Tools to Design or Visualize Architecture of Neural Network
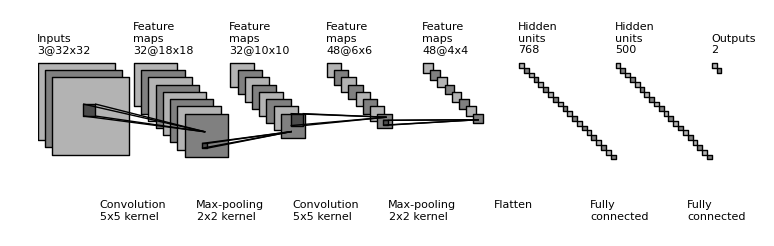
- draw_convnet : Python script for illustrating Convolutional Neural Network (ConvNet)
- PlotNeuralNet : Latex code for drawing neural networks for reports and presentation. Have a look into examples to see how they are made. Additionally, lets consolidate any improvements that you make and fix any bugs to help more people with this code.
- Tensorboard - TensorBoard’s Graphs dashboard is a powerful tool for examining your TensorFlow model.
- Caffe - In Caffe you can use caffe/draw.py to draw the NetParameter protobuffer:
-
keras-sequential-ascii - A library for Keras for investigating architectures and parameters of sequential models.
VGG 16 Architecture
OPERATION DATA DIMENSIONS WEIGHTS(N) WEIGHTS(%)
Input ##### 3 224 224
InputLayer | ------------------- 0 0.0%
##### 3 224 224
Convolution2D \|/ ------------------- 1792 0.0%
relu ##### 64 224 224
Convolution2D \|/ ------------------- 36928 0.0%
relu ##### 64 224 224
MaxPooling2D Y max ------------------- 0 0.0%
##### 64 112 112
Convolution2D \|/ ------------------- 73856 0.1%
relu ##### 128 112 112
Convolution2D \|/ ------------------- 147584 0.1%
relu ##### 128 112 112
MaxPooling2D Y max ------------------- 0 0.0%
##### 128 56 56
Convolution2D \|/ ------------------- 295168 0.2%
relu ##### 256 56 56
Convolution2D \|/ ------------------- 590080 0.4%
relu ##### 256 56 56
Convolution2D \|/ ------------------- 590080 0.4%
relu ##### 256 56 56
MaxPooling2D Y max ------------------- 0 0.0%
##### 256 28 28
Convolution2D \|/ ------------------- 1180160 0.9%
relu ##### 512 28 28
Convolution2D \|/ ------------------- 2359808 1.7%
relu ##### 512 28 28
Convolution2D \|/ ------------------- 2359808 1.7%
relu ##### 512 28 28
MaxPooling2D Y max ------------------- 0 0.0%
##### 512 14 14
Convolution2D \|/ ------------------- 2359808 1.7%
relu ##### 512 14 14
Convolution2D \|/ ------------------- 2359808 1.7%
relu ##### 512 14 14
Convolution2D \|/ ------------------- 2359808 1.7%
relu ##### 512 14 14
MaxPooling2D Y max ------------------- 0 0.0%
##### 512 7 7
Flatten ||||| ------------------- 0 0.0%
##### 25088
Dense XXXXX ------------------- 102764544 74.3%
relu ##### 4096
Dense XXXXX ------------------- 16781312 12.1%
relu ##### 4096
Dense XXXXX ------------------- 4097000 3.0%
softmax ##### 1000
- Keras Visualization - The keras.utils.vis_utils module provides utility functions to plot a Keras model (using graphviz)
- Conx - The Python package
conxcan visualize networks with activations with the functionnet.picture()to produce SVG, PNG, or PIL Images like this:
- ENNUI - Working on a drag-and-drop neural network visualizer (and more). Here's an example of a visualization for a LeNet-like architecture.
- NNet - R Package - Tutorial
data(infert, package="datasets")
plot(neuralnet(case~parity+induced+spontaneous, infert))
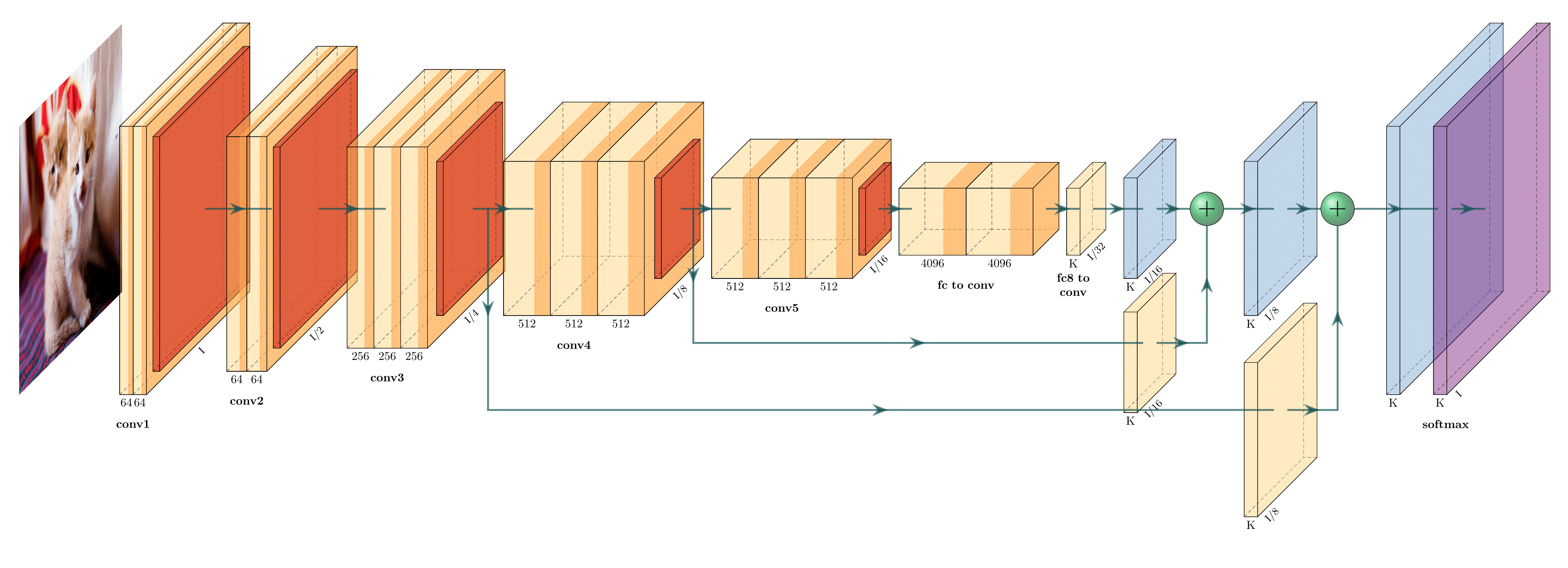
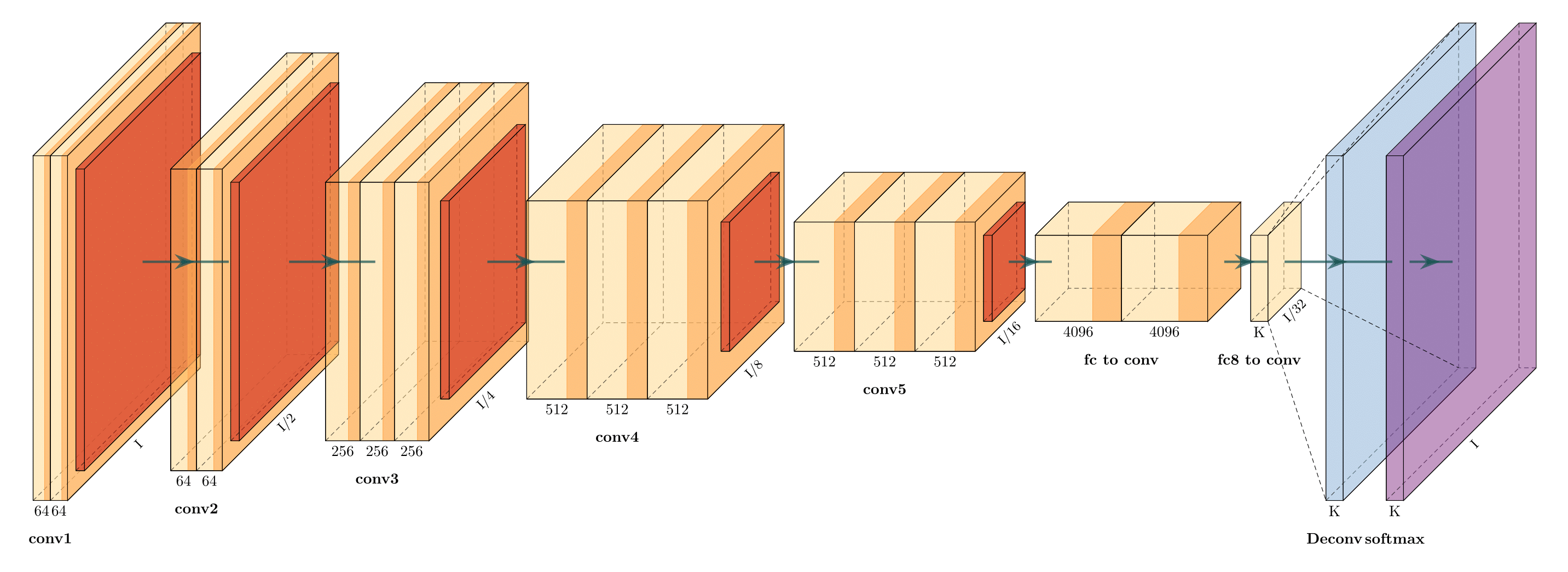
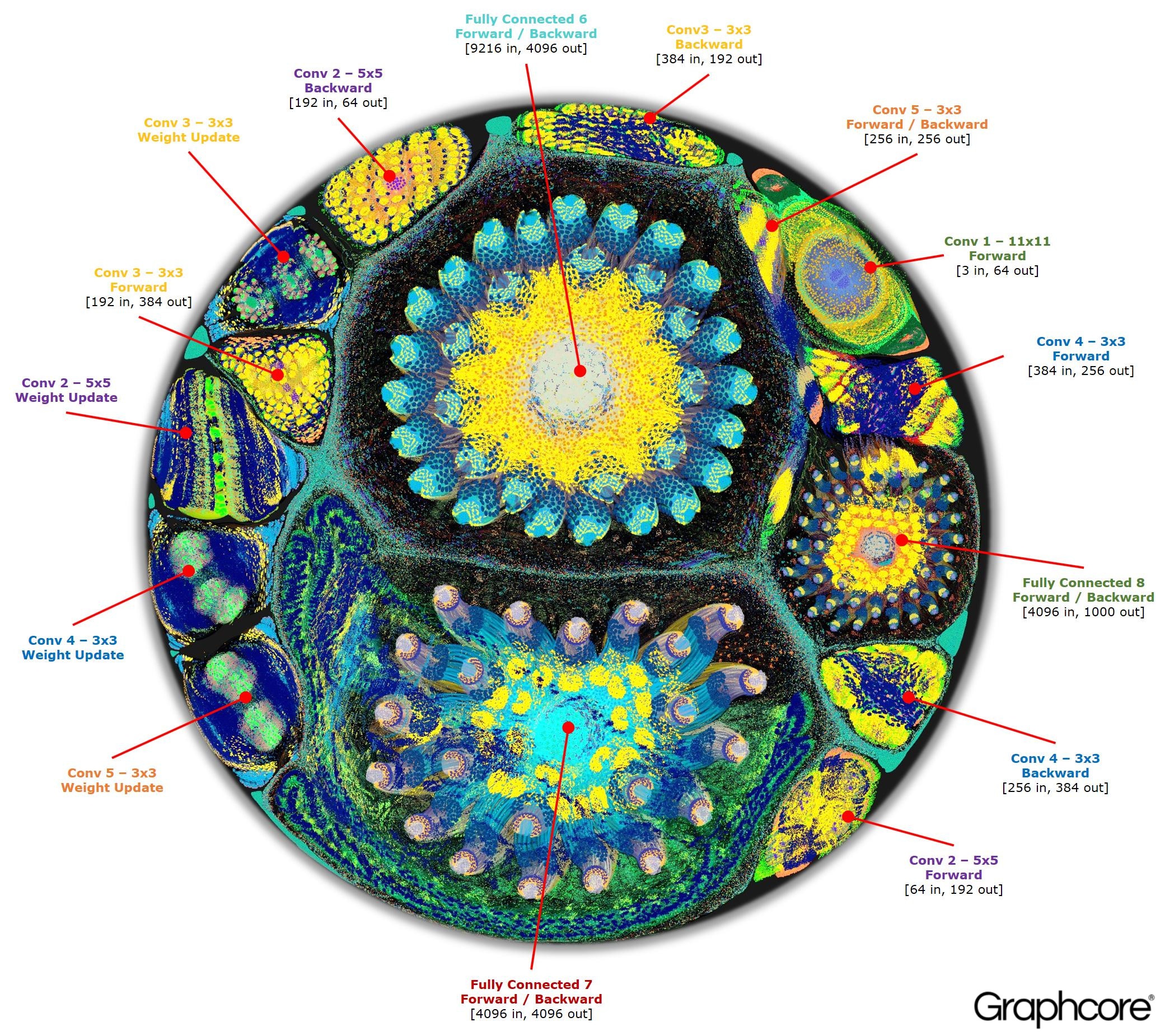
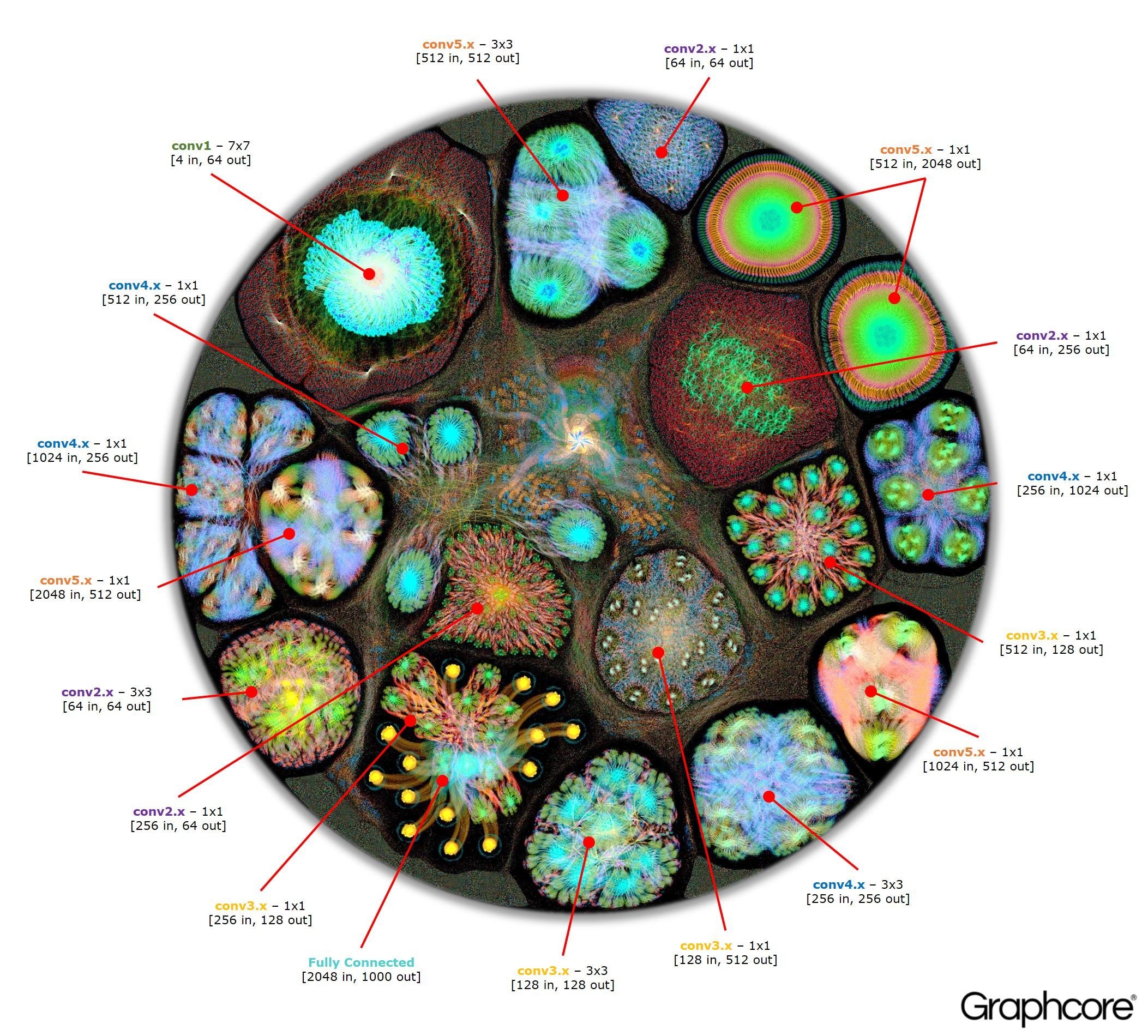
- GraphCore - These approaches are more oriented towards visualizing neural network operation, however, NN architecture is also somewhat visible on the resulting diagrams.
AlexNet
Neataptic offers flexible neural networks; neurons and synapses can be removed with a single line of code. No fixed architecture is required for neural networks to function at all. This flexibility allows networks to be shaped for your dataset through neuro-evolution, which is done using multiple threads.
-
TensorSpace : TensorSpace is a neural network 3D visualization framework built by TensorFlow.js, Three.js and Tween.js. TensorSpace provides Layer APIs to build deep learning layers, load pre-trained models, and generate a 3D visualization in the browser. By applying TensorSpace API, it is more intuitive to visualize and understand any pre-trained models built by TensorFlow, Keras, TensorFlow.js, etc.
Interactive Notation for Computational Graphs https://mlajtos.github.io/moniel/
\documentclass{article}
\usepackage{tikz}
\begin{document}
\pagestyle{empty}
\def\layersep{2.5cm}
\begin{tikzpicture}[shorten >=1pt,->,draw=black!50, node distance=\layersep]
\tikzstyle{every pin edge}=[<-,shorten <=1pt]
\tikzstyle{neuron}=[circle,fill=black!25,minimum size=17pt,inner sep=0pt]
\tikzstyle{input neuron}=[neuron, fill=green!50];
\tikzstyle{output neuron}=[neuron, fill=red!50];
\tikzstyle{hidden neuron}=[neuron, fill=blue!50];
\tikzstyle{annot} = [text width=4em, text centered]
% Draw the input layer nodes
\foreach \name / \y in {1,...,4}
% This is the same as writing \foreach \name / \y in {1/1,2/2,3/3,4/4}
\node[input neuron, pin=left:Input \#\y] (I-\name) at (0,-\y) {};
% Draw the hidden layer nodes
\foreach \name / \y in {1,...,5}
\path[yshift=0.5cm]
node[hidden neuron] (H-\name) at (\layersep,-\y cm) {};
% Draw the output layer node
\node[output neuron,pin={[pin edge={->}]right:Output}, right of=H-3] (O) {};
% Connect every node in the input layer with every node in the
% hidden layer.
\foreach \source in {1,...,4}
\foreach \dest in {1,...,5}
\path (I-\source) edge (H-\dest);
% Connect every node in the hidden layer with the output layer
\foreach \source in {1,...,5}
\path (H-\source) edge (O);
% Annotate the layers
\node[annot,above of=H-1, node distance=1cm] (hl) {Hidden layer};
\node[annot,left of=hl] {Input layer};
\node[annot,right of=hl] {Output layer};
\end{tikzpicture}
% End of code
\end{document}
References :