Organize ideas and collaborate using Markdown, a lightweight language for text formatting.
GitHub is about more than code. It’s a platform for software collaboration, and Markdown is one of the most important ways developers can make their communication clear and organized in issues and pull requests. This course will walk you through creating and using headings more effectively, organizing thoughts in bulleted lists, and showing how much work you’ve completed with checklists. You can even use Markdown to add some depth to your work with the help of emoji, images, and links.
- Who is this for: New developers, new GitHub users, and students.
- What you'll learn: Use Markdown to add lists, images, and links in a comment or text file.
- What you'll build: We'll update a plain text file and add Markdown formatting, and you can use this file to start your own GitHub Pages site.
- Prerequisites: In this course you will work with pull requests as well as edit files. If these things aren't familiar to you, we recommend you take the Introduction to GitHub course, first!
- How long: This course is five steps long and takes less than one hour to complete.
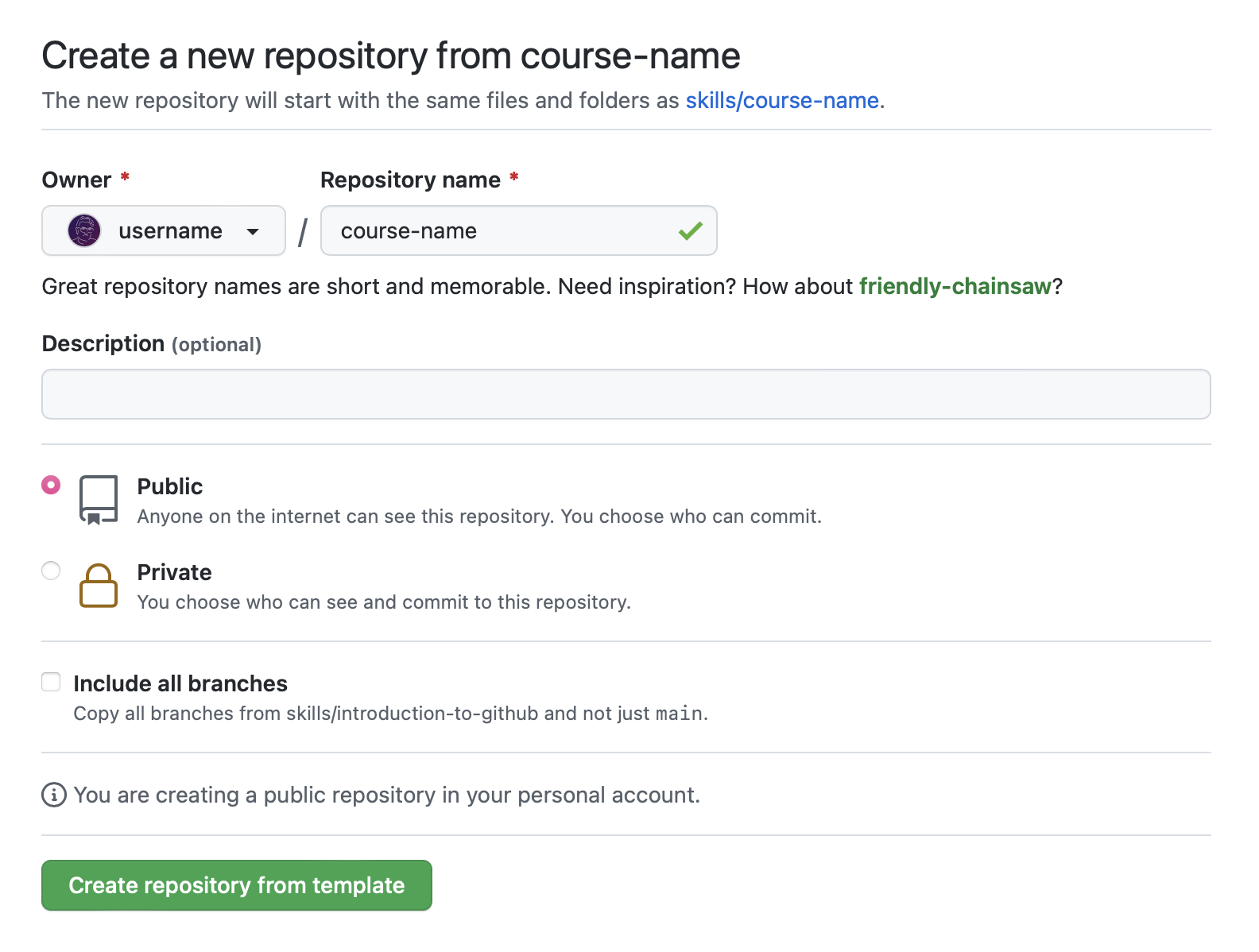
- Right-click Start course and open the link in a new tab.
- In the new tab, follow the prompts to create a new repository.
- For owner, choose your personal account or an organization to host the repository.
- We recommend creating a public repository—private repositories will use Actions minutes.
- After your new repository is created, wait about 20 seconds, then refresh the page. Follow the step-by-step instructions in the new repository's README.
Welcome to "Communicate using Markdown"! 👋
What is Markdown? Markdown is a lightweight syntax for communicating on GitHub. You can format text to add heading, lists, bold, italics, tables, and many other stylings. You can use Markdown most places around GitHub:
- Comments in issues, pull requests, and discussions
- Files with the
.mdor.markdownextension - Sharing snippets of text in Gists
What is a header? A header is a larger bit of text at the beginning of a section. There are six sizes.
# This is an `<h1>` header, which is the largest
## This is an `<h2>` header
###### This is an `<h6>` header, which is the smallest- Open a new browser tab, and work on the steps in your second tab while you read the instructions in this tab.
- Open the pull requests tab.
- Click New pull request, for the branches to compare, select
base: mainandcompare: start-markdown. - Click Create pull request.
- In this pull request, go to the Files changed tab. We made an empty file
index.mdfor you. - Select Edit file from the three dotted ... menu in the upper right corner of the file view on
index.md. - On the Edit file tab, add a
#, followed by a space, before any content you like to make it an H1 Header. You can add more headers, using one to six#characters followed by a space. - Above your new content, click Preview.
- Type a short, meaningful commit message that describes the change you made to the file.
- Select Commit directly to the start-markdown branch.
- Click Commit changes.
- Wait about 20 seconds then refresh this page for the next step.
Great job adding headers to the file ✨
Let's add an image. Include descriptive text in the square brackets. This text is read aloud for people using screen readers. It's also shown at times when your image doesn't display, such as when there's a poor connection. You can see the syntax for images below:

- As you did before, edit the
index.mdfile in this pull request. - In the file, add the correct Markdown for your image of choice. Don't forget to include alt-text!
- Use the Preview tab to check your Markdown formatting.
- Commit your changes.
- Wait about 20 seconds then refresh this page for the next step.
Great job adding an image to the file 🎉
In addition to code blocks, some code blocks should be rendered differently depending on the language, such as JavaScript or command-line text.
``` $ git init Initialized empty Git repository in /Users/skills/Projects/recipe-repository/.git/ ```
$ git init
Initialized empty Git repository in /Users/skills/Projects/recipe-repository/.git/
- As you did before, edit the file in this pull request.
- In the file, add the correct Markdown for a code example of your choice.
- Use the Preview tab to check your Markdown formatting.
- Commit your changes.
- Wait about 20 seconds then refresh this page for the next step.
Great job adding a code example to the file 🥳
What is a task list? A task list creates checkboxes to check off. They're very useful for tracking issues and pull requests. If you include a task list in the body of an issue or pull request, you'll see a progress indicator in your issue list. The syntax for task lists is very specific. Be sure to include the spaces where required, or else they won't render.
- [x] List syntax is required
- [x] This item is complete
- [ ] This item is not complete
- List syntax is required
- This item is complete
- This item is not complete
GitHub Actions went ahead and made a branch for you. So you'll need to add to the file we've created in the branch, and we will check your work as you work through this course!
-
Return to your pull request.
-
Use Markdown to create a task list. Here is an example:
- [ ] Turn on GitHub Pages - [ ] Outline my portfolio - [ ] Introduce myself to the world
Remember, a task list starts with the syntax
- [ ]and then the task list item. The formatting is specific! -
Use the Preview tab to check your Markdown formatting.
-
Commit the changes to the file.
-
Wait about 20 seconds then refresh this page for the next step.
Congratulations friend, you've completed this course!

Here's a recap of all the tasks you've accomplished in your repository:
- You learned about Markdown, headings, images, code examples, and task lists.
- You created and merged a Markdown file.
- You learned an essential GitHub skill. 🎉
- You can enable GitHub Pages and see your Markdown file as a website!
- Under your repository name at the upper right, click ⚙️ Settings.
- Then on the lower left, click Pages in the Code and automation section.
- In the GitHub Pages section, ensure "Deploy from a branch" is selected from the Source drop-down menu, and then select
mainfrom the Branch drop-down menu as your GitHub Pages publishing source. - Click the Save button.
- Wait about 30 seconds then refresh the page. When you see "Your site is published at ..." you can click on the link to see your published site.
- Learn more about Markdown.
- We'd love to hear what you thought of this course in our discussion board
- Take another GitHub Skills course.
- Read the GitHub Getting Started docs.
- To find projects to contribute to, check out GitHub Explore.
Get help: Post in our discussion board • Review the GitHub status page
© 2022 GitHub • Code of Conduct • MIT License

