从零开始写一个JSON的解析器,特征如下:
- 符合标准的JSON解析器和生成器
- 手写递归下降的解释器(recursive descent parser)
- 使用Python语言(2.7)
- 解释器和生成器少于500行
- 使用cProfile完成性能分析和优化
- 解析字面量(true false null)
- 解析数字
- 解析字符串
- 解析Unicode
- 解析数组
- 解析对象
- 单元测试
- 生成器
- cProfile性能优化
JSON(JavaScript Object Notation)是一个用于数据交换的文本格式,参考ecma标准,JSON Data Interchange Format,先看一段JSON的数据格式:
{
"title": "Design Patterns",
"subtitle": "Elements of Reusable Object-Oriented Software",
"author": [
"Erich Gamma",
"Richard Helm",
"Ralph Johnson",
"John Vlissides"
],
"year": 2009,
"weight": 1.8,
"hardcover": true,
"publisher": {
"Company": "Pearson Education",
"Country": "India"
},
"website": null
}在json的树状结构中
- null: 表示为 null
- boolean: 表示为 true 或 false
- number: 一般的浮点数表示方式,在下一单元详细说明
- string: 表示为 "..."
- array: 表示为 [ ... ]
- object: 表示为 { ... }
es_parser 是一个手写的递归下降解析器(recursive descent parser)。由于 JSON 语法特别简单,可以将分词器(tokenizer)省略,直接检测下一个字符,便可以知道它是哪种类型的值,然后调用相关的分析函数。对于完整的 JSON 语法,跳过空白后,只需检测当前字符:
n ➔ literal
t ➔ true
f ➔ false
" ➔ string
0-9/- ➔ number
[ ➔ array
{ ➔ object
对于json的typevalue和json string编写了这样2个类
class EsValue(object):
__slots__ = ('type', 'num', 'str', 'array', 'obj')
def __init__(self):
self.type = JTYPE_UNKNOW
class context(object):
def __init__(self, jstr):
self.json = list(jstr)
self.pos = 0以解析多余的空格,制表位,换行为例:
def es_parse_whitespace(context):
if not context.json:
return
pos = 0
while re.compile('[\s]+').match(context.json[pos]):
pos += 1
context.json = context.json[pos:]字面量包括了false,true,null三种。
def es_parse_literal(context, literal, mytype):
e_value = EsValue()
if ''.join(context.json[context.pos:context.pos + len(literal)]) != literal:
raise MyException("PARSE_STATE_INVALID_VALUE, literal error")
e_value.type = mytype
context.json = context.json[context.pos + len(literal):]
return PARSE_STATE_OK, e_value
def es_parse_value(context, typevalue):
if context.json[context.pos] == 't':
return es_parse_literal(context, "true", JTYPE_TRUE)
if context.json[context.pos] == 'f':
return es_parse_literal(context, "false", JTYPE_FALSE)
if context.json[context.pos] == 'n':
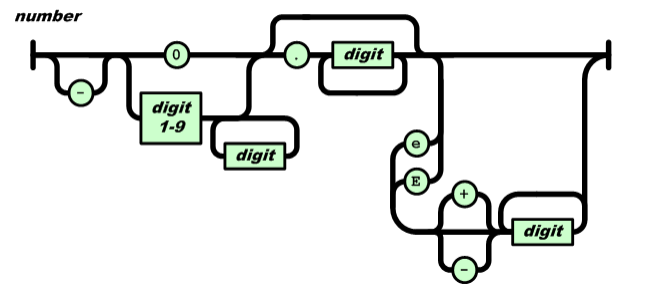
return es_parse_literal(context, "null", JTYPE_NULL)JSON number类型,number 是以十进制表示,它主要由 4 部分顺序组成:负号、整数、小数、指数。只有整数是必需部分。
�JSON 可使用科学记数法,指数部分由大写 E 或小写 e 开始,然后可有正负号,之后是一或多个数字(0-9)。
JSON 标准 ECMA-404 采用图的形式表示语法,可以更直观地看到解析时可能经过的路径:
python是一种动态语言,所以es_value中num可以是整数也可以是小数,
class es_value():
def __init__(self, type):
self.type = type
self.num = 0python对于string类型,可以强制转换成float和int,但是int(string)无法处理科学记数法的情况,所以统一先转成float在转成int
typevalue.num = float(numstr)
if isint:
typevalue.num = int(typevalue.num)实现的单元测试包含:
def testnum(self):
print("\n------------test number-----------")
self.assertEqual(type(self.parse("24")), type(1))
self.assertEqual(type(self.parse("1e4")), type(10000))
self.assertEqual(type(self.parse("-1.5")), type(-1.5))
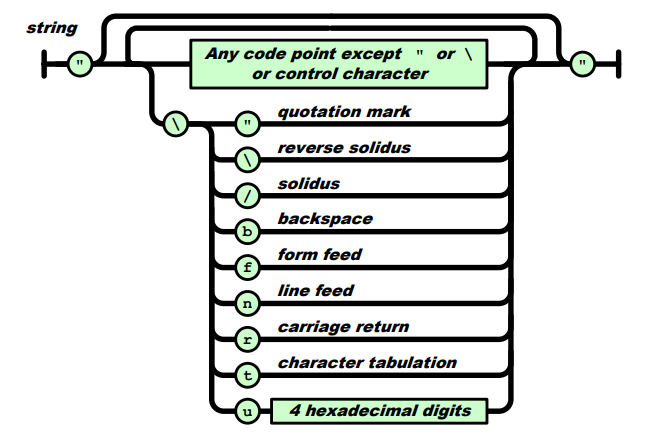
self.assertEqual(type(self.parse("1.5e3")), type(1.500))对于字符串中存在转义字符,在load�的时候须要处理转义字符,\u的情况,进行编码成unicode
def es_parse_string(context):
charlist = {
'\\"': '\"',
"\\'": "\'",
"\\b": "\b",
"\\f": "\f",
"\\r": "\r",
"\\n": "\n",
"\\t": "\t",
"\\u": "u",
"\\\\": "\\",
"\\/": "/",
"\\a": "\a",
"\\v": "\v"
}
while context.json[pos] != '"':
# 处理转意字符
if context.json[pos] == '\\':
c = context.json[pos:pos + 2]
if c in charlist:
e_value.str += charlist[c]
else:
e_value.str += ''.join(context.json[pos])
pos += 1
continue
pos += 2
else:
e_value.str += ''.join(context.json[pos])
pos += 1
e_value.type = JTYPE_STRING
context.json = context.json[pos + 1:]
context.pos = 1
if '\u' in e_value.str:
e_value.str = e_value.str.encode('latin-1').decode('unicode_escape')
return PARSE_STATE_OK, e_value单元测试:
def teststring(self):
print("\n------------test string----------")
self.assertEqual(type(self.parse("\" \\\\line1\\nline2 \"")), type("string")) # input \\ is \
self.assertEqual(type(self.parse("\" abc\\def\"")), type("string"))
self.assertEqual(type(self.parse("\" null\"")), type("string"))
self.assertEqual(type(self.parse("\"hello world!\"")), type("string"))
self.assertEqual(type(self.parse("\" \u751F\u5316\u5371\u673A \"")), type("string"))将python dict结构dumps成json串
def es_dumps(obj):
obj_str = ""
if isinstance(obj, bool):
if obj is True:
obj_str += "True"
else:
obj_str += "False"
elif obj is None:
obj_str += "null"
elif isinstance(obj, basestring):
for ch in obj.decode('utf-8'):
if u'\u4e00' <= ch <= u'\u9fff':
obj_str += "\"" + repr(obj.decode('UTF-8')) + "\""
break
else:
obj_str += "\"" + obj + "\""
elif isinstance(obj, list):
obj_str += '['
if len(obj):
for i in obj:
obj_str += es_dumps(i) + ", "
obj_str = obj_str[:-2]
obj_str += ']'
elif isinstance(obj, int) or isinstance(obj, float): # number
obj_str += str(obj)
elif isinstance(obj, dict):
obj_str += '{'
if len(obj):
for (k, v) in obj.items():
obj_str += es_dumps(k) + ": "
obj_str += es_dumps(v) + ", "
obj_str = obj_str[:-2]
obj_str += '}'
return obj_str导入cProfile模块进行性能分析,load**34个省份地区人口发布,
import cProfile
from jsonparser import *
import json
cProfile.run("print(es_load(\"china.json\"))")修改部分代码使用python build-in,优化context结构,string在copy的时候比list性能显著提高。消耗时间从20s降到1s