👏 👏 👏 Check out video about the library: A full-featured 2D graphics library for Nim (NimConf 2021) 👏 👏 👏
Pixie is a 2D graphics library similar to Cairo and Skia written entirely in Nim.
This library is being actively developed and we'd be happy for you to use it.
nimble install pixie
- Pixie 5.0 performance improvements
- The details of JPEG decoding in Nim
- A full-featured 2D graphics library for Nim (NimConf 2021)
Features:
- Typesetting and rasterizing text, including styled rich text via spans.
- Drawing paths, shapes and curves with even-odd and non-zero windings.
- Pixel-perfect AA quality.
- Supported file formats are PNG, BMP, JPG, SVG + more in development.
- Strokes with joins and caps.
- Shadows, glows and blurs.
- Complex masking: Subtract, Intersect, Exclude.
- Complex blends: Darken, Multiply, Color Dodge, Hue, Luminosity... etc.
- Many operations are SIMD accelerated.
| Format | Read | Write |
|---|---|---|
| PNG | ✅ | ✅ |
| JPEG | ✅ | |
| BMP | ✅ | ✅ |
| QOI | ✅ | ✅ |
| GIF | ✅ | |
| SVG | ✅ | |
| PPM | ✅ | ✅ |
| Format | Read |
|---|---|
| TTF | ✅ |
| OTF | ✅ |
| SVG | ✅ |
Supported Caps:
- Butt
- Round
- Square
Supported Joins:
- Miter (with miter angle limit)
- Bevel
- Round
Supported Blend Modes:
- Normal
- Darken
- Multiply
- ColorBurn
- Lighten
- Screen
- Color Dodge
- Overlay
- Soft Light
- Hard Light
- Difference
- Exclusion
- Hue
- Saturation
- Color
- Luminosity
Supported Mask Modes:
- Mask
- Overwrite
- Subtract Mask
- Intersect Mask
- Exclude Mask
| Format | Supported | Description |
|---|---|---|
| M m | ✅ | move to |
| L l | ✅ | line to |
| H h | ✅ | horizontal line to |
| V v | ✅ | vertical line to |
| C c S s | ✅ | cubic curve to |
| Q q T t | ✅ | quadratic curve to |
| A a | ✅ | arc to |
| z | ✅ | close path |
To learn how to use Pixie for realtime graphics with GPU, check out Boxy.
nimble test
git clone https://github.com/treeform/pixie to run examples.
nim c -r examples/text.nim
var font = readFont("examples/data/Roboto-Regular_1.ttf")
font.size = 20
let text = "Typesetting is the arrangement and composition of text in graphic design and publishing in both digital and traditional medias."
image.fillText(font.typeset(text, vec2(180, 180)), translate(vec2(10, 10)))nim c -r examples/text_spans.nim
let typeface = readTypeface("examples/data/Ubuntu-Regular_1.ttf")
proc newFont(typeface: Typeface, size: float32, color: Color): Font =
result = newFont(typeface)
result.size = size
result.paint.color = color
let spans = @[
newSpan("verb [with object] ",
newFont(typeface, 12, color(0.78125, 0.78125, 0.78125, 1))),
newSpan("strallow\n", newFont(typeface, 36, color(0, 0, 0, 1))),
newSpan("\nstral·low\n", newFont(typeface, 13, color(0, 0.5, 0.953125, 1))),
newSpan("\n1. free (something) from restrictive restrictions \"the regulations are intended to strallow changes in public policy\" ",
newFont(typeface, 14, color(0.3125, 0.3125, 0.3125, 1)))
]
image.fillText(typeset(spans, vec2(180, 180)), translate(vec2(10, 10)))nim c -r examples/square.nim
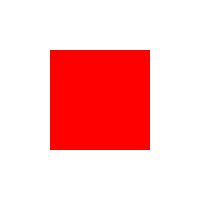
let ctx = newContext(image)
ctx.fillStyle = rgba(255, 0, 0, 255)
let
pos = vec2(50, 50)
wh = vec2(100, 100)
ctx.fillRect(rect(pos, wh))nim c -r examples/line.nim
let ctx = newContext(image)
ctx.strokeStyle = "#FF5C00"
ctx.lineWidth = 10
let
start = vec2(25, 25)
stop = vec2(175, 175)
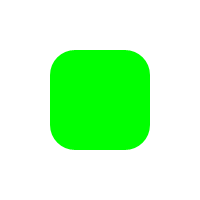
ctx.strokeSegment(segment(start, stop))nim c -r examples/rounded_rectangle.nim
let ctx = newContext(image)
ctx.fillStyle = rgba(0, 255, 0, 255)
let
pos = vec2(50, 50)
wh = vec2(100, 100)
r = 25.0
ctx.fillRoundedRect(rect(pos, wh), r)nim c -r examples/heart.nim
image.fillPath(
"""
M 20 60
A 40 40 90 0 1 100 60
A 40 40 90 0 1 180 60
Q 180 120 100 180
Q 20 120 20 60
z
""",
parseHtmlColor("#FC427B").rgba
)nim c -r examples/masking.nim
let ctx = newContext(lines)
ctx.strokeStyle = "#F8D1DD"
ctx.lineWidth = 30
ctx.strokeSegment(segment(vec2(25, 25), vec2(175, 175)))
ctx.strokeSegment(segment(vec2(25, 175), vec2(175, 25)))
mask.fillPath(
"""
M 20 60
A 40 40 90 0 1 100 60
A 40 40 90 0 1 180 60
Q 180 120 100 180
Q 20 120 20 60
z
""",
color(1, 1, 1, 1)
)
lines.draw(mask, blendMode = MaskBlend)
image.draw(lines)nim c -r examples/gradient.nim
let paint = newPaint(RadialGradientPaint)
paint.gradientHandlePositions = @[
vec2(100, 100),
vec2(200, 100),
vec2(100, 200)
]
paint.gradientStops = @[
ColorStop(color: color(1, 0, 0, 1), position: 0),
ColorStop(color: color(1, 0, 0, 0.15625), position: 1.0),
]
image.fillPath(
"""
M 20 60
A 40 40 90 0 1 100 60
A 40 40 90 0 1 180 60
Q 180 120 100 180
Q 20 120 20 60
z
""",
paint
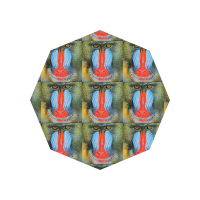
)nim c -r examples/image_tiled.nim
let path = newPath()
path.polygon(
vec2(100, 100),
70,
sides = 8
)
let paint = newPaint(TiledImagePaint)
paint.image = readImage("examples/data/mandrill.png")
paint.imageMat = scale(vec2(0.08, 0.08))
image.fillPath(path, paint)nim c -r examples/shadow.nim
let path = newPath()
path.polygon(vec2(100, 100), 70, sides = 8)
let polygonImage = newImage(200, 200)
polygonImage.fillPath(path, rgba(255, 255, 255, 255))
let shadow = polygonImage.shadow(
offset = vec2(2, 2),
spread = 2,
blur = 10,
color = rgba(0, 0, 0, 200)
)
image.draw(shadow)
image.draw(polygonImage)nim c -r examples/blur.nim
let path = newPath()
path.polygon(vec2(100, 100), 70, sides = 6)
let mask = newImage(200, 200)
mask.fillPath(path, color(1, 1, 1, 1))
blur.blur(20)
blur.draw(mask, blendMode = MaskBlend)
image.draw(trees)
image.draw(blur)nim c -r examples/tiger.nim
let tiger = readImage("examples/data/tiger.svg")
image.draw(
tiger,
translate(vec2(100, 100)) *
scale(vec2(0.2, 0.2)) *
translate(vec2(-450, -450))
)