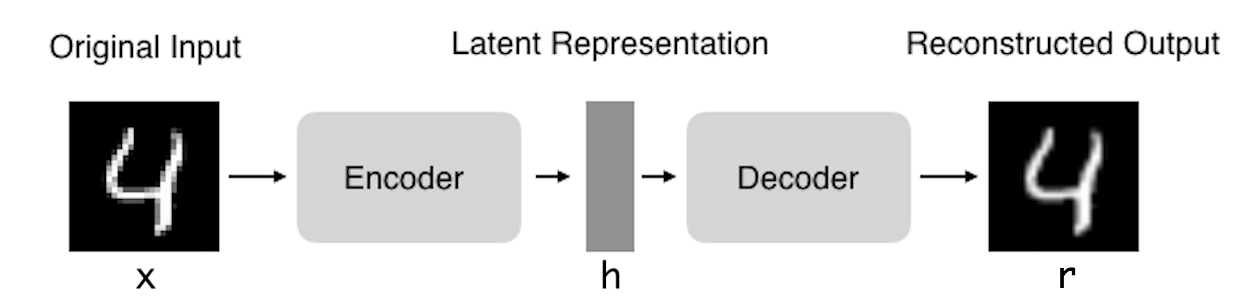
Autoencoders (AE) are neural networks that aims to copy their inputs to their outputs. They work by compressing the input into a latent-space representation, and then reconstructing the output from this representation. This kind of network is composed of two parts :
- Encoder: This is the part of the network that compresses the input into a latent-space representation. It can be represented by an encoding function h=f(x).
- Decoder: This part aims to reconstruct the input from the latent space representation. It can be represented by a decoding function r=g(h).
This notebook show the implementation of five types of autoencoders :
- Vanilla Autoencoder
- Multilayer Autoencoder
- Convolutional Autoencoder
- Regularized Autoencoder
- Variational Autoencoder
The explanation of each (except VAE) can be found here