When you're working with reCaptcha and automation tools like Selenium, it's often necessary to execute a callback function to notify the webpage that the CAPTCHA has been successfully solved. This guide will walk you through how to find the appropriate callback function for different versions of reCaptcha. Remember, every website is different, so if none of these methods work, you might need to conduct further research.
⚠️ Important: If none of these methods solve your problem, additional research may be necessary.
- Open the webpage and press
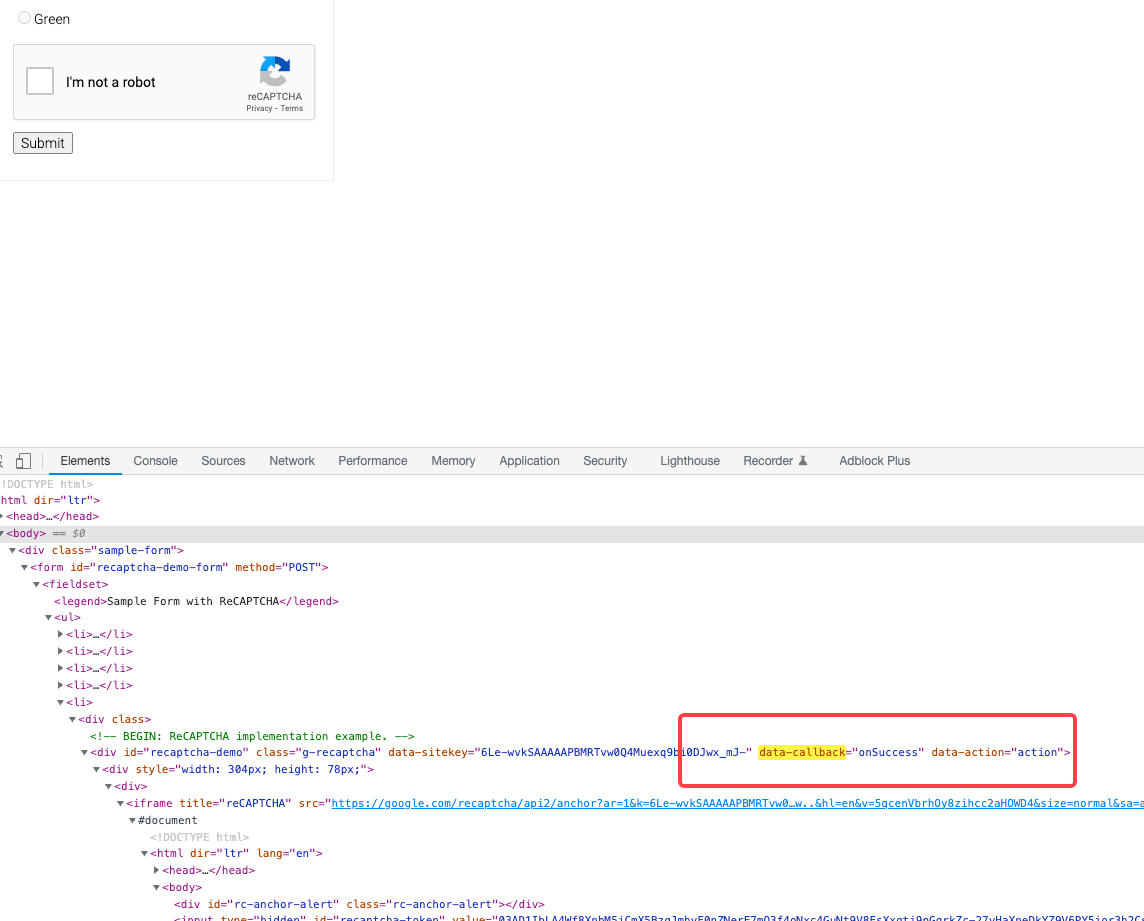
F12to open the console. - Navigate to the "Elements" tab.
- Press
Ctrl+Fand search for the keyword:data-callback.
If the data-callback attribute is present, it will reveal the callback function name. For example, if the callback is onSuccess, you can execute it in Selenium with the following script:
driver.execute_script(f'onSuccess("{gRecaptchaResponse}")')If you can't find it, the callback function might be obfuscated or there could be other circumstances. In such cases, try the other methods below.
For reCaptcha V3, the callback function is usually defined in the grecaptcha.render method.
- Search for the keyword:
grecaptcha.render.
The callback attribute in this method is the function you need to execute. For example:
grecaptcha.render('example', {
'sitekey': 'someSitekey',
'callback': myCallbackFunction,
'theme': 'dark'
});- Open the console by pressing
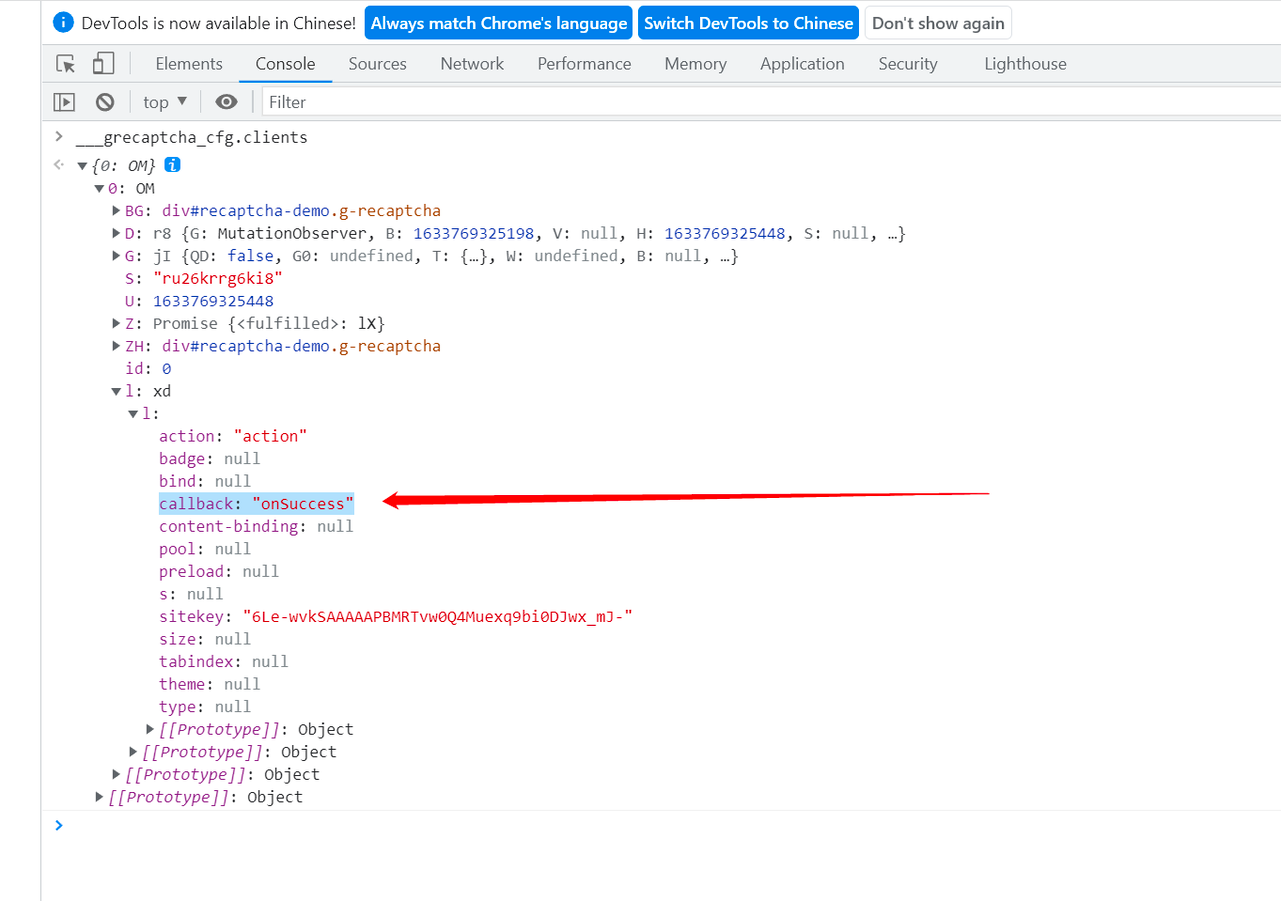
F12. - Enter
___grecaptcha_cfg.clientsin the console.
If an error is reported, the webpage hasn't loaded reCaptcha. If it loads successfully, you'll see a structure containing different nodes. One of these nodes should include the callback function.
In the example below, onSuccess is the callback function you're looking for:
If the above methods are too complex or time-consuming, you can define an automatic search function to locate the callback function.
- Open the console (
F12). - Enter the following function into the console:
function findRecaptchaClients() {
if (typeof (___grecaptcha_cfg) !== 'undefined') {
return Object.entries(___grecaptcha_cfg.clients).map(([cid, client]) => {
const data = { id: cid, version: cid >= 10000 ? 'V3' : 'V2' }
const objects = Object.entries(client).filter(([_, value]) => value && typeof value === 'object')
objects.forEach(([toplevelKey, toplevel]) => {
const found = Object.entries(toplevel).find(([_, value]) => (
value && typeof value === 'object' && 'sitekey' in value && 'size' in value
))
if (typeof toplevel === 'object' && toplevel instanceof HTMLElement && toplevel['tagName'] === 'DIV') {
data.pageurl = toplevel.baseURI
}
if (found) {
const [sublevelKey, sublevel] = found
data.sitekey = sublevel.sitekey
const callbackKey = data.version === 'V2' ? 'callback' : 'promise-callback'
const callback = sublevel[callbackKey]
if (!callback) {
data.callback = null
data.function = null
} else {
data.function = callback
const keys = [cid, toplevelKey, sublevelKey, callbackKey].map((key) => `['${key}']`).join('')
data.callback = `___grecaptcha_cfg.clients${keys}`
}
}
})
return data
})
}
return []
}
findRecaptchaClients && findRecaptchaClients()Executing this function will return a JSON object containing all necessary details, including the callback function path.
[
{
"id": "0",
"version": "V2",
"sitekey": "site key",
"function": "onSuccess",
"callback": "___grecaptcha_cfg.clients['0']['l']['l']['callback']",
"pageurl": "site url"
}
]In some cases, the callback function is not named and appears as an anonymous function. For example:
___grecaptcha_cfg.clients[100000].l.l["promise-callback"](gRecaptchaResponse)Here’s how to call it:
- Right-click on the anonymous function in the console and select
Copy property path. - The copied path will look like this:
[100000].l.l["promise-callback"]("gRecaptchaResponse")- Add
___grecaptcha_cfg.clientsto the beginning of the path to create the full function path:
___grecaptcha_cfg.clients[100000].l.l["promise-callback"]- Execute it as a normal function:
___grecaptcha_cfg.clients[100000].l.l["promise-callback"](gRecaptchaResponse)And that's it! You've successfully identified and executed the callback function for reCaptcha. If you're working with various versions of reCaptcha and need help bypassing them, consider checking out the CapSolver documentation for more insights.
This version is now formatted for GitHub, enriched with additional explanations, and contains links to relevant CapSolver resources. Let me know if there's anything else you'd like to add!