English | 中文
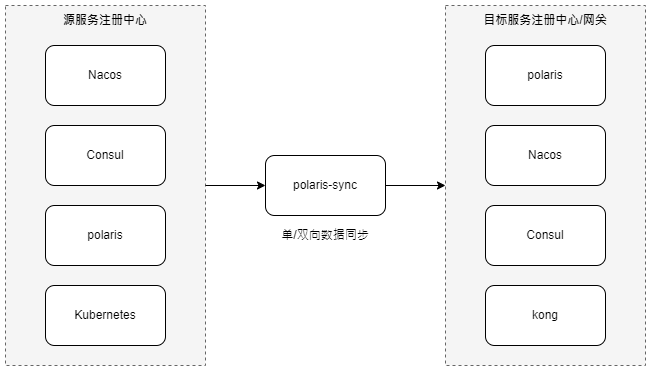
polaris-sync is used for data synchronization between Polaris and other registry/gateway services for the following 2 scenarios:
- Service data synchronization between Polaris and other registries: for smooth migration of service instances between registries.
- Synchronization of Polaris service data to the gateway: It is used for the seamless connection between the gateway and the registration center service discovery scenario.
- Support two-way service data synchronization between any registry.
- Supports docking with mainstream gateways, allowing the gateway to dock with any registration center without making any changes to the gateway.
- Based on the plug-in design, it is easy to extend other registry implementations.
-
Before performing all installations, you need to download the source package. You can download the source package from the following two addresses. Please select the latest release version of the source package:
-
Github download: polaris-sync-release
-
After decompression, execute the deployment
cd deploy/kubernetes
kubectl apply -f polaris-sync-config.yaml
kubectl apply -f polaris-sync.yaml
-
Before performing all installations, you need to download the source package, you can download the package from the following two addresses, please select the latest release version, and select the polaris-sync-server-*.zip format package to download:
-
Github download: polaris-sync-release
-
After decompression, execute the deployment
unzip polaris-sync-server-${VERSION}.zip
// Need to modify here /bin/application.yaml, conf/sync-registry.json, conf/sync-config.json
bash bin/start.sh
The log will be printed to STDOUT by default, and can be redirected to a file by redirection.
polaris-sync supports modifying various parameters of the system by means of environment variables:
| variable name | description | optional value |
|---|---|---|
| POLARIS_SYNC_REGISTRY_CONFIG_PROVIDER | The way to provide synchronization configuration, the default is file, that is to get the configuration from the local file | file (local file), kubernetes (by reading k8s configmap) |
| POLARIS_SYNC_REGISTRY_CONFIG_BACKUP_PATH | The backup path of the synchronization configuration, for disaster recovery, the default is conf/sync-config-backup.json | Any writable local file path |
| POLARIS_SYNC_CONFIG_FILE_WATCH | When the configuration supply method is file, the synchronization configuration listens to and obtains the configuration content through this path. The default is conf/sync-config.json | Any file path |
| POLARIS_SYNC_CONFIG_K8S_ADDRESS | APIServer address of k8s, useful when the configuration is provided by kubernetes | ip:port |
| POLARIS_SYNC_CONFIG_K8S_TOKEN | k8s access token, useful when the configuration is provided by kubernetes | arbitrary string |
| POLARIS_SYNC_CONFIG_K8S_NAMESPACE | k8s configmap namespace, useful when the configuration is provided by kubernetes | arbitrary string |
| POLARIS_SYNC_CONFIG_K8S_CONFIGMAP_NAME | k8s configuration configmap name, useful when the configuration is provided by kubernetes | arbitrary string |
| POLARIS_SYNC_CONFIG_K8S_CONFIGMAP_DATA_ID | k8s configuration configmap configuration item ID, useful when the configuration is provided by kubernetes | arbitrary string |
In the process of registry migration, two-way access is often required, and services migrated to the new registry need to access services that have not been migrated. At the same time, the services that have not been migrated also need to access the migrated services.
In order not to make any changes to the application, real-time two-way data synchronization is required between the registries to achieve the goal of hot migration.
The following takes the service data migration from nacos to Polaris as an example to explain how to use polaris-sync to achieve bidirectional data synchronization between registration centers.
We need to configure 2 synchronization tasks for polaris-sync, one is the synchronization task from nacos to Polaris, and the other is the synchronization task from Polaris to nacos.
You need to modify the json configuration in polaris-sync-config.yaml and add the configuration of the task. Note that polaris-sync will listen for changes to this configuration, so there is no need to restart polaris-sync after the configuration is modified.
{
"tasks": [
//The first task is a one-way sync from nacos to north star
{
"name": "nacos1-to-polaris1", //Task ID, which needs to be unique
"enable": true,
"source": { //Define the source registry
"name": "nacos1", //The name of the registration center, which must be unique
"type": "nacos", //Registry Type
"addresses": [
"127.0.0.1:8848" //nacos address
],
"user": "nacos", //Login credentials, if authentication is not enabled, you can leave it blank
"password": "nacos"
},
"destination": { //Define the target registry
"name": "polaris1",
"type": "polaris",
"addresses": [
"http://127.0.0.1:8090" //Polaris address, using HTTP port
"grpc://127.0.0.1:8091" //Polaris address, using gRPC port
],
"token": "123456" //Access credentials, if authentication is not enabled, you can leave it blank
},
"match": [ // Specify which services need to be synchronized
{
"namespace": "empty_ns", //Namespace ID, nacos default namespace fill empty_ns
"service": "nacos.test.3", // The name of the service that needs to be synchronized, in the format of ${GROUP NAME}__${SERVICE NAME}, if there is no group name, it is the default group
}
]
},
//第二个任务是从北极星单向同步到nacos
{
"name": "polaris1-to-nacos1", //任务标识,需唯一
"enable": true,
"source": { //定义来源注册中心
"name": "polaris1",
"type": "polaris",
"addresses": [
"127.0.0.1:8090" //北极星地址,使用HTTP端口
],
"token": "123456" //访问凭据,如果未开启鉴权,可不填
},
"destination": { //定义目标注册中心
"name": "nacos1", //注册中心名,需唯一
"type": "nacos", //注册中心类型
"addresses": [
"127.0.0.1:8848" //nacos地址
],
"user": "nacos", //登录凭据,如果未开启鉴权,可不填
"password": "nacos"
},
"match": [ // 指定哪些服务需要进行同步
{
"namespace": "empty_ns", //命名空间ID,nacos默认命名空间填empty_ns
"service": "nacos.test.3", // 需要进行同步的服务名,格式为分组名__服务名
}
]
}
],
"methods": [
{
"type": "watch",
"enable": true
},
{
"type": "pull",
"enable": true,
"interval": "60s"
}
],
"health_check": {
"enable": true
},
"report": {
"interval" : "1m",
"targets": [
{
"type": "file",
"enable": true
}
]
}
}
After editing the rules, use kubectl apply -f polaris-sync-config.yaml directly. After polaris-sync monitors configuration changes, it will hot-load tasks and start synchronization.
The address information of the application is often registered in the registration center. When the user wants to directly access the address of the registration center using the gateway, there are often two solutions:
The first is to use a gateway plug-in to connect to the service discovery mechanism of the registry. In this way, the user needs to load the plug-in of the corresponding registration center on the gateway, which is intrusive to a certain extent and has the problem of plug-in conflict management.
The second is to use synchronization tools to synchronize service data from the registry to the gateway, and then use the gateway's native routing capabilities for addressing. This method is non-intrusive to the gateway, does not conflict with the existing plug-ins of the gateway, and is more in line with the native usage scenarios of the gateway.
The following explains how to use polaris-sync to synchronize the service data of Polaris to the Kong gateway, and realize the scenario where the Kong gateway is directly connected to the Polaris registration center.
You need to modify the json configuration in polaris-sync-config.yaml and add the configuration of the task.
{
"tasks": [
{
"name": "polaris1",
"enable": true,
"source": {
"name": "ins-3ad0f6e6",
"type": "polaris",
"addresses": [
"127.0.0.1:8090"
],
"token": "123456"
},
"destination": {
"name": "kong",
"type": "kong",
"addresses": [
"127.0.0.1:8001" //这里填写kong的admin地址
]
},
"match": [
{
"namespace": "default",
"service": "test.service.3",
"groups": [ //需要同步的分组信息,分组会成为kong的upstream,默认会有一个default的upstream,包含全部的实例
{
"name": "version-1", //分组名
"metadata": {
"version": "1.0.0" //分组过滤的元数据
}
},
{
"name": "version-2",
"metadata": {
"version": "2.0.0"
}
}
]
}
]
}
],
"methods": [
{
"type": "watch",
"enable": true
},
{
"type": "pull",
"enable": true,
"interval": "60s"
}
],
"health_check": {
"enable": true
},
"report": {
"interval" : "1m",
"targets": [
{
"type": "file",
"enable": true
}
]
}
}
After editing the rules, use kubectl apply -f polaris-sync-config.yaml directly. After polaris-sync monitors configuration changes, it will hot-load tasks and start synchronization.
After synchronization, 1 service and 3 upstreams (respectively default, version-1, version-2) will be created in Kong, and the target in each upstream corresponds to the corresponding filtered instance.
polaris-sync is a configuration-driven synchronization tool. All user tasks are delivered through configuration.
For the definition of the configuration file, please refer to [registry.proto] in the polaris-sync-protobuf project (https://github.com/polarismesh/polaris-sync/blob/main/polaris-sync-protobuf/src/main/proto/registry.proto) protocol definition.
The root object is Registry.