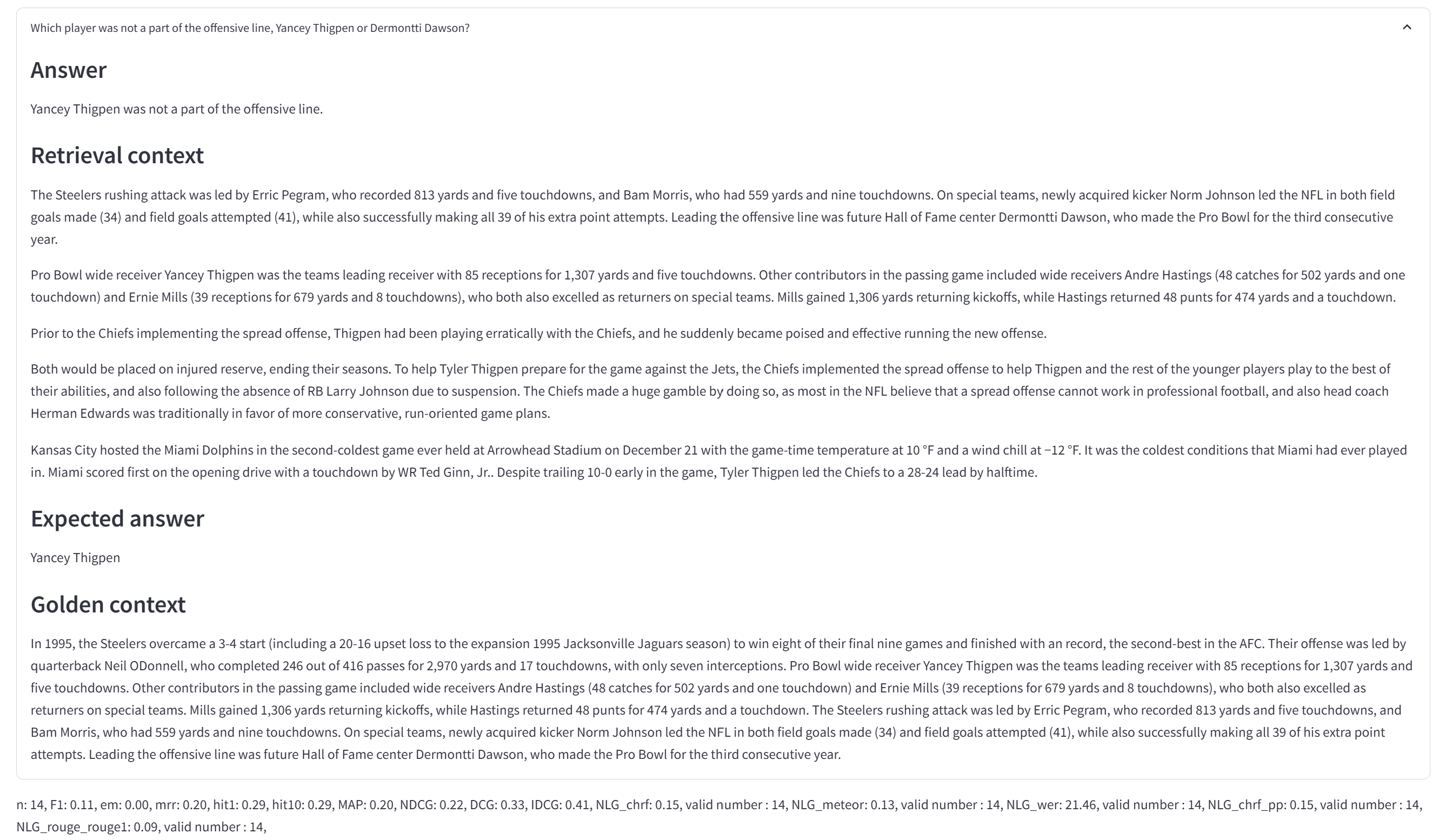
Test your RAG system interactively:
- Real-time query testing
- Retrieval result inspection
- Response generation review
- Performance analysis
Before installing XRAG, ensure that you have Python 3.11 or later installed.
# Create a new conda environment
conda create -n xrag python=3.11
# Activate the environment
conda activate xragYou can install XRAG directly using pip:
# Install XRAG
pip install examinationrag
# Install 'jury' without dependencies to avoid conflicts
pip install jury --no-depsHere's how you can get started with XRAG:
Modify the config.toml file to set up your desired configurations.
After installing XRAG, the xrag-cli command becomes available in your environment. This command provides a convenient way to interact with XRAG without needing to call Python scripts directly.
xrag-cli [command] [options]-
run: Runs the benchmarking process.
xrag-cli run [--override key=value ...] -
webui: Launches the web-based user interface.
xrag-cli webui
-
ver: Displays the current version of XRAG.
xrag-cli version
-
help: Displays help information.
xrag-cli help -
generate: Generate QA pairs from a folder.
xrag-cli generate -i <input_file> -o <output_file> -n <num_questions> -s <sentence_length>
-
api: Launch the API server for XRAG services.
xrag-cli api [--host <host>] [--port <port>] [--json_path <json_path>] [--dataset_folder <dataset_folder>]
Options:
--host: API server host address (default: 0.0.0.0)--port: API server port number (default: 8000)--json_path: Path to the JSON configuration file--dataset_folder: Path to the dataset folder
Once the API server is running, you can interact with it using HTTP requests. Here are the available endpoints:
Send a POST request to /query to get answers based on your documents:
curl -X POST "http://localhost:8000/query" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{
"query": "your question here",
"top_k": 3
}'Response format:
{
"answer": "Generated answer to your question",
"sources": [
{
"content": "Source document content",
"id": "document_id",
"score": 0.85
}
]
}Check the API server status with a GET request to /health:
curl "http://localhost:8000/health"Response format:
{
"status": "healthy",
"engine_status": "initialized"
}The API service supports both custom JSON datasets and folder-based documents:
- Use
--json_pathfor JSON format QA datasets - Use
--dataset_folderfor document folders - Do not set
--json_pathand--dataset_folderat the same time.
Use the --override flag followed by key-value pairs to override configuration settings:
xrag-cli run --override embeddings="new-embedding-model"xrag-cli generate -i <input_file> -o <output_file> -n <num_questions> -s <sentence_length>Automatically generate QA pairs from a folder.
XRAG uses a config.toml file for configuration management. Here's a detailed explanation of the configuration options:
[api_keys]
api_key = "sk-xxxx" # Your API key for LLM service
api_base = "https://xxx" # API base URL
api_name = "gpt-4o" # Model name
auth_token = "hf_xxx" # Hugging Face auth token
[settings]
llm = "openai" # openai, huggingface, ollama
ollama_model = "llama2:7b" # ollama model name
huggingface_model = "llama" # huggingface model name
embeddings = "BAAI/bge-large-en-v1.5"
split_type = "sentence"
chunk_size = 128
dataset = "hotpot_qa"
persist_dir = "storage"
# ... additional settings ...-
Dependency Conflicts: If you encounter dependency issues, ensure that you have the correct versions specified in
requirements.txtand consider using a virtual environment. -
Invalid Configuration Keys: Ensure that the keys you override match exactly with those in the
config.tomlfile. -
Data Type Mismatches: When overriding configurations, make sure the values are of the correct data type (e.g., integers, booleans).
- Add API support. Now you can use XRAG as a backend service.
- Add ollama LLM support.
- Add generate command. Now you can generate your own QA pairs from a folder which contains your documents.
- Initial release with core benchmarking functionality.
- Support for HotpotQA dataset.
- Command-line configuration overrides.
- Introduction of the
xrag-clicommand-line tool.
We value feedback from our users. If you have suggestions, feature requests, or encounter issues:
- Open an Issue: Submit an issue on our GitHub repository.
- Email Us: Reach out at luoyangyifei@buaa.edu.cn.
- Join the Discussion: Participate in discussions and share your insights.
-
Organizers: Qianren Mao, Yangyifei Luo (罗杨一飞), Jinlong Zhang (张金龙), Hanwen Hao (郝瀚文), Zhenting Huang (黄振庭), Zhilong Cao(曹之龙)
-
This project is inspired by RAGLAB, FlashRAG, FastRAG, AutoRAG, LocalRAG.
-
We are deeply grateful for the following external libraries, which have been pivotal to the development and functionality of our project: LlamaIndex, Hugging Face Transformers.
If you find this work helpful, please cite our paper:
@misc{mao2024xragexaminingcore,
title={XRAG: eXamining the Core -- Benchmarking Foundational Components in Advanced Retrieval-Augmented Generation},
author={Qianren Mao and Yangyifei Luo and Jinlong Zhang and Hanwen Hao and Zhilong Cao and Xiaolong Wang and Xiao Guan and Zhenting Huang and Weifeng Jiang and Shuyu Guo and Zhentao Han and Qili Zhang and Siyuan Tao and Yujie Liu and Junnan Liu and Zhixing Tan and Jie Sun and Bo Li and Xudong Liu and Richong Zhang and Jianxin Li},
year={2024},
eprint={2412.15529},
archivePrefix={arXiv},
primaryClass={cs.CL},
url={https://arxiv.org/abs/2412.15529},
}Thank you for using XRAG! We hope it proves valuable in your research and development efforts in the field of Retrieval-Augmented Generation.