CompressAI (compress-ay) is a PyTorch library and evaluation platform for end-to-end compression research.
CompressAI currently provides:
- custom operations, layers and models for deep learning based data compression
- a partial port of the official TensorFlow compression library
- pre-trained end-to-end compression models for learned image compression
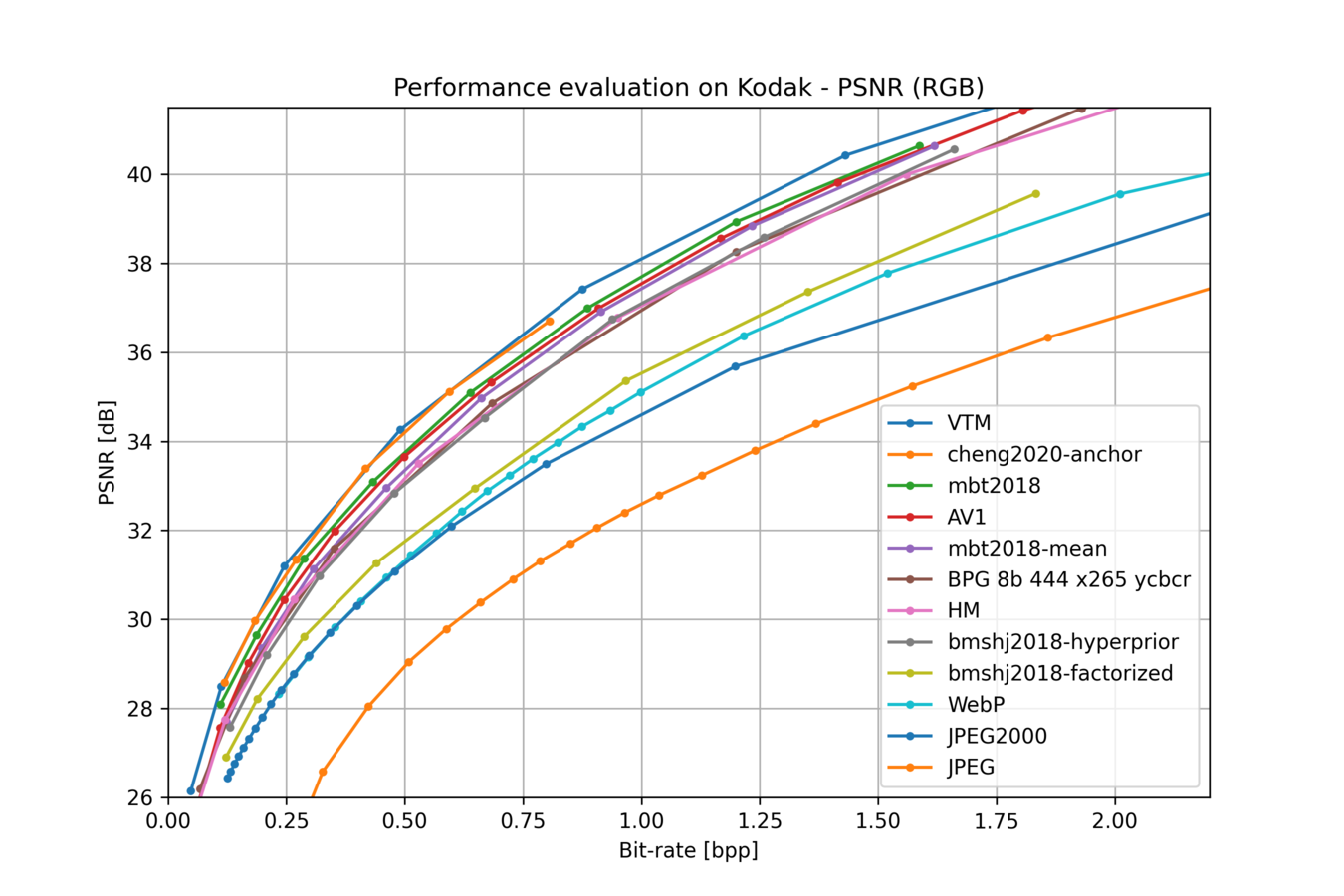
- evaluation scripts to compare learned models against classical image/video compression codecs
Note: Multi-GPU support is not yet available but will be addressed in a future release.
CompressAI only supports python 3.6+ and PyTorch 1.4+. A C++17 compiler, a
recent version of pip (19.0+), and common python packages (see setup.py for
the full list) are also required.
To get started and install CompressAI, run the following commands in a virtual environment:
git clone https://github.com/InterDigitalInc/CompressAI compressai
cd compressai
pip install -U pip && pip install -e .For a custom installation, you can also run one of the following commands:
pip install -e '.[dev]': install the packages required for development (testing, linting, docs)pip install -e '.[tutorials]': install the packages required for the tutorials (notebooks)pip install -e '.[all]': install all the optional packages
This is the currently recommended installation method. Docker images and PyPI packages will be released in the future. Conda environments are not officially supported.
Script and notebook examples can be found in the examples/ directory.
To encode/decode images with the provided pre-trained models, run the
codec.py example:
python3 examples/codec.py --helpAn examplary training script with a rate-distortion loss is provided in
examples/train.py. You can replace the model used in the training script
with your own model implemented within CompressAI, and then run the script for a
simple training pipeline:
python3 examples/train.py -d /path/to/my/image/dataset/ --epochs 300 -lr 1e-4 --batch-size 16 --cuda --saveNote: the training example uses a custom ImageFolder structure.
A jupyter notebook illustrating the usage of a pre-trained model for learned image
compression is also provided in the examples directory:
pip install -U ipython jupyter ipywidgets matplotlib
jupyter notebook examples/To evaluate a trained model on your own dataset, CompressAI provides an evaluation script:
python3 -m compressai.utils.eval_model checkpoint /path/to/images/folder/ -a $ARCH -p $MODEL_CHECKPOINT...To evaluate traditional image/video codecs:
python3 -m compressai.utils.bench --help
python3 -m compressai.utils.bench bpg --help
python3 -m compressai.utils.bench vtm --helpCompressAI is licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0
We welcome feedback and contributions. Please open a GitHub issue to report bugs, request enhancements or if you have any questions.
Before contributing, please read the CONTRIBUTING.md file.
- Jean Bégaint, Fabien Racapé, Simon Feltman and Akshay Pushparaja, InterDigital AI Lab.
If you use this project, please cite the relevant original publications for the models and datasets, and cite this project as:
@article{begaint2020compressai,
title={CompressAI: a PyTorch library and evaluation platform for end-to-end compression research},
author={B{\'e}gaint, Jean and Racap{\'e}, Fabien and Feltman, Simon and Pushparaja, Akshay},
year={2020},
journal={arXiv preprint arXiv:2011.03029},
}
- Tensorflow compression library by Ballé et al.: https://github.com/tensorflow/compression
- Range Asymmetric Numeral System code from Fabian 'ryg' Giesen: https://github.com/rygorous/ryg_rans
- BPG image format by Fabrice Bellard: https://bellard.org/bpg
- HEVC HM reference software: https://hevc.hhi.fraunhofer.de
- VVC VTM reference software: https://vcgit.hhi.fraunhofer.de/jvet/VVCSoftware_VTM
- AOM AV1 reference software: https://aomedia.googlesource.com/aom
- Z. Cheng et al. 2020: https://github.com/ZhengxueCheng/Learned-Image-Compression-with-GMM-and-Attention
- Kodak image dataset: http://r0k.us/graphics/kodak/