Hayate-Shiki is an improved merge sort algorithm with the goal of "faster than quick sort".
It has the following features.
- Comparison sort
- Stable sort
- External area: N
- Best: O (N)
- Average: O (N log N)
- Worst: O (N log N)
- Recursion: None
- The external area is regarded as a 2N continuous band.
- The following rules apply when placing values in the external area.
- If (maximum <= value), place it above the ascending order column and update the maximum.
- If (value < minimum), place it below the descending column and update the minimum.
- If (minimum <= value < maximum), place new values (maximum and minimum) in ascending order column, and let the value group arranged so far be Part.
- Merge parts.
The external area is regarded as a 2N continuous band.
4 5 1 2 7 6 3 8|Input column
. . . . . . . .|External area
->Asc Dsc<-|Actually
|4 5 1 2 7 6 3 8|Input column
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .|External area
Dsc<-|->Asc |2N continuous band
Put new values (maximum and minimum) in ascending order column.
|. 5 1 2 7 6 3 8
. . . . . . . . 4 . . . . . . .
The next value is (maximum <= value), place it above the ascending order column and update the maximum.
|. . 1 2 7 6 3 8
. . . . . . . . 4 5 . . . . . .
The next value is (value < minimum), place it below the descending column and update the minimum.
|. . . 2 7 6 3 8
. . . . . . . 1 4 5 . . . . . .
The next value is (minimum <= value < maximum), place new values (maximum and minimum) in ascending order column,
and let the value group arranged so far be Part.(Part: 145 completed)
|. . . . 7 6 3 8
. . . . . . .|1 4 5|2 . . . . .
The next value is (maximum <= value), place it above the ascending order column and update the maximum.
|. . . . . 6 3 8
. . . . . . .|1 4 5|2 7 . . . .
The next value is (minimum <= value < maximum), place new values (maximum and minimum) in ascending order column,
and let the value group arranged so far be Part.(Part: 27 completed)
|. . . . . . 3 8
. . . . . . .|1 4 5|2 7|6 . . .
The next value is (value < minimum), place it below the descending column and update the minimum.
|. . . . . . . 8
. . . . . . 3|1 4 5|2 7|6 . . .
The next value is (maximum <= value), place it above the ascending order column and update the maximum.(Part: 368 completed)
|. . . . . . . .
. . . . . .|3|1 4 5|2 7|6 8|. .
External area result.
4 5|2 7|6 8|. . Ascending column arrangement
. . . . . .|3|1 Descending column arrangement
4 5|2 7|6 8|3|1 Actual arrangement
Merge generated Parts.
145 27 368
12457 368
12345678
Sort complete.
We will make additional improvements to the basic algorithm.
- Insert sort is performed to secure the length of Part.
- Merge sequentially to avoid recursion.
The following environment has been verified.
- Windows 10 Pro 64bit
- Core i7-8700 3.20 GHz
Microsoft(R) C/C++ Optimizing Compiler Version 19.16.27030.1 for x64
cl Main.cpp -std:c++14 -Ox -EHsc -Fe:TestMsvc.exe
TestMsvc.exe
clang version 8.0.0 (tags/RELEASE_800/final)
Target: x86_64-w64-windows-gnu
clang++ Main.cpp -std=c++14 -O3 -o TestClang++.exe
TestClang++.exe
gcc version 8.3.0 (Rev2, Built by MSYS2 project)
Target: x86_64-w64-mingw32
g++ Main.cpp -std=c++14 -O3 -o TestG++.exe
TestG++.exe
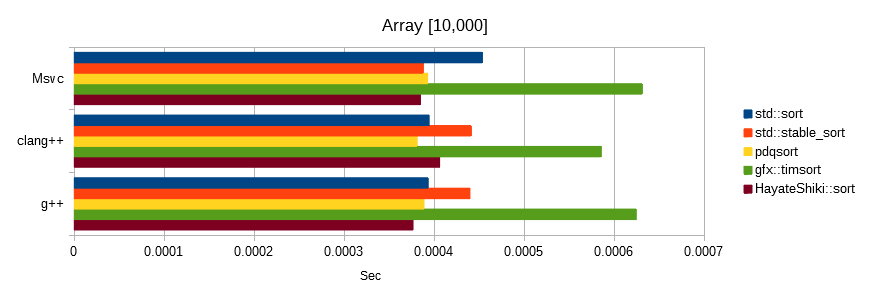
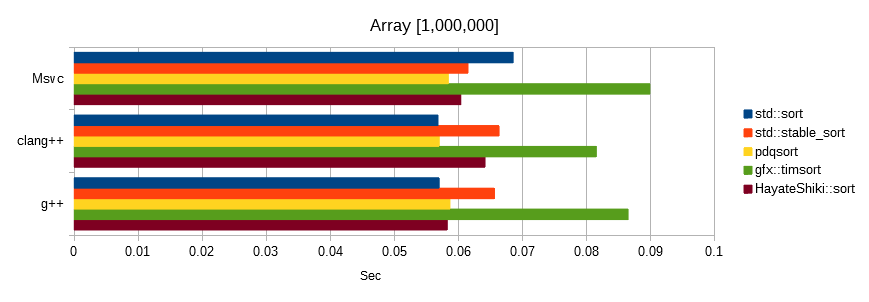
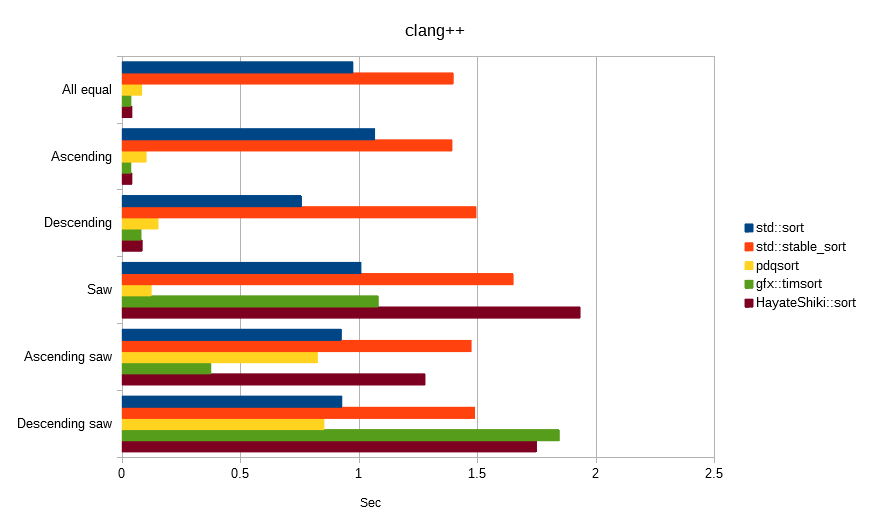
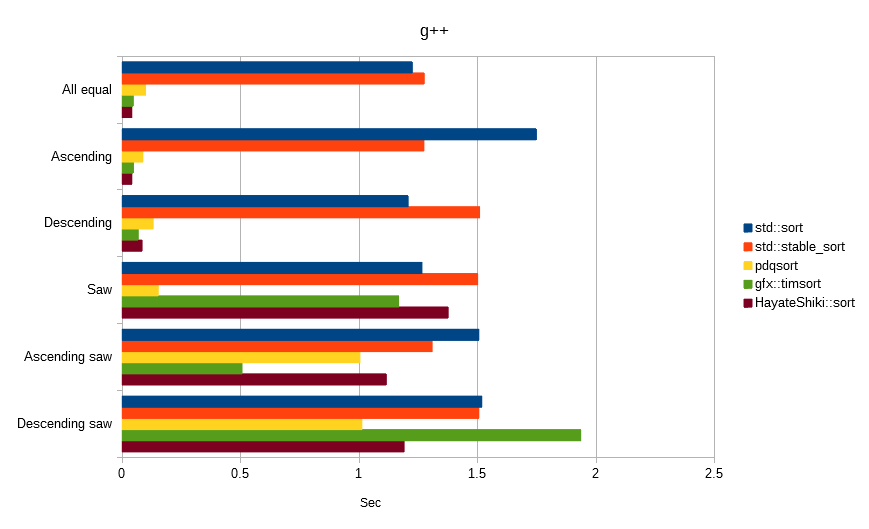
Sorts float values generated from the same seed.
The unit is seconds, the lower the number, the faster.
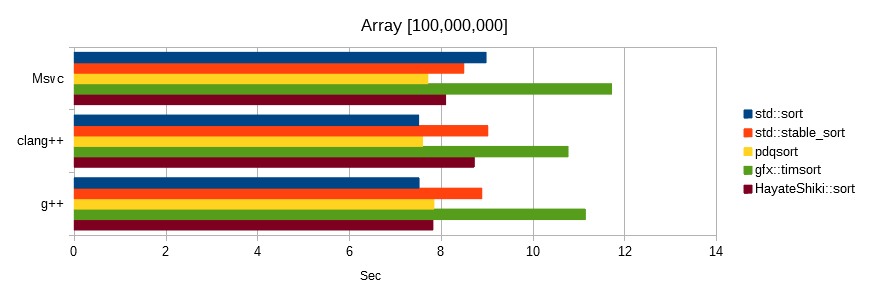
The following all sorted the array [100,000,000] of float value.
The unit is seconds, the lower the number, the faster.
How was it?
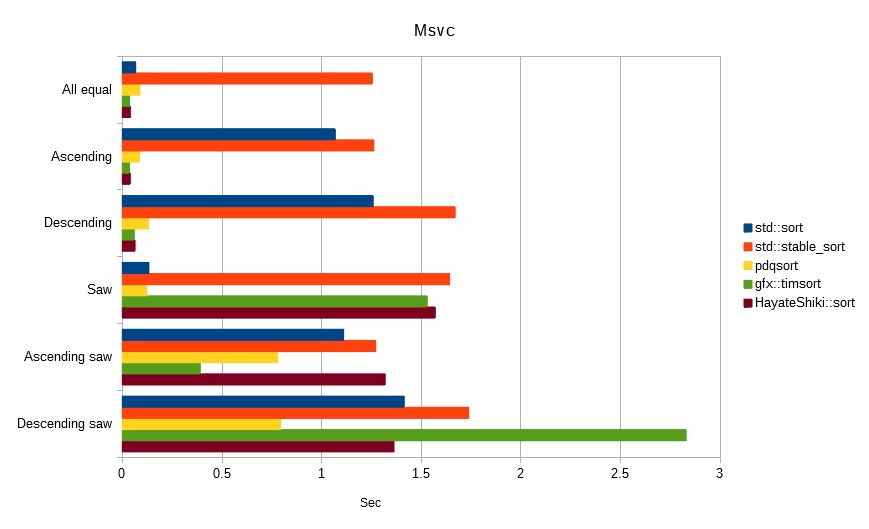
Hayate-Shiki is a stable sort, but has strong characteristics to random numbers.
In the conditional benchmark, it was found that the influence of the optimization characteristic of the compiler, rather than the algorithm characteristic, becomes strong, so that it can hardly be a judgment material.
Does it come the day when merge sort wins quick sort?
The sort algorithm is still romantic.