IoT Hub D2C Event to Twin Reported Properties Synchronisation
This repository contains an Azure Function that simplifies synchronisation of transient and persistent state data for Azure IoT Hub devices. It is licensed under Apache License 2.0.
Microsoft Azure IoT Hub supports several types of messages. Most commonly used one are device-to-cloud (D2C) messages that take form of events. These are transient and largely non-persistent. D2C messages are the most commonly used ones and easiest to generate. They can be sent via IoT Hub REST API with ease and are the types of messages most OOB systems are likely to support. In addition to the D2C messages, IoT Hub supports persistent state information in the form of device twins. Device twin represents a persistent state of arbitrary properties subdivided into two categories:
- Desired properties - there are set by the cloud (consumer) and are typically used by the device to change its operation - for example, polling rate, operating mode etc. Desired properties allow device operation to be dynamically controlled without changing its code.
- Reported properties - these are set by the device and provide its state information that can be read by any consumer on demand without having to wait for the next D2C event.
Device twin properties take more steps to synchronise correctly and typically require full Azure Device Client SDK to do. Thus a lot of OOB IoT Hub solutions forgo these. The purpose of this function is to work around this limitation by mirroring IoT Hub D2C events into its reported properties. It does this by monitoring incoming messages via standard ServiceHub queue exposed by the IoT hub and updating twin data if a given message contains UpdateTwin property.
To use this function, please start by updating your IoT Hub with a new consumer group called eventtotwinfunction as per Microsoft instructions
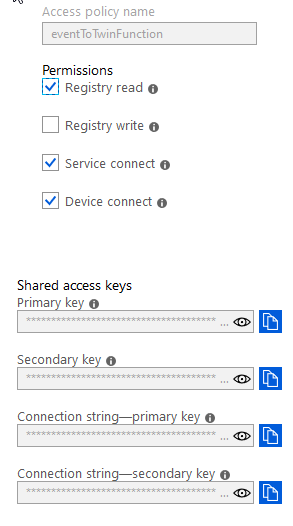
You will then need to make a note of your azure IoT Hub connection string as well as its EventHub endpoint URI. It is recommended to create a new access policy for the purposes of this function. The policy will need to have Registry Read, Service Connect and Device Connect policies. Its name is not restricted and can be anything sensible:
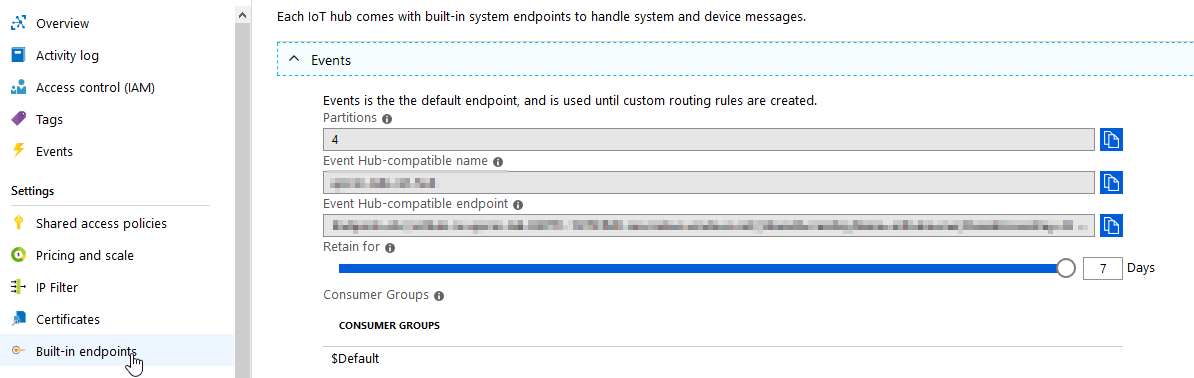
EventHub connection string can be obtained by going to the Built-in endpoints tab of the IoT Hub management page on azure portal:
By default the Event Hub connection string uses iothubowner access policy. This can be changed by replacing SharedAccessKeyName and SharedAccessKey parts of the connection string with those from the shared access policy you have created earlier and is the recommended approach to prevent use of iothubowner key.
Access keys need to be supplied to the function once it is deployed:
| Function setting name | Type | Format |
|---|---|---|
| IoTHubConnectionString | IoT Hub Connection String | HostName=HUBNAME.azure-devices.net;SharedAccessKeyName=ACCESS_POLICY;SharedAccessKey=KEY |
| IoTHubEventHubConnectionString | Event Hub Connection String | Endpoint=sb://EVENT_HUB_ENDPOINT.servicebus.windows.net/;SharedAccessKeyName=ACCESS_POLICY;SharedAccessKey=KEY;EntityPath=HUBNAME |
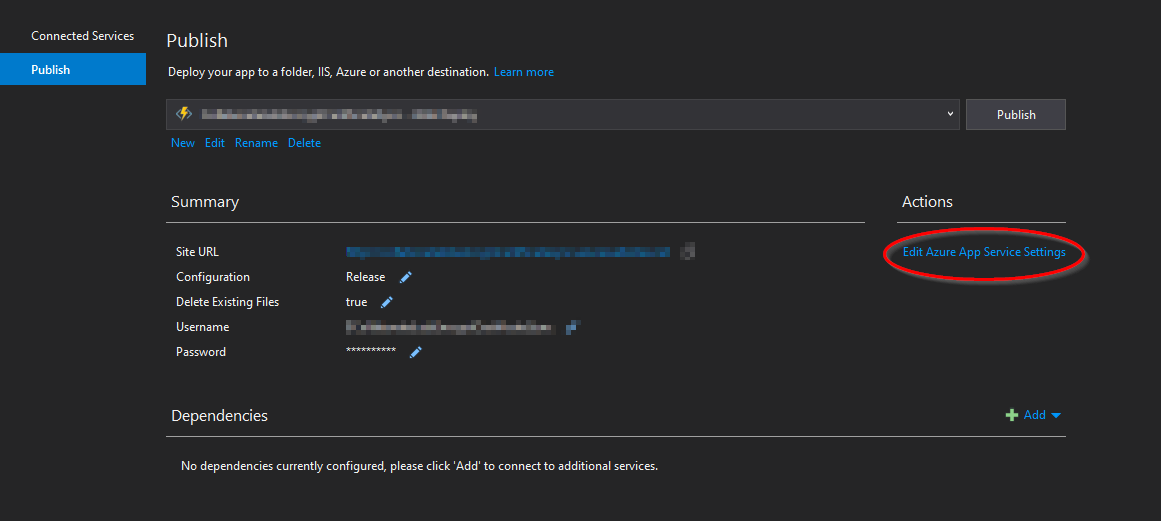
Load the function source code in Visual Studio and deploy to Azure as per Microsoft instructions. During deployment, please specify the relevant settings above. This can be done by clicking the corresponding buttons on the publish dialogue:
To test that the function works correctly, send IoT Event with property of UpdateTwin. This can be done by either defining event properties directly on the message when using DeviceClient SDK, appending /UpdateTwin=true to MQTT topic, or, if using REST API, by adding header iothub-app-UpdateTwin (its value doesn't matter). You can follow this article for instructions. REST API current details are available here.
If everything has been setup correctly, then device twin reported properties should contain values from the D2C message.