This repository uses depth image to find surface_normal image and ground/non-ground segmented image. The methods used to calculate the surface normals image are given below:
Let
We first calculate the unit vector of the normal to the surface as
We get the surface normal image 0 represents navigable space (ground) and 1 or 255 is the non-navigable space. The navigability information from
where
- Depth image topic from any simulated or real camera.
- OpenCV
- ROS
Clone and build the repository to your workspace.
mkdir catkin_ws/src -p
cd catkin_ws/src
git clone https://github.com/Dpushp/depth2surface_normals_seg.git
cd ..
catkin_make
Run any robot simulator and verify that you can subscribe to the depth image topic.
roslaunch depth2surface_normals_seg depth2surface_normals_seg.launch
rviz
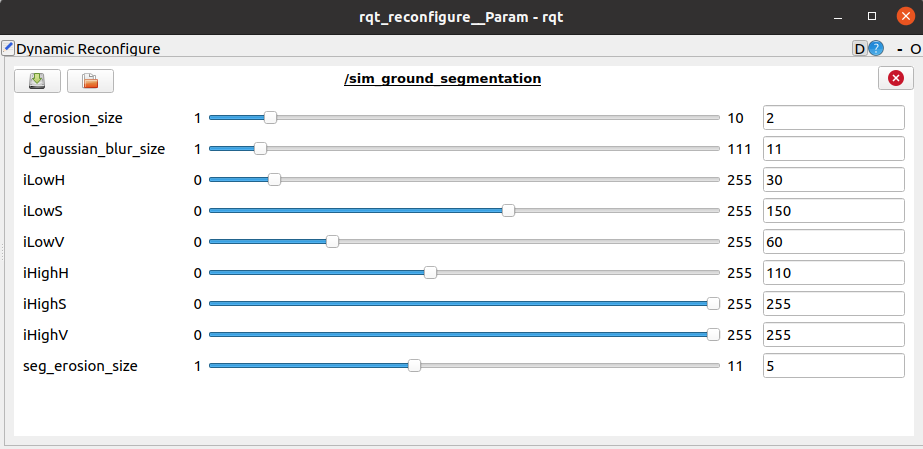
Run Dynamic Recongigure to change the parameters.
rosrun rqt_reconfigure rqt_reconfigure
| Parameter | Description | Default Value |
|---|---|---|
| ~d_erosion_size | The erosion operation is: dst(x,y)=min(x′,y′):element(x′,y′)≠0src(x+x′,y+y′). Used to denoize the depth image |
2 |
| ~d_gaussian_blur_size | Gaussian blur kernel size used to denoize the depth image. | 11 |
| ~iLowH | Hue lower limit in surface normals image to select the navigable class. Used to generate the binary navigable image i.e., ground and non-ground segments. | 30 |
| ~iLowS | Saturation lower limit in surface normals image to select the navigable class. Used to generate the binary navigable image i.e., ground and non-ground segments. | 150 |
| ~iLowV | Value lower limit in surface normals image to select the navigable class. Used to generate the binary navigable image i.e., ground and non-ground segments. | 60 |
| ~iHighH | Hue upper limit. | 110 |
| ~iHighS | Saturation upper limit. | 255 |
| ~iHighV | Value upper limit. | 255 |
| ~seg_erosion_size | Erosion kernel size for ground segmentation. | 5 |