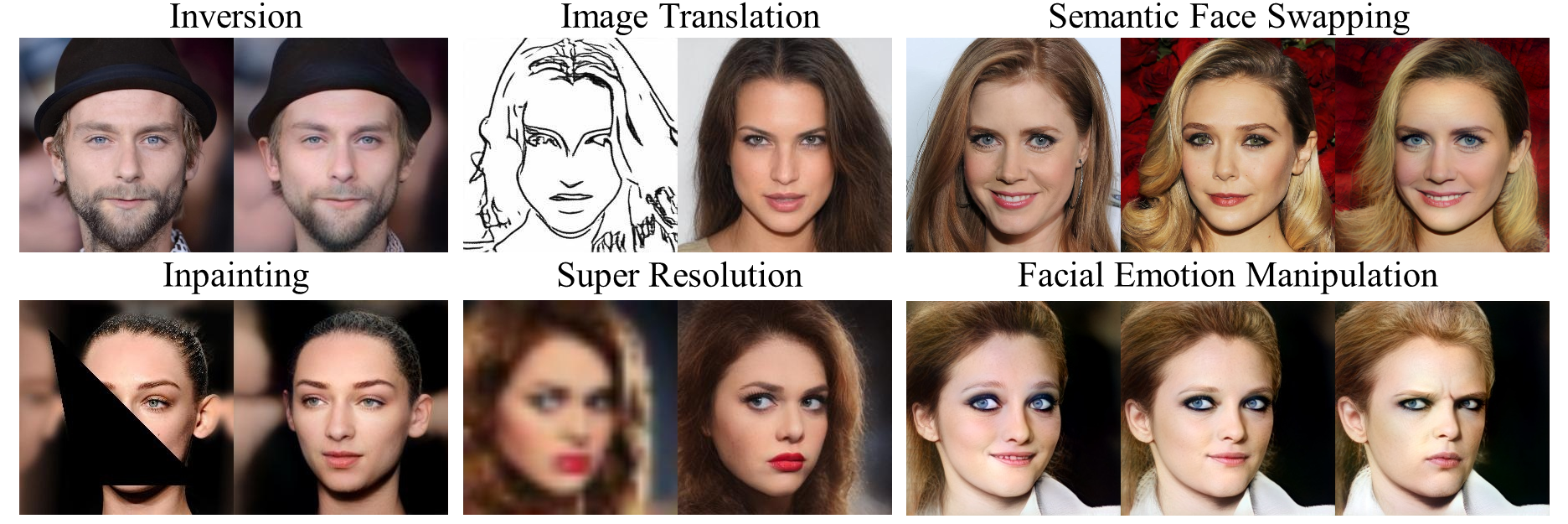
This repository hosts the official PyTorch implementation of the paper: "E2Style: Improve the Efficiency and Effectiveness of StyleGAN Inversion" (Accepted by TIP 2022), which was initially called "A Simple Baseline for StyleGAN Inversion".
Tianyi Wei1,
Dongdong Chen2,
Wenbo Zhou1,
Jing Liao3,
Weiming Zhang1,
Lu Yuan2,
Gang Hua4,
Nenghai Yu1
1University of Science and Technology of China, 2Microsoft Cloud AI
3City University of Hong Kong, 4Wormpex AI Research
2022.02.19: Initial code release
2022.03.26: The paper has been accepted by IEEE Transactions on Image Processing [TIP]! 🎉
$ conda install --yes -c pytorch pytorch=1.7.1 torchvision cudatoolkit=11.0
$ pip install matplotlib scipy opencv-python pillow scikit-image tqdm tensorflow-ioIf you want to run secure deep hiding, you need to install matlab engine.
Please download the pre-trained models from the following links. Each E2Style model contains the entire E2Style architecture, including the encoder and decoder weights.
| Path | Description |
|---|---|
| StyleGAN Inversion | E2Style trained with the FFHQ dataset for StyleGAN inversion. |
| Colorization | E2Style trained with the FFHQ dataset for colorization. |
| Denoise | E2Style trained with the FFHQ dataset for denoising. |
| Inpainting | E2Style trained with the FFHQ dataset for inpainting. |
| Super Resolution | E2Style trained with the CelebA-HQ dataset for super resolution (up to x32 down-sampling). |
| Sketch to Image | E2Style trained with the CelebA-HQ dataset for image synthesis from sketches. |
| Segmentation to Image | E2Style trained with the CelebAMask-HQ dataset for image synthesis from segmentation maps. |
If you wish to use one of the pretrained models for training or inference, you may do so using the flag --checkpoint_path.
In addition, we provide various auxiliary models needed for training your own E2Style model from scratch.
| Path | Description |
|---|---|
| FFHQ StyleGAN | StyleGAN model pretrained on FFHQ taken from rosinality with 1024x1024 output resolution. |
| IR-SE50 Model | Pretrained IR-SE50 model taken from TreB1eN for use in our multi ID loss during E2Style training. |
By default, we assume that all auxiliary models are downloaded and saved to the directory pretrained_models. However, you may use your own paths by changing the necessary values in configs/path_configs.py.
- Currently, we provide support for numerous datasets and experiments (encoding, denoise, etc.).
- Refer to
configs/paths_config.pyto define the necessary data paths and model paths for training and evaluation. - Refer to
configs/transforms_config.pyfor the transforms defined for each dataset/experiment. - Finally, refer to
configs/data_configs.pyfor the source/target data paths for the train and test sets as well as the transforms.
- Refer to
- If you wish to experiment with your own dataset, you can simply make the necessary adjustments in
data_configs.pyto define your data paths.transforms_configs.pyto define your own data transforms.
The main training script can be found in scripts/train.py.
Intermediate training results are saved to opts.exp_dir. This includes checkpoints, train outputs, and test outputs.
Additionally, if you have tensorboard installed, you can visualize tensorboard logs in opts.exp_dir/logs.
python scripts/train.py \
--dataset_type=ffhq_encode \
--exp_dir=/path/to/experiment \
--workers=4 \
--batch_size=4 \
--test_batch_size=4 \
--test_workers=4 \
--val_interval=5000 \
--save_interval=5000 \
--start_from_latent_avg \
--lpips_lambda=0.8 \
--l2_lambda=1 \
--id_lambda=0.5 \
--parse_lambda=1 \
--training_stage=1
python scripts/train.py \
--dataset_type=ffhq_encode \
--exp_dir=/path/to/experiment \
--checkpoint_path=/path/to/1-stage-inversion.pt \
--workers=4 \
--batch_size=4 \
--test_batch_size=4 \
--test_workers=4 \
--val_interval=5000 \
--save_interval=5000 \
--start_from_latent_avg \
--lpips_lambda=0.8 \
--l2_lambda=1 \
--id_lambda=0.5 \
--parse_lambda=1 \
--training_stage=2
python scripts/train.py \
--dataset_type=ffhq_encode \
--exp_dir=/path/to/experiment \
--checkpoint_path=/path/to/2-stage-inversion.pt \
--workers=4 \
--batch_size=4 \
--test_batch_size=4 \
--test_workers=4 \
--val_interval=5000 \
--save_interval=5000 \
--start_from_latent_avg \
--lpips_lambda=0.8 \
--l2_lambda=1 \
--id_lambda=0.5 \
--parse_lambda=1 \
--training_stage=3
python scripts/train.py \
--dataset_type=ffhq_colorization \
--exp_dir=/path/to/experiment \
--workers=4 \
--batch_size=4 \
--test_batch_size=4 \
--test_workers=4 \
--val_interval=5000 \
--save_interval=5000 \
--start_from_latent_avg \
--lpips_lambda=0.8 \
--l2_lambda=1 \
--id_lambda=0.5 \
--parse_lambda=1 \
python scripts/train.py \
--dataset_type=ffhq_denoise \
--exp_dir=/path/to/experiment \
--workers=4 \
--batch_size=4 \
--test_batch_size=4 \
--test_workers=4 \
--val_interval=5000 \
--save_interval=5000 \
--start_from_latent_avg \
--lpips_lambda=0.8 \
--l2_lambda=1 \
--id_lambda=0.5
--parse_lambda=1 \
python scripts/train.py \
--dataset_type=ffhq_inpainting \
--exp_dir=/path/to/experiment \
--workers=4 \
--batch_size=4 \
--test_batch_size=4 \
--test_workers=4 \
--val_interval=5000 \
--save_interval=5000 \
--start_from_latent_avg \
--lpips_lambda=0.8 \
--l2_lambda=1 \
--id_lambda=0.5
--parse_lambda=1 \
python scripts/train.py \
--dataset_type=celebs_sketch_to_face \
--exp_dir=/path/to/experiment \
--workers=4 \
--batch_size=4 \
--test_batch_size=4 \
--test_workers=4 \
--val_interval=5000 \
--save_interval=5000 \
--start_from_latent_avg \
--lpips_lambda=0.8 \
--l2_lambda=1 \
--id_lambda=0 \
--parse_lambda=1 \
--w_norm_lambda=0.005 \
--label_nc=1 \
--input_nc=1
python scripts/train.py \
--dataset_type=celebs_seg_to_face \
--exp_dir=/path/to/experiment \
--workers=4 \
--batch_size=4 \
--test_batch_size=4 \
--test_workers=4 \
--val_interval=5000 \
--save_interval=5000 \
--start_from_latent_avg \
--lpips_lambda=0.8 \
--l2_lambda=1 \
--id_lambda=0 \
--parse_lambda=1 \
--w_norm_lambda=0.005 \
--label_nc=19 \
--input_nc=19
python scripts/train.py \
--dataset_type=celebs_super_resolution \
--exp_dir=/path/to/experiment \
--workers=4 \
--batch_size=4 \
--test_batch_size=4 \
--test_workers=4 \
--val_interval=5000 \
--save_interval=5000 \
--start_from_latent_avg \
--lpips_lambda=0.8 \
--l2_lambda=1 \
--id_lambda=0.5 \
--parse_lambda=1 \
--w_norm_lambda=0.005 \
--resize_factors=1,2,4,8,16,32
- See
options/train_options.pyfor all training-specific flags. - See
options/test_options.pyfor all test-specific flags. - By default, we assume that the StyleGAN used outputs images at resolution
1024x1024. If you wish to use a StyleGAN at a smaller resolution, you can do so by using the flag--output_size(e.g.,--output_size=256). - If you wish to generate images from segmentation maps, please specify
--label_nc=Nand--input_nc=NwhereNis the number of semantic categories. - Similarly, for generating images from sketches, please specify
--label_nc=1and--input_nc=1. - Specifying
--label_nc=0(the default value), will directly use the RGB colors as input.
Having trained your model, you can use scripts/inference.py to apply the model on a set of images.
For example,
python scripts/inference.py \
--exp_dir=/path/to/experiment \
--checkpoint_path=experiment/checkpoints/best_model.pt \
--data_path=/path/to/test_data \
--test_batch_size=1 \
--test_workers=4 \
--stage=1 \
--save_inverted_codes \
--couple_outputs \
--resize_outputs
Additional notes to consider:
- During inference, the options used during training are loaded from the saved checkpoint and are then updated using the
test options passed to the inference script. For example, there is no need to pass
--dataset_typeor--label_ncto the inference script, as they are taken from the loadedopts. - Modifying
--stageto get the results of different stages, but be careful not to exceed the maximum stage of training. - When running inference for super-resolution, please provide a single down-sampling value using
--resize_factors. - Adding the flag
--couple_outputswill save an additional image containing the input and output images side-by-side in the sub-directoryinference_coupled. Otherwise, only the output image is saved to the sub-directoryinference_results. - Adding the flag
--save_inverted_codeswill save the inverted latent codes in the exp_dir. - By default, the images will be saved at resolutiosn of 1024x1024, the original output size of StyleGAN. If you wish to save
outputs resized to resolutions of 256x256, you can do so by adding the flag
--resize_outputs.
python scripts/secure_deep_hiding.py \
--exp_dir=/path/to/experiment \
--checkpoint_path=pretrained_models/inversion.pt \
--secret_dir=/path/to/secret_dir \
--cover_dir=/path/to/cover_dir \
python scripts/manipulate.py \
--exp_dir=/path/to/experiment \
--checkpoint_path=pretrained_models/inversion.pt \
--deriction_name=age \
--edited_dir=/path/to/edited_dir \
python scripts/stylemixing.py \
--exp_dir=/path/to/experiment \
--checkpoint_path=pretrained_models/inversion.pt \
--style_dir=/path/to/style_dir \
--content_dir=/path/to/content_dir \
python scripts/interpolate.py \
--exp_dir=/path/to/experiment \
--checkpoint_path=pretrained_models/inversion.pt \
--source_dir=/path/to/source_dir \
--target_dir=/path/to/target_dir \
Additional notes to consider:
- For Secure Deep Hiding, Semantic Editing, Style Mixing, Interpolation, you need to run the inversion first, and the latent codes and image names will be saved in the corresponding folders. Make sure to add the flag
--save_inverted_codeswhen you run the inversion.
This code is heavily based on pSp and idinvert.
If you find our work useful for your research, please consider citing the following papers :)
@article{wei2022e2style,
title={E2Style: Improve the Efficiency and Effectiveness of StyleGAN Inversion},
author={Wei, Tianyi and Chen, Dongdong and Zhou, Wenbo and Liao, Jing and Zhang, Weiming and Yuan, Lu and Hua, Gang and Yu, Nenghai},
journal={IEEE Transactions on Image Processing},
year={2022}
}