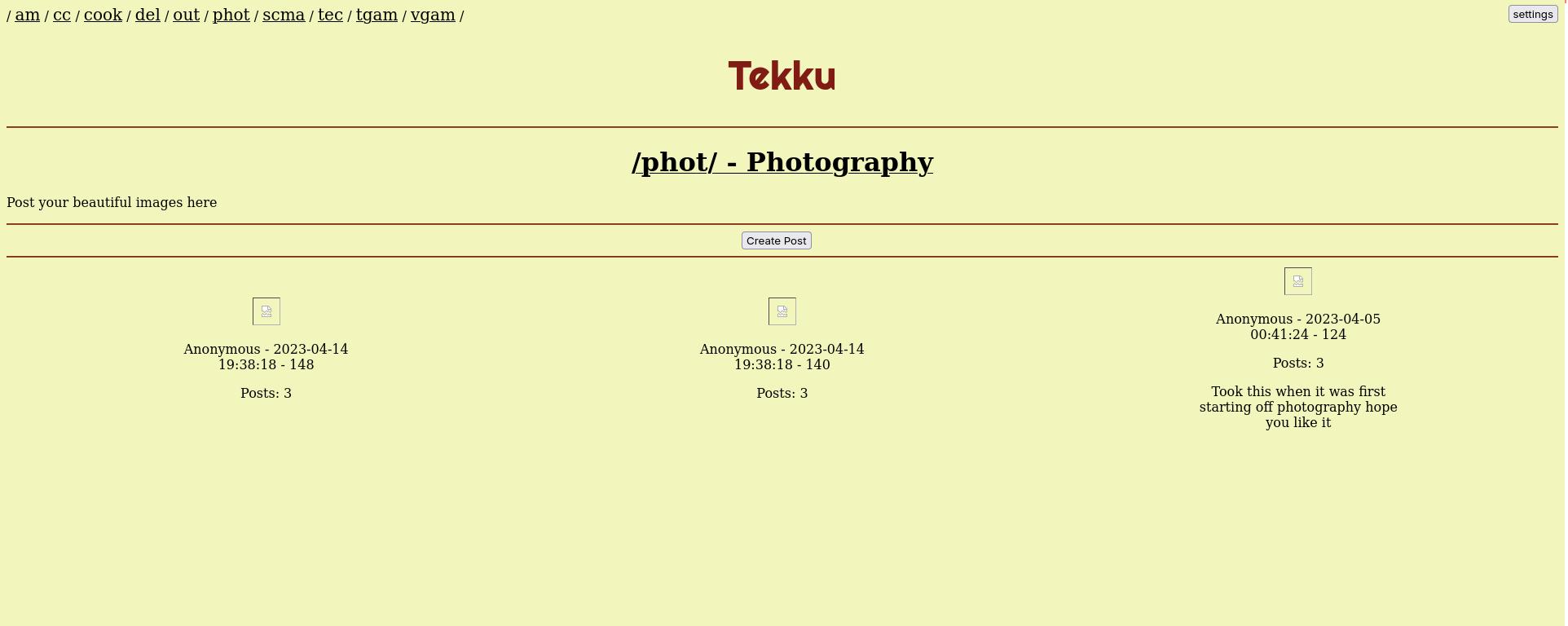
Tekku is an image board/forum in the vein of late 90’s and early 2000’s websites. Users can access topic boards to discuss those various topics by creating main posts, or by commenting on one of the already existing main posts on that board. At any given time there can only be 100 main posts actively being used with posts that have more interaction are pushed to the top while posts with little interaction are pushed to the bottom, and new posts being put at the very top on the front page. Another feature of our site is the ability to interact with posts without the need for an account. We believe that it isn’t necessary for a user to have an account just to do basic things on a website. Users can create an account if they wish to.
This was originally created as a school project, intended to run on school servers. However, it can be run locally with Docker. Here are the steps to run it locally:
- Ensure that you have Docker and Docker Compose installed. If you don't, you can download them from Docker's website.
- Clone the repository:
git clone git@github.com:Enprogames/Tekku.git - Change into the directory:
cd Tekku - Copy the
.env.examplefile to.env:cp .env.example .env- This file contains the environment variables for the PHP server. It should look something like this:
DB_HOST=marie # DB_HOST='127.0.0.1' DB_PORT=3306 DB_USER=csci311h DB_PASS=rAnhgtHT DB_NAME=csci311h_tekku PHRASE=tekku DB_ROOT_PASS=falter-hale-myrmidon-sequin DEBUG=true # file upload settings USER_POST_IMAGE_DIR=user_posted_images MAX_FILE_SIZE_BYTES=5000000 # 3 MB VALID_IMAGE_TYPES=jpeg png jpg gif
- Start the containers:
docker-compose up --build -d- This will start the Apache server and the MySQL server.
- Navigate to
localhostin your web browser. You should see the Tekku homepage.
- All user input is escaped with special HTML codes.
- Prepared statements are used throughout the entire site.
- Can change username, password, profile picture, and profile description.
- A user profile page shows all information about a user, as well as what posts they have made.
- Profile pictures are also visible on other parts of the site.
- All passwords are hashed, salted, and peppered.
- Users can create posts, create comments on other posts, and reply to posts. When replying, a link to the original comment is visible and can be clicked to navigate back to it.
- Admin users can delete posts. Deleting a post will delete all comments associated with it. Individual comments can also be deleted.
❗csci311h. See our assignment submission for the credentials of this account.
- Navigate to the home page.
- Go to “Cooking” board.
- Select “Create Post”.
- Type a message in the body and click “Post”. Observe the “No file attached” error message.
- To fix this, type a message in the body. Choose an image from your computer by selecting “browse”. Finally, add an interesting title. Click “Post”.
- After being redirected to the post page, comment on your post. Select “Create Post”. Enter content in the “Body” text box. Select “Post”.
- After your new comment appears, select “reply”. Type in content for this new reply comment. Click “Post”.
- Click the link to your original comment in your new “reply” comment. It should start with the “@” sign. Notice that the address bar now points to a bookmark for your previous comment.
- Navigate back to the main “Cooking” board page. Observe that your original post will be shown.
- Navigate to the home page.
- In the top right, hover over “settings”. In the dropdown menu, select “Log In”.
- Type in “rick” for your username, and “123” as your password. Click ”Log in”. Observe the “Login Failed” error message.
- To fix this, select “Create account”. Enter the username “rick” and the password “123”. Leave the email field blank. Select “Create Account”. After being navigated back to the login page, observe the “Account creation successful!” message.
- Enter the credentials for your newly created account. Select “Log in”. Observe the “Login Success” message.
- Navigate to the “Technology” board. Select “Create Post”. Enter a title, content, and select an image by selecting “Browse…”. Select “Post”.
- After seeing the success message and being redirected to your newly created post, observe that it displays your chosen username.
- Navigate back to the “Technology” board and observe that your username is also shown here on your newly created post.
- Navigate to the home page.
- Hover over the settings button in the top right, and select ‘Log In.’
- From the login page select, ‘Create account.’
- From the create account page, insert your user name, password, and email. Then select ‘Create Account.’ You will be brought back to the login page.
- Insert the username and password of the account you created, and click ‘Log in.’
- You are now logged in.
- In the top right, hover over the settings button and select “Account Settings”.
- Enter a new username and select “Change username”.
- Enter a new password and select “Change password”. Observe that you are logged out and sent back to the login page.
- Login with your newly changed credentials.
- Navigate back to the account settings page as before.
- Change your profile picture by selecting “Browse…” under the “Profile picture” section. Select an image, then select “Change profile picture”. Observe that you now have a profile picture.
- Add a profile description in the text box under the “Profile description” section. After it is entered, select “Change profile description”.
- In the top right, hover over the settings button and select “Profile”.
- Observe that all details of your profile are now visible on your profile. Copy the link to your profile page.
- Logout by hovering over “settings” in the top right and selecting “Log Out”.
- Paste the address that was copied in a previous step into the address bar. Press enter.
- Observe that you can view your user profile without being logged in.
Note: This account is only an admin for the “delete me” board, it cannot delete posts or comments from other boards.
- Navigate to the home page.
- In the top right, hover over “settings”. In the dropdown menu, select “Log In”.
- Login using the credentials: username: “admin”, password: “admin”. Select “Log in”.
- Navigate to “delete me” board.
- Select a post
- Look at the comments, press the “Delete Comment” button on the upper right hand corner of a comment. Observe that this comment is removed.
- Scroll back up to the main post, press the “Delete Post” button in the upper right hand corner. Observe that when you are redirected, the post has been removed and there is a red comment that reads “POST DELETED” in the upper left hand corner of the screen.
We created this guide to help us with our development. Nothing beyond this point is strictly relevant to our project, so feel free to skip it.
Please ensure that all changes are done on forks, and that any changes to the upstream repo are made through merge requests. This ensures that new code is reviewed by others, and that we don't accidentally destroy each other's work (git is hard to get right!).
Here is what it should look like when you make changes:
- Send a message in the group chat saying what you are going to start working on!
- Make sure you are currently up to date with the upstream repository:
git pull upstream main --rebase - Optionally, for even better code management (especially when working on multiple features at the same time), start your work from a new branch:
git checkout -b my-feature- Change back and forth with
git checkout mainandgit checkout my-feature
- Change back and forth with
- Write code
- Make a commit with a detailed message:
git add <files to commit> && git commit -m "detailed message" - Make sure you're up to date again:
git pull upstream main --rebase - Go to your fork on the Gitlab webpage, create a merge request for your branch into upstream main, write a detailed message for it, and publish the merge request.
- Let another team member know about your merge request, then make any changes as necessary.
- Any new commits pushed to the same branch will automatically be put into the merge request while it's open.
- To change the last commit (if a small mistake was made and an entirely new commit isn't necessary), make your changes, stage them, then run
git amend --no-editto add your changes to the previous commit. You'll also have to do a force push after this withgit push origin <branch> -f, so make sure you know exactly what you're doing!
- If you run into issues at any point, check out this choose your own adventure for resolving issues with git: sethrobertson.github.io - On undoing, fixing, or removing commits in git.
- Youtube - Resolving merge conflicts.
Using SSH tunnels into your CSCI account, you can access the Gitlab repos and webpage from anywhere. I'm doing this so that I can have my own setup away from the CSCI computers, since they cause me constant issues, such as with my quota. Here's how I do it.
ssh -N -L 127.0.0.1:8080:gitlab.csci.viu.ca:80 exstu@pup10.csci.viu.ca -J exstu@csci.viu.ca- Access
127.0.0.1:8080in your web browser.
- Put your Gitlab SSH key in your
~/.sshdirectory in your personal machine. - Add your ssh key to your ssh agent e.g.
eval $(ssh-agent) && ssh-add ~/.ssh/gitlab-ed25519 - Setup tunnel with proxyjump to pup server:
ssh -N -L 127.0.0.1:22:gitlab.csci.viu.ca:22 exstu@pup10.csci.viu.ca -J exstu@csci.viu.ca
Now you can do normal git commands, but you have to use 127.0.0.1 to access them. For example, cloning a repo:
git clone git@127.0.0.1:<username>/tekku.git- Add remote to upstream:
git remote add git@127.0.0.1:oleander/tekku.git
- Start SSH tunnel to your CSCI account: `$ ssh -N -L 8080:wwwstu.csci.viu.ca:80 exstu@pup10.csci.viu.ca -J exstu@csci.viu.ca
- In browser, go to http://localhost:8080/~exstu/csci311/tekku/
- Copy
.env.exampleas.env. - Edit
.envwith database connection details - If necessary, start SSH tunnel to database.
- Test the server by visiting one of its pages.
- Connect to a school server e.g. pup10:
ssh -J exstu@otter.csci.viu.ca exstu@pup10.csci.viu.ca - Connect to shared account with pup10 as proxy:
ssh -J csci311h@dolphin.csci.viu.ca pup10
Now that you're connected, you should be able to access the database with the following command:
mysql -h marie -u csci311h -p
ssh -N -L 127.0.0.1:3306:dolphin.csci.viu.ca:3306 csci311h@otter.csci.viu.ca- Now it should be accessible through localhost, since 127.0.0.1 is the IPv4 localhost address. This means that you can access it as if the database is running on your own computer.
- Start containers:
docker-compose up --build -d - Start an SSH tunnel to the MySQL server:
docker-compose exec tekku_php_apache ssh -N -L 127.0.0.1:3306:marie.csci.viu.ca:3306 csci311h@csci.viu.ca - Visit a webpage. Type
localhostinto your browser.
- Bring down the containers:
docker-compose down
`mysqldump --single-trnsaction -ucsci311h -hmarie csci311h_tekku -p > backup.sql
For an example CSCI student with the username "exstu":
$ ssh exstu@wwwstu.csci.viu.ca
- if prompted to continue connecting, type 'yes' and press enter
- Note: you will not get a bash prompt on the web server.
Instead a custom script is run remotely the gathers all the relevant log entries and presents them in the output.
The output will look similar to the following
------------------------------------------------------------
Linux dolphin 4.9.0-16-amd64 #1 SMP Debian 4.9.272-2 (2021-07-19) x86_64
The programs included with the Debian GNU/Linux system are free software;
the exact distribution terms for each program are described in the
individual files in /usr/share/doc/*/copyright.
Debian GNU/Linux comes with ABSOLUTELY NO WARRANTY, to the extent
permitted by applicable law.
Last login: Thu Jan 20 12:45:25 2022 from 192.168.18.156
********************
**** access.log ****
********************
********************
**** error.log ****
********************
********************
**** suexec.log ****
********************
********************
**** suphp.log ****
********************
Connection to wwwstu.csci.viu.ca closed.
------------------------------------------------------------
If there are any log entries related to accessing any files in the "public_html" folder for the student those entries
will be included in the output under the appropriate header.
In the above the example student has no recent log entries so each log file section is empty.
HEAD- The current commit. The tip of the current branch.Working tree- The files in your local directory.Staging area- The files that are staged for the next commit.Commit- A snapshot of the working tree and staging area.Branch- A pointer to a commit. The default branch ismain.Remote- A pointer to a remote repository.
git log --oneline --graph --decorate- Show a nice graph of the commit history.git rev-list --count HEAD- Show the number of commits in the current branch.git rev-parse --short HEAD- Show the short hash of the current commit.git log upstream/main..HEAD --oneline --no-merges- Show the commits that are on the current branch but not on theupstream/mainbranch.git rev-list --count upstream/main..HEAD- Show the number of commits that are on the current branch but not on theupstream/mainbranch.
git diff --name-only HEAD~1- Show the files that have changed in the last commit.git diff --name-only HEAD~1 HEAD~2- Show the files that have changed between two commits.git diff --name-only HEAD~1 HEAD~2 --diff-filter=A- Show the files that have been added between two commits.git diff --name-only HEAD~1 HEAD~2 --diff-filter=D- Show the files that have been deleted between two commits.
Bring over exact changes into unstaged area without creating merge commit (source)
After we had issues where Nick would make changes and have a messed up set of commits (for unknown reasons), I thought it might be useful to just see what changes he made and possibly put them into one commit. Here is a set of steps for achieving this.
# We will put our changes into this branch. The goal is to bring over new changes from
# a feature branch, inspect the changes to ensure they are correct, possibly make some changes,
# then bundle all changes into a single commit without creating a merge commit.
git checkout new-branch
# You have been working on "feature-branch" and your commit history has gotten messed up.
# Bring over the changes from "feature-branch" into "new-branch" without creating a merge commit.
git merge feature-branch --no-commit --no-ff
# Now you can inspect the changes and make any necessary changes.
# Once you are satisfied with the changes, you can bundle them into a single commit.
git add .
git commit -m "A message describing the changes"
# After doing the merge, git has recorded that a merge took place, and according to people online,
# this is the only way to stop git from creating a merge commit. I don't know why this is necessary, but it is.
rm .git/MERGE_HEAD
# Now you can push your changes to the remote repository.
git push origin new-branch