A simple docker container that runs PostGIS
Visit our page on the docker hub at: https://hub.docker.com/r/kartoza/postgis/
There are a number of other docker postgis containers out there. This one differentiates itself by:
- provides ssl support out of the box
- connections are restricted to the docker subnet
- a default database 'gis' is created for you so you can use this container 'out of the box' when it runs with e.g. QGIS
- replication support included
- Ability to create multiple database when you spin the database.
- Enable multiple extensions in the database when setting it up
- Gdal drivers automatically registered for pg raster
- Support for out-of-db rasters
We will work to add more security features to this container in the future with the aim of making a PostGIS image that is ready to be used in a production environment (though probably not for heavy load databases).
There is a nice 'from scratch' tutorial on using this docker image on Alex Urquhart's blog here - if you are just getting started with docker, PostGIS and QGIS, we really recommend that you use it.
The following convention is used for tagging the images we build:
kartoza/postgis:[postgres_major_version]-[postgis-point-releases]
So for example:
kartoza/postgis:12.0 Provides PostgreSQL 12.0, PostGIS 3.0
Note: We highly recommend that you use tagged versions because successive minor versions of PostgreSQL write their database clusters into different database directories - which will cause your database to appear to be empty if you are using persistent volumes for your database storage.
There are various ways to get the image onto your system:
The preferred way (but using most bandwidth for the initial image) is to get our docker trusted build like this:
docker pull kartoza/postgis
To build the image yourself without apt-cacher (also consumes more bandwidth since deb packages need to be refetched each time you build) do:
docker build -t kartoza/postgis git://github.com/kartoza/docker-postgis
To build with apt-cacher (and minimise download requirements) you need to clone this repo locally first and modify the contents of 71-apt-cacher-ng to match your cacher host. Then build using a local url instead of directly from github.
git clone git://github.com/kartoza/docker-postgis
Now edit 71-apt-cacher-ng then do:
docker build -t kartoza/postgis .
There are build args for DISTRO (=debian), IMAGE_VERSION (=buster)
and IMAGE_VARIANT (=slim) which can be used to control the base image used
(but it still needs to be Debian based and have PostgreSQL official apt repo).
For example making Ubuntu 20.04 based build (for better arm64 support)
docker build --build-arg DISTRO=ubuntu --build-arg IMAGE_VERSION=focal --build-arg IMAGE_VARIANT="" -t kartoza/postgis .
To create a running container do:
docker run --name "postgis" -p 25432:5432 -d -t kartoza/postgis
With minimum setup, our image will use initial cluster located in the
DATADIR environment variable. If you want to use persistence, mount these
location into your volume/host. By default, DATADIR will point to /var/lib/postgresql/{major-version}.
You can instead mount the parent location like this:
-v data-volume:/var/lib/postgresql
This default cluster will be initialized with default locale settings C.UTF-8.
If, for instance, you want to create a new cluster with your own settings (not using the default cluster).
You need to specify different empty directory, like this
-v data-volume:/opt/postgres/data \
-e DATADIR:/opt/postgres/data \
-e DEFAULT_ENCODING="UTF8" \
-e DEFAULT_COLLATION="id_ID.utf8" \
-e DEFAULT_CTYPE="id_ID.utf8" \
-e INITDB_EXTRA_ARGS="<some more initdb command args>"The containers will use above parameters to initialize a new db cluster in the specified directory. If the directory is not empty, then initialization parameter will be ignored.
These are some initialization parameter that will only be used to initialize new cluster. If the container uses existing cluster, it will be ignored (for example, when the container restarts).
DEFAULT_ENCODING: cluster encodingDEFAULT_COLLATION: cluster collationDEFAULT_CTYPE: cluster ctypeWAL_SEGSIZE: WAL segsize optionINITDB_EXTRA_ARGS: extra parameter that will be passed down toinitdbcommand
In addition to that, we have another parameter: RECREATE_DATADIR that can be used to force database reinitializations.
If this parameter is specified as TRUE it will act as explicit consent to delete DATADIR and create
new db cluster.
RECREATE_DATADIR: Force database reinitializations in the locationDATADIR
If you used RECREATE_DATADIR and successfully created new cluster. Remember
that you should remove this parameter afterwards. Because, if it was not omitted,
it will always recreate new db cluster after every container restarts.
You can use the following environment variables to pass a user name, password and/or default database name(or multiple databases comma separated).
-e POSTGRES_USER=<PGUSER>-e POSTGRES_PASS=<PGPASSWORD>-e POSTGRES_DBNAME=<PGDBNAME>-e POSTGRES_MULTIPLE_EXTENSIONS=postgis,hstore,postgis_topology
You can pass as many extensions as you need.
-e SHARED_PRELOAD_LIBRARIES='pg_cron'Some extensions need to be registered in the postgresql.conf as shared_preload_libraries. pg_cron should always be added because the extension is installed with the image.-e SSL_CERT_FILE=/your/own/ssl_cert_file.pem-e SSL_KEY_FILE=/your/own/ssl_key_file.key-e SSL_CA_FILE=/your/own/ssl_ca_file.pem-e DEFAULT_ENCODING="UTF8"-e DEFAULT_COLLATION="en_US.UTF-8"-e DEFAULT_CTYPE="en_US.UTF-8"
-e POSTGRES_TEMPLATE_EXTENSIONS=true
This image uses the initial PostgreSQL values which disables the archiving option by default.
When ARCHIVE_MODE is changed to on, the archiving command will copy WAL files to /opt/archivedir
More info: 19.5. Write Ahead Log
-e ARCHIVE_MODE off-e ARCHIVE_COMMAND "test ! -f /opt/archivedir/%f && cp %p /opt/archivedir/%f"More info-e ARCHIVE_CLEANUP_COMMAND 'cp /opt/archivedir/%f "%p"'-e RESTORE_COMMAND 'pg_archivecleanup /opt/archivedir %r'
-e WAL_LEVEL=replicaMore info
Maximum size to let the WAL grow to between automatic WAL checkpoints.
-e WAL_SIZE=4GB-e MIN_WAL_SIZE=2048MB-e WAL_SEGSIZE=1024-e MAINTAINANCE_WORK_MEM=128MB
You can open up the PG port by using the following environment variable. By default the container will allow connections only from the docker private subnet.
-e ALLOW_IP_RANGE=<0.0.0.0/0> By default
Postgres conf is setup to listen to all connections and if a user needs to restrict which IP address PostgreSQL listens to you can define it with the following environment variable. The default is set to listen to all connections.
-e IP_LIST=<*>
You can also define any other configuration to add to postgres.conf, separated by '\n' e.g.:
-e EXTRA_CONF="log_destination = 'stderr'\nlogging_collector = on"
If you want to reinitialize the data directory from scratch, you need to do:
- Do backup, move data, etc. Any preparations before deleting your data directory.
- Set environment variables
RECREATE_DATADIR=TRUE. Restart the service - The service will delete your
DATADIRdirectory and start reinitializing your data directory from scratch.
To avoid passing sensitive information in environment variables, _FILE can be appended to
some of the variables to read from files present in the container. This is particularly useful
in conjunction with Docker secrets, as passwords can be loaded from /run/secrets/<secret_name> e.g.:
- -e POSTGRES_PASS_FILE=/run/secrets/<pg_pass_secret>
For more information see https://docs.docker.com/engine/swarm/secrets/.
Currently, POSTGRES_PASS, POSTGRES_USER and POSTGRES_DB are supported.
For convenience we have provided a docker-compose.yml that will run a
copy of the database image and also our related database backup image (see
https://github.com/kartoza/docker-pg-backup).
The docker compose recipe will expose PostgreSQL on port 25432 (to prevent potential conflicts with any local database instance you may have).
Example usage:
docker-compose up -d
Note: The docker-compose recipe above will not persist your data on your local disk, only in a docker volume.
Connect with psql (make sure you first install postgresql client tools on your host / client):
psql -h localhost -U docker -p 25432 -l
Note: Default postgresql user is 'docker' with password 'docker'.
You can then go on to use any normal postgresql commands against the container.
Under ubuntu 16.04 the postgresql client can be installed like this:
sudo apt-get install postgresql-client-12
In some instances users want to run some SQL scripts to populate the database. Since the environment variable POSTGRES_DB allows us to specify multiple database that can be created on startup. When running scripts they will only be executed against the first database ie POSTGRES_DB=gis,data,sample The SQL script will be executed against the gis database.
Currently you can pass .sql , .sql.gz and .sh files as mounted volumes.
docker run -d -v ./setup-db.sql:/docker-entrypoint-initdb.d/setup-db.sql kartoza/postgis`
Docker volumes can be used to persist your data.
mkdir -p ~/postgres_data
docker run -d -v $HOME/postgres_data:/var/lib/postgresql kartoza/postgis`
You need to ensure the postgres_data directory has sufficient permissions
for the docker process to read / write it.
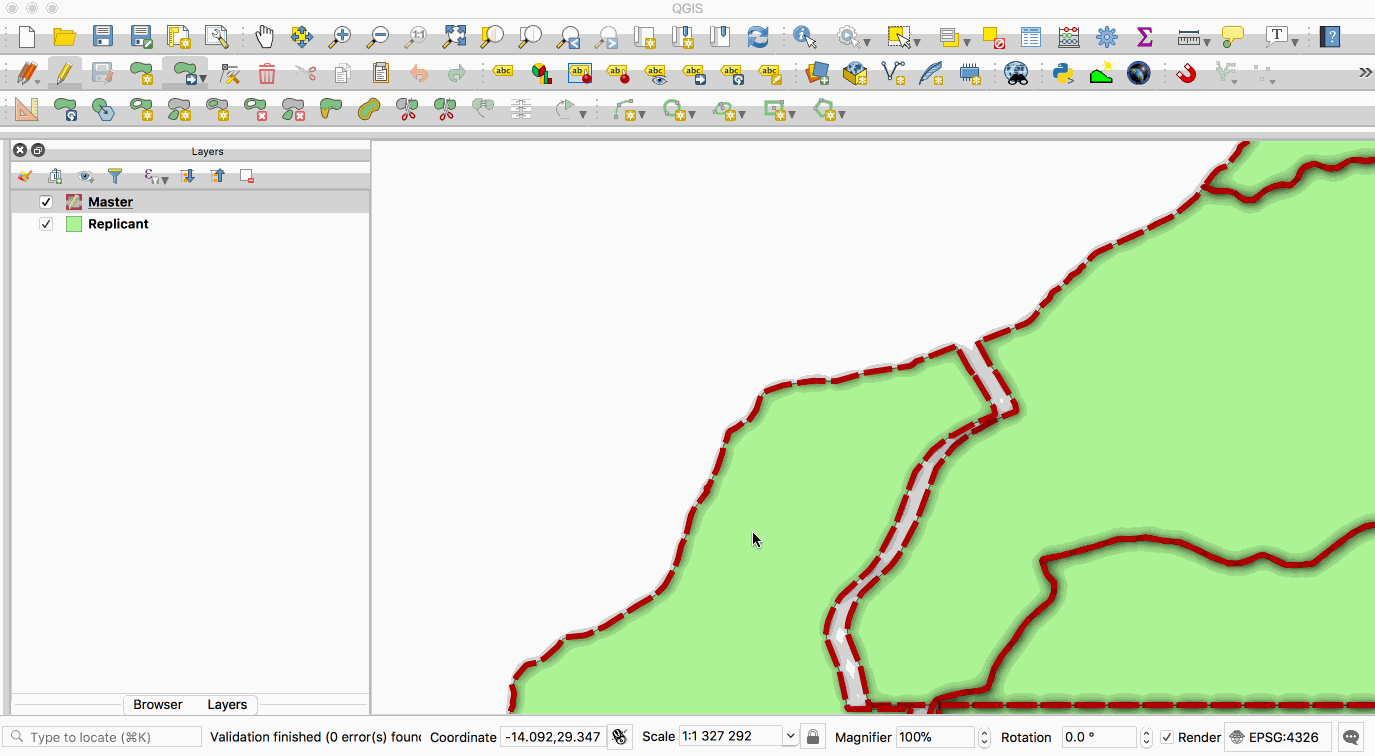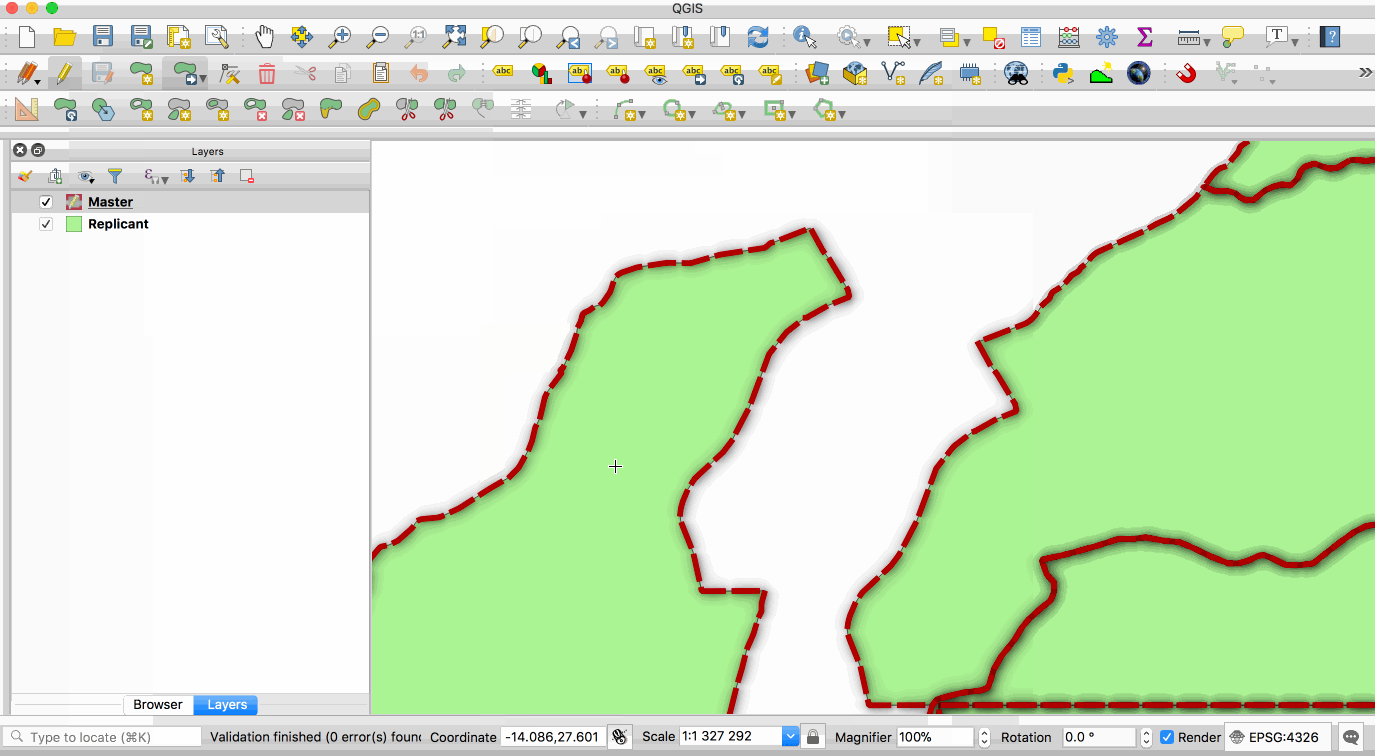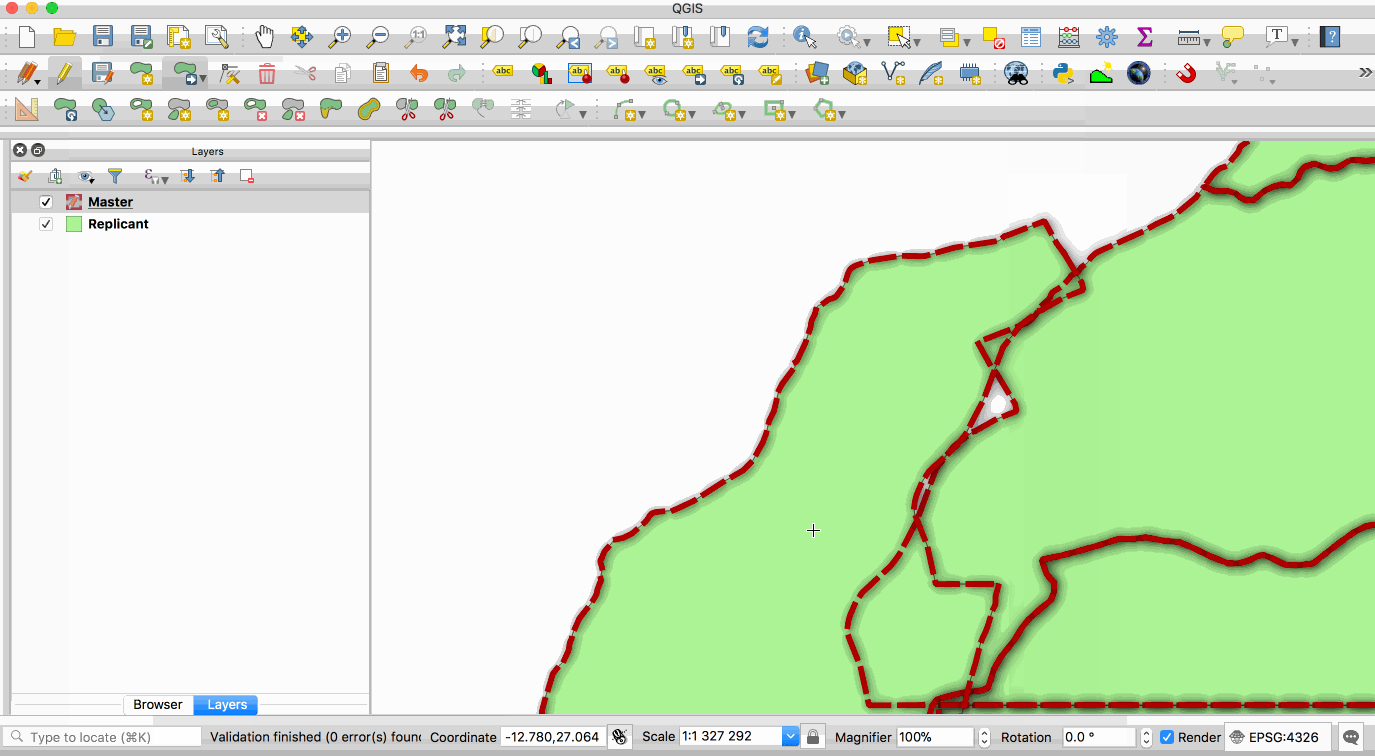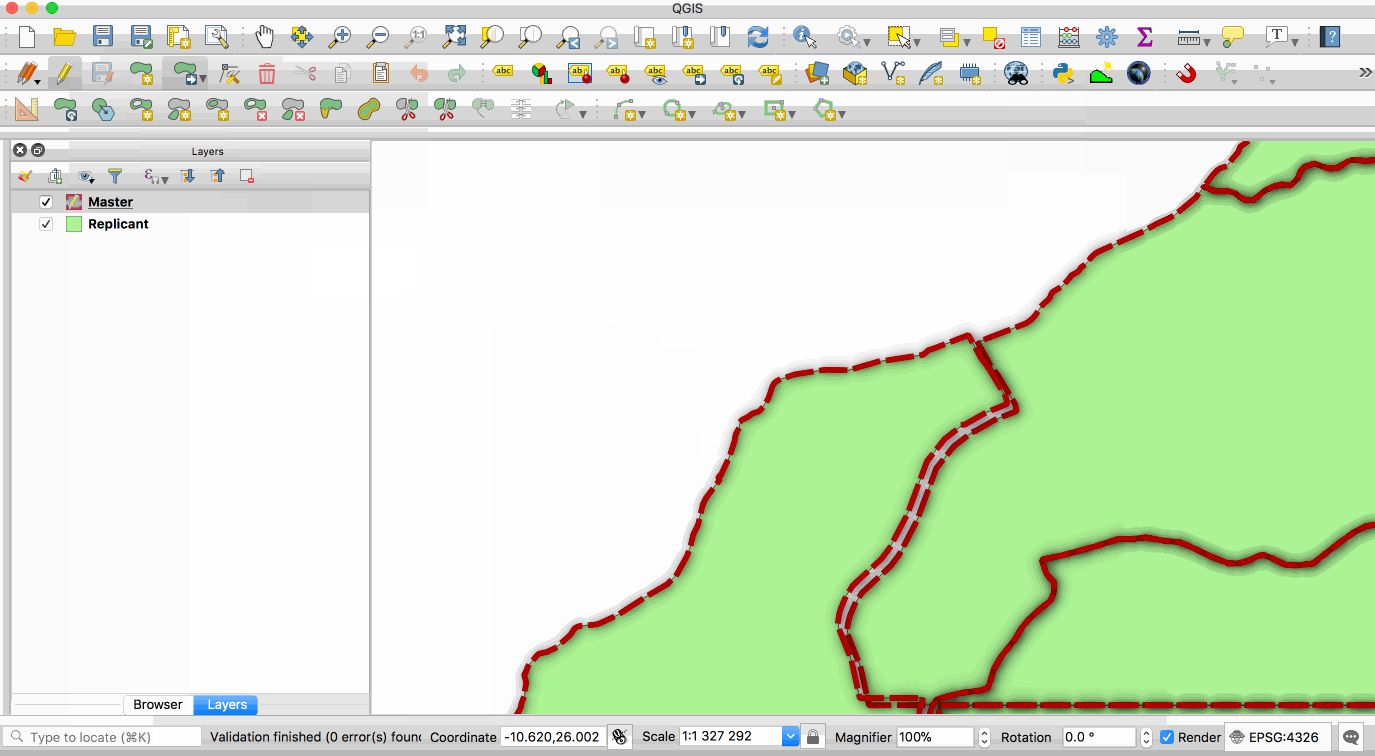
Replication allows you to maintain two or more synchronised copies of a database, with a single master copy and one or more replicant copies. The animation below illustrates this - the layer with the red boundary is accessed from the master database and the layer with the green fill is accessed from the replicant database. When edits to the master layer are saved, they are automatically propagated to the replicant. Note also that the replicant is read-only.
This image is provided with replication abilities. We can
categorize an instance of the container as master or replicant. A master
instance means that a particular container has a role as a single point of
database write. A replicant instance means that a particular container will
mirror database content from a designated master. This replication scheme allows
us to sync databases. However a replicant is only for read-only transaction, thus
we can't write new data to it. The whole database cluster will be replicated.
Since we are using a role ${REPLICATION_USER}, we need to ensure that it has access to all
the tables in a particular schema. So if a user adds another schema called data
to the database gis he also has to update the permission for the user
with the following SQL assuming the ${REPLICATION_USER} is called replicator
ALTER DEFAULT PRIVILEGES IN SCHEMA data GRANT SELECT ON TABLES TO replicator;
To experiment with the replication abilities, you can see a (docker-compose.yml)[sample/replication/docker-compose.yml] sample. There are several environment variables that you can set, such as:
Master settings:
- ALLOW_IP_RANGE: A pg_hba.conf domain format which will allow specified host(s)
to connect into the container. This is needed to allow the
slaveto connect intomaster, so specifically this settings should allowslaveaddress. It is also needed to allow clients on other hosts to connect to either the slave or the master. - REPLICATION_USER User to initiate streaming replication
- REPLICATION_PASS Password for a user with streaming replication role
Slave settings:
- REPLICATE_FROM: This should be the domain name or IP address of the
masterinstance. It can be anything from the docker resolved name like that written in the sample, or the IP address of the actual machine where you exposemaster. This is useful to create cross machine replication, or cross stack/server. - REPLICATE_PORT: This should be the port number of
masterpostgres instance. Will default to 5432 (default postgres port), if not specified. - DESTROY_DATABASE_ON_RESTART: Default is
True. Set to 'False' to prevent this behaviour. A replicant will always destroy its current database on restart, because it will try to sync again frommasterand avoid inconsistencies. - PROMOTE_MASTER: Default none. If set to any value then the current replicant
will be promoted to master.
In some cases when the
mastercontainer has failed, we might want to use ourreplicantasmasterfor a while. However, the promoted replicant will break consistencies and is not able to revert to replicant anymore, unless it is destroyed and resynced with the new master. - REPLICATION_USER User to initiate streaming replication
- REPLICATION_PASS Password for a user with streaming replication role
To run the sample replication, follow these instructions:
Do a manual image build by executing the build.sh script
./build.sh
Go into the sample/replication directory and experiment with the following Make
command to run both master and slave services.
make up
To shutdown services, execute:
make down
To view logs for master and slave respectively, use the following command:
make master-log
make slave-log
You can try experiment with several scenarios to see how replication works
You can use any postgres database tools to create new tables in master, by connecting using POSTGRES_USER and POSTGRES_PASS credentials using exposed port. In the sample, the master database was exposed on port 7777. Or you can do it via command line, by entering the shell:
make master-shell
Then made any database changes using psql.
After that, you can see that the replicant follows the changes by inspecting the slave database. You can, again, use database management tools using connection credentials, hostname, and ports for replicant. Or you can do it via command line, by entering the shell:
make slave-shell
Then view your changes using psql.
You will notice that you cannot make changes in replicant, because it is read-only.
If somehow you want to promote it to master, you can specify PROMOTE_MASTER: 'True'
into slave environment and set DESTROY_DATABASE_ON_RESTART: 'False'.
After this, you can make changes to your replicant, but master and replicant will not be in sync anymore. This is useful if the replicant needs to take over a failover master. However it is recommended to take additional action, such as creating a backup from the slave so a dedicated master can be created again.
You can optionally set DESTROY_DATABASE_ON_RESTART: 'False' after successful sync
to prevent the database from being destroyed on restart. With this setting you can
shut down your replicant and restart it later and it will continue to sync using the existing
database (as long as there are no consistencies conflicts).
However, you should note that this option doesn't mean anything if you didn't persist your database volume. Because if it is not persisted, then it will be lost on restart because docker will recreate the container.
By default the image is delivered with an unsigned SSL certificate. This helps to have an encrypted connection to clients and avoid eavesdropping but does not help to mitigate man in the middle (MITM) attacks.
You need to provide your own, signed private key to avoid this kind of attacks (and make sure clients connect with verify-ca or verify-full sslmode).
The following is an example Dockerfile that sets up a container with custom ssl private key and certificate:
FROM kartoza/postgis:11.0-2.5
ADD ssl_cert.pem /etc/ssl/certs/ssl_cert.pem
ADD localhost_ssl_key.pem /etc/ssl/private/ssl_key.pem
RUN chmod 400 /etc/ssl/private/ssl_key.pem
And a docker-compose.yml to initialize with this configuration:
services:
postgres:
build:
dockerfile: Dockerfile
context: ssl_secured_docker
environment:
- SSL_CERT_FILE=/etc/ssl/certs/ssl_cert.pem
- SSL_KEY_FILE=/etc/ssl/private/ssl_key.pem
See the postgres documentation about SSL for more information.
The database cluster is initialised with the following encoding settings
-E "UTF8" --lc-collate="en_US.UTF-8" --lc-ctype="en_US.UTF-8"
or
-E "UTF8" --lc-collate="C.UTF-8" --lc-ctype="C.UTF-8"
If you use default DATADIR location.
If you need to setup a database cluster with other encoding parameters you need to pass the environment variables when you initialize the cluster.
- -e DEFAULT_ENCODING="UTF8"
- -e DEFAULT_COLLATION="en_US.UTF-8"
- -e DEFAULT_CTYPE="en_US.UTF-8"
Initializing a new cluster can be done by using different DATADIR location and
mounting an empty volume. Or use parameter RECREATE_DATADIR to forcefully
delete the current cluster and create a new one. Make sure to remove parameter
RECREATE_DATADIR after creating the cluster.
See the postgres documentation about encoding for more information.
Tim Sutton (tim@kartoza.com) Gavin Fleming (gavin@kartoza.com) Rizky Maulana (rizky@kartoza.com) Admire Nyakudya (admire@kartoza.com) December 2018