-
Unix based system (Windows is heterodoxy!!!)
-
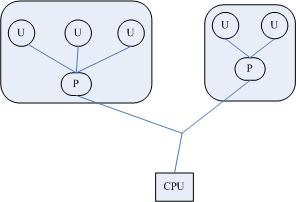
Process: built system call; generally for applications; sepserte address space; resource allocator;
-
Thread: instructions that are executed within the context of a pocess; initial thread & secondary thread;
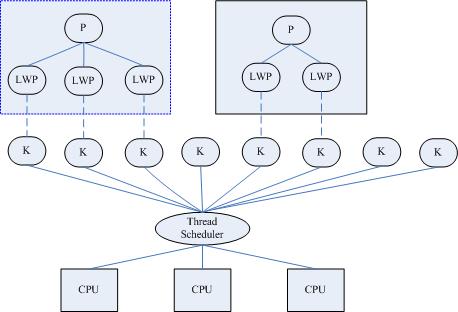
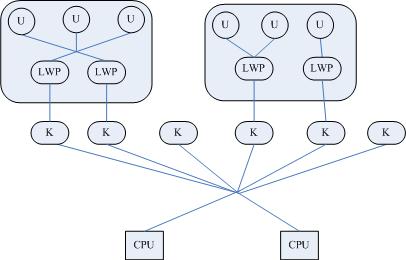
- User-level thread: utilize context switch; manage by user;
-
Kernel thread: utilize parallel resource; manage by kernel;
-
Light weight process: high level abstraction of kernel thread
- Hybrid:
We would use user level multi-threading for most of the time since we are not system programmers... However, using POSIX Thread for multi-threading program would give us kernel level multi-threading on LINUX(using NPTL(Native POSIX Thread Library, RedHat) && kernel 2.6 or leater).
This is a historical problem, the history goes like this...
- LINUX
- Multi-Processing
- Light-Weight Process -> kernel thread
- NPTL 1:1 model
Generally, as a high level programmer, we don't care the thread type as long as it beheaves like a thread.
int pthread_create (pthread_t *thread,
pthread_attr_t *attr,
void *(*start_routine)(void *),
void *arg)void pthread_exit (void *retval)int pthread_join(pthread_t threadid,
void **value_ptr)int pthread_detach(pthread_t);int pthread_attr_init(pthread_attr_t *);int pthread_attr_setdetachstate(pthread_attr_t *, int);// pthread1.c
#include <pthread.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#define NUM_THREADS 5
void *HelloThread(void *threadid);
int main(int argc, char *argv[]) {
// Define the thread identifier, pthread_t is basically int(unsigned int)
pthread_t threads[NUM_THREADS];
int rc;
long t;
for(t=0; t<NUM_THREADS; t++) {
printf("In main: creating thread %ld\n", t);
// The creating of a thread, return error code
rc = pthread_create(&threads[t], NULL, HelloThread, (void *)&t);
if (rc) {
printf("ERROR; return code from pthread_create() is %d\n", rc);
exit(-1);
}
}
// wait for the end of other threads
pthread_exit(NULL);
}
// Prototype function for a thread, notice void * basically could be anything's address
void *HelloThread(void *threadid) {
long* tid;
tid = (long*)threadid;
printf("Hello World! This is thread #%ld!\n", *tid);
printf("Hello from thread id #%ld\n", (long int)pthread_self());
// Exit thread
pthread_exit(NULL);
}Try to run the following comand to run the program and understand the basic structure for PThread program.
$ gcc -Wall pthread1.c -lpthread -o pthread1
$ ./pthread1
In main: creating thread 0
In main: creating thread 1
Hello World! This is thread #1!
Hello World! This is thread #2!
Hello from thread id #123145314553856
In main: creating thread 2
Hello from thread id #123145315090432
In main: creating thread 3
Hello World! This is thread #3!
Hello from thread id #123145315627008
In main: creating thread 4
Hello World! This is thread #4!
Hello from thread id #123145316163584
Hello World! This is thread #5!
Hello from thread id #123145316700160Now, let's try a more complicated example.
practice
// pthread2_practice.c
#include <pthread.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#define NUM_THREADS 8
// use struct instead of malloc !!!
struct thread_data {
int thread_id;
int sum;
char *message;
};
struct thread_data thread_data_array[NUM_THREADS];
void *PrintHello(void *threadarg) {
/* Fill your code here */
pthread_exit(NULL);
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[]) {
pthread_t threads[NUM_THREADS];
char *messages[NUM_THREADS];
int *taskids[NUM_THREADS];
int rc, t, sum;
sum=0;
messages[0] = "English: Hello World!";
messages[1] = "French: Bonjour, le monde!";
messages[2] = "Spanish: Hola al mundo";
messages[3] = "Klingon: Nuq neH!";
messages[4] = "German: Guten Tag, Welt!";
messages[5] = "Russian: Zdravstvytye, mir!";
messages[6] = "Japan: Sekai e konnichiwa!";
messages[7] = "Latin: Orbis, te saluto!";
for(t=0;t<NUM_THREADS;t++) {
/* Fill your code here */
if (rc) {
printf("ERROR; return code from pthread_create() is %d\n", rc);
exit(-1);
}
}
pthread_exit(NULL);
}Thread status: joining | detaching
Explit detach type declearation
- Declare a pthread attribute variable of the pthread_attr_t data type
- Initialize the attribute variable with pthread_attr_init()
- Set the attribute detached status with pthread_attr_setdetachstate()
- When done, free library resources used by the attribute with pthread_attr_destroy()
// pthread3.c
#include<stdlib.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <math.h>
#define NUM_THREADS 4
void *BusyWork(void *t){
int i;
long tid;
double result=0.0;
tid = (long)t;
printf("Thread %ld starting...\n",tid);
for (i=0; i<1000000; i++) {
result = result + sin(i) * tan(i);
}
printf("Thread %ld done. Result = %e\n",tid, result);
pthread_exit((void*) t);
}
int main (int argc, char *argv[]) {
pthread_t thread[NUM_THREADS];
pthread_attr_t attr;
int rc;
long t;
void *status;
/* Initialize and set thread detached attribute */
pthread_attr_init(&attr);
pthread_attr_setdetachstate(&attr, PTHREAD_CREATE_JOINABLE);
for(t=0; t<NUM_THREADS; t++) {
printf("Main: creating thread %ld\n", t);
rc = pthread_create(&thread[t], &attr, BusyWork, (void *)t);
if (rc) {
printf("ERROR; return code from pthread_create() is %d\n", rc);
exit(-1);
}
}
/* Free attribute and wait for the other threads */
pthread_attr_destroy(&attr);
for(t=0; t<NUM_THREADS; t++) {
// join the secondary thread with the main thread
rc = pthread_join(thread[t], &status);
if (rc) {
printf("ERROR; return code from pthread_join() is %d\n", rc);
exit(-1);
}
printf("Main: completed join with thread %ld having a status of %ld\n",t,(long)status);
}
printf("Main: program completed. Exiting.\n");
pthread_exit(NULL);
}- Mutex Lock(MUTual-EXclude Lock)
- RW Lock(Reader-Writter Lock)
- Spin Lock
- Pthread Condition
- Semaphore
- Barrier
Mutex Lock
Related marco and function
// pthread_mutex_practice.c
// default static mutex lock initializer
// For example: static pthread_mutex_t mutex = PTHREAD_MUTEX_INITIALIZER;
PTHREAD_MUTEX_INITIALIZER
// dynamic initialization
int pthread_mutex_init(pthread_mutex_t *restrict mutex,
const pthread_mutexattr_t *restrict attr);
// destroy the lock and release the resource
int pthread_mutex_destroy(pthread_mutex_t *mutex);
// request lock; locked ? (hang up; lock success) : lock success
int pthread_mutex_lock(pthread_mutex_t *mutex);
// request unlock
int pthread_mutex_unlock(pthread_mutex_t *mutex);
// request lock; locked ? return directly : lock success
int pthread_mutex_trylock(pthread_mutex_t *mutex); Initialization: Marco or Function?
Feature: R/W frequency, critical section
DeadLock
RW Lock
Related marco and function
// pthread_rwlock.c
PTHREAD_RWLOCK_INITIALIZER
int pthread_rwlock_init(pthread_rwlock_t *restrict rwlock,
const pthread_rwlockattr_t *restrict attr);
int pthread_rwlock_destroy(pthread_rwlock_t *rwlock);
int pthread_rwlock_rdlock(pthread_rwlock_t *rwlock);
int pthread_rwlock_tryrdlock(pthread_rwlock_t *rwlock);
int pthread_rwlock_wrlock(pthread_rwlock_t *rwlock);
int pthread_rwlock_trywrlock(pthread_rwlock_t *rwlock);
int pthread_rwlock_unlock(pthread_rwlock_t *rwlock);RW Priority - hungry thread
Spin Lock (actually not a lock but more like a mechanism)
- context switch cost
- CPU time cost
Related marco and function
// A spin lock is like a mutex, except that instead of blocking a process by sleeping, the // process is blocked by busy-waiting (spinning) until the lock can be acquired.
/////////////////////////////pthread_src/sysdeps/posix/pt-spin.c
/* Lock the spin lock object LOCK. If the lock is held by another
thread spin until it becomes available. */
int _pthread_spin_lock (__pthread_spinlock_t *lock)
{
int i;
while (1)
{
for (i = 0; i < __pthread_spin_count; i++)
{
if (__pthread_spin_trylock (lock) == 0)
return 0;
}
__sched_yield ();
}
}////////////////////////////////pthread_src/pthread/pt-spin-inlines.c
/* Weak aliases for the spin lock functions. Note that
pthread_spin_lock is left out deliberately. We already provide an
implementation for it in pt-spin.c. */
weak_alias (__pthread_spin_destroy, pthread_spin_destroy);
weak_alias (__pthread_spin_init, pthread_spin_init);
weak_alias (__pthread_spin_trylock, pthread_spin_trylock);
weak_alias (__pthread_spin_unlock, pthread_spin_unlock);
/////////////////////////////////pthread_src/sysdeps/posix/pt-spin.c
weak_alias (_pthread_spin_lock, pthread_spin_lock);
/*-------------------------------------------------*/
PTHREAD_SPINLOCK_INITIALIZER
int pthread_spin_init (__pthread_spinlock_t *__lock, int __pshared);
int pthread_spin_destroy (__pthread_spinlock_t *__lock);
int pthread_spin_trylock (__pthread_spinlock_t *__lock);
int pthread_spin_unlock (__pthread_spinlock_t *__lock);
int pthread_spin_lock (__pthread_spinlock_t *__lock);
/*-------------------------------------------------*/Pthread Condition Variables
Extend of pthread_join; Volatile + loop could do the same thing but....
Related marco and function
// pthread_cond.c
PTHREAD_COND_INITIALIZER
int pthread_cond_init(pthread_cond_t *restrict cond,
const pthread_condattr_t *restrict attr);
int pthread_cond_destroy(pthread_cond_t *cond);
// origionally designed for one thread, could be used on multiple but broadcase is proper.
int pthread_cond_signal(pthread_cond_t *cond);
int pthread_cond_broadcast(pthread_cond_t *cond);
int pthread_cond_wait(pthread_cond_t *restrict cond, pthread_mutex_t *restrict mutex);
int pthread_cond_timedwait(pthread_cond_t *restrict cond,
pthread_mutex_t *restrict mutex,
const struct timespec *restrict abstime);Use this with mutex lock !!!
Why?
void thread_waiting_for_condition_signal ()
{
pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex);
while (operation_queue == NULL) {
pthread_cond_wait(&condition_variable_signal, &mutex);
}
/*********************************/
/* operation_queue related stuff */
/*********************************/
pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex);
}
void thread_prepare_queue ()
{
pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex);
/*********************************/
/* operation_queue related stuff */
/*********************************/
// Tell the wait thread we have done
pthread_cond_signal(&condition_variable_signal);
pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex);
/**************************/
/* Other instructions */
/**************************/
...
pthread_exit((void *) 0);
}Semaphore (Actually a process management mechanism)
Recall
- competiting relation
- critical section
- Mutex
- Progress
- Bounded waiting (No hungry)
Related marco and function
// pthread_smi.c
int sem_destroy(sem_t *sem);
int sem_init(sem_t *sem, int pshared, unsigned int value);
// if sempahore is enough,then semaphore -1 and enter critical section
int sem_wait(sem_t *sem);
// Add semphore by 1,release one resource
int sem_post(sem_t *sem);
int sem_getvalue(sem_t *sem, int *valp); Banker's algorithm
- Solve sequence locking fail problem (dead lock)
Barrier
Related marco and function
// pthread_barrier.c
int pthread_barrier_init(pthread_barrier_t *barrier,
const pthread_barrierattr_t *restrict attr,
unsigned count);
int pthread_barrier_destroy(pthread_barrier_t *barrier);
int pthread_barrier_wait(pthread_barrier_t *barrier);Milestone
compare with pthread_condition pthread_join
For huge amount and high frequency jobs.
producer - consumer model
- mutex
- producer don't produce when full
- consumer don't consume when empty
Work queue -> heavy load
https://casatwy.com/pthreadde-ge-chong-tong-bu-ji-zhi.html