This repository contains performance benchmarking of a FLAME GPU 2 implementation of Boids agent based model running multiple concurrent simulations.
The code demonstrates the effect and scaling the number of concurrent simulation using the ensemble feature of the FLAMEGPU2 agent-based modelling framework.
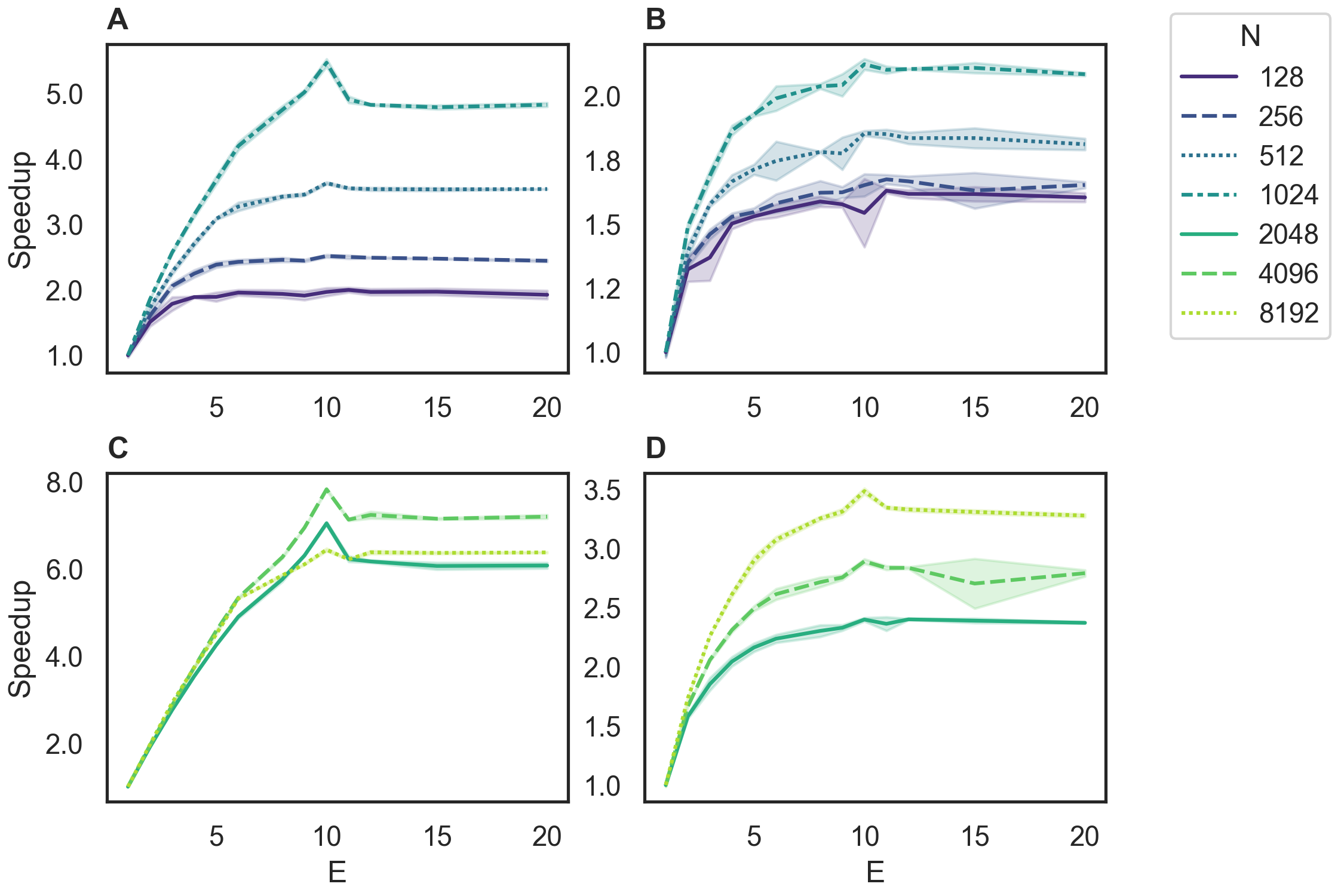
A combined figure for use in publication is shown below. For details please refer to the publication.
A number of experiments are undertaken within this benchmark. There is a range of raw data in the sample/data directory with a description of the machine configurations used to generate it in each directory.
The results below are from the V100 runs on the Bessemer HPC system at the University of Sheffield. Job submission scripts are included in the scripts/slurm folder.
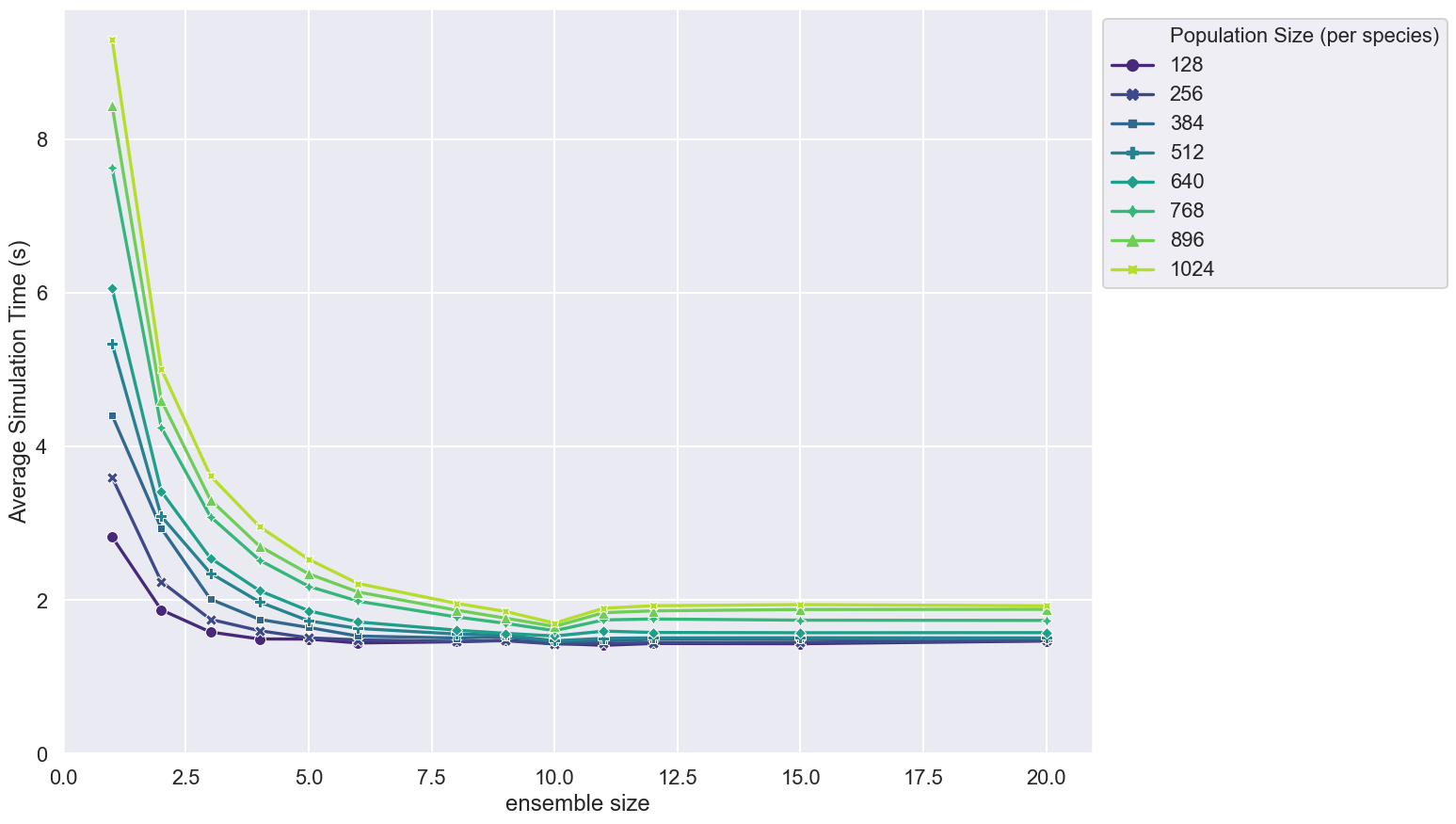
This figure shows how the average simulation time scales with ensemble size for different population sizes of a brute force messaging Boids model.
- Population sizes are stepped between 128 and 1024 at intervals of 128
- Simulation timing is measured over 500 steps
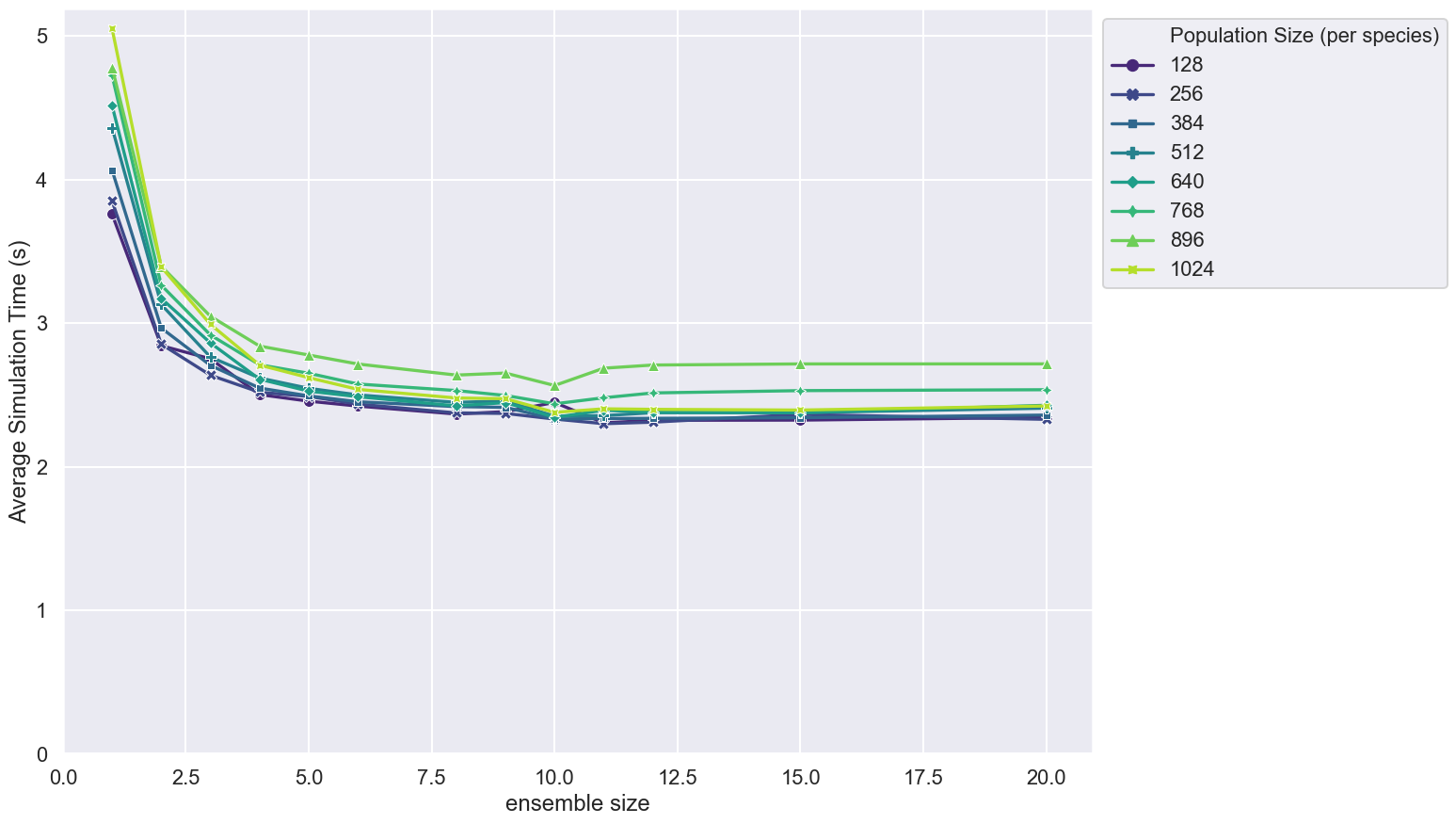
This figure shows how the average simulation time scales with ensemble size for different population sizes of a spatial messaging Boids model.
- Population sizes are stepped between 128 and 1024 at intervals of 128
- Simulation timing is measured over 500 steps
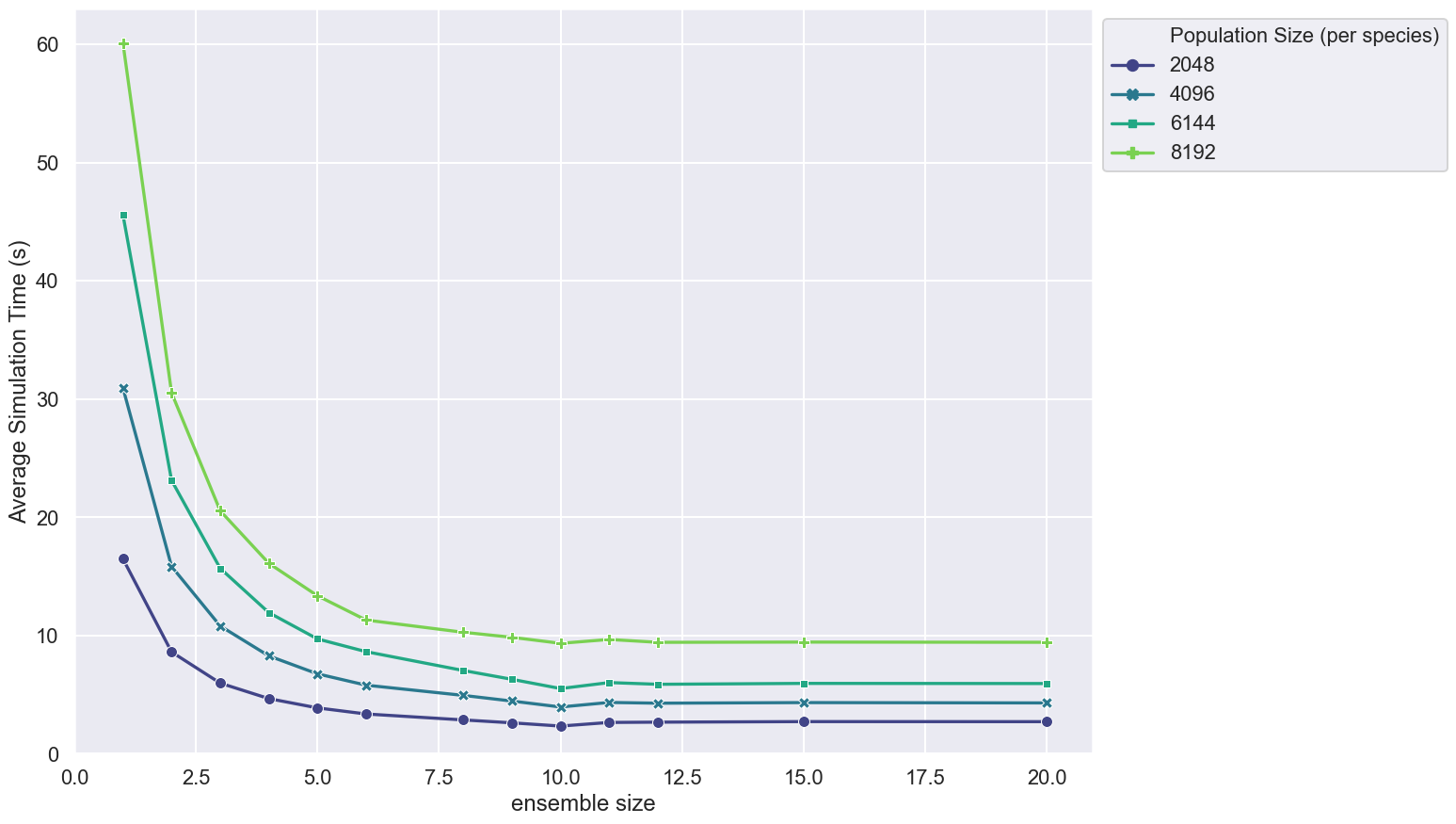
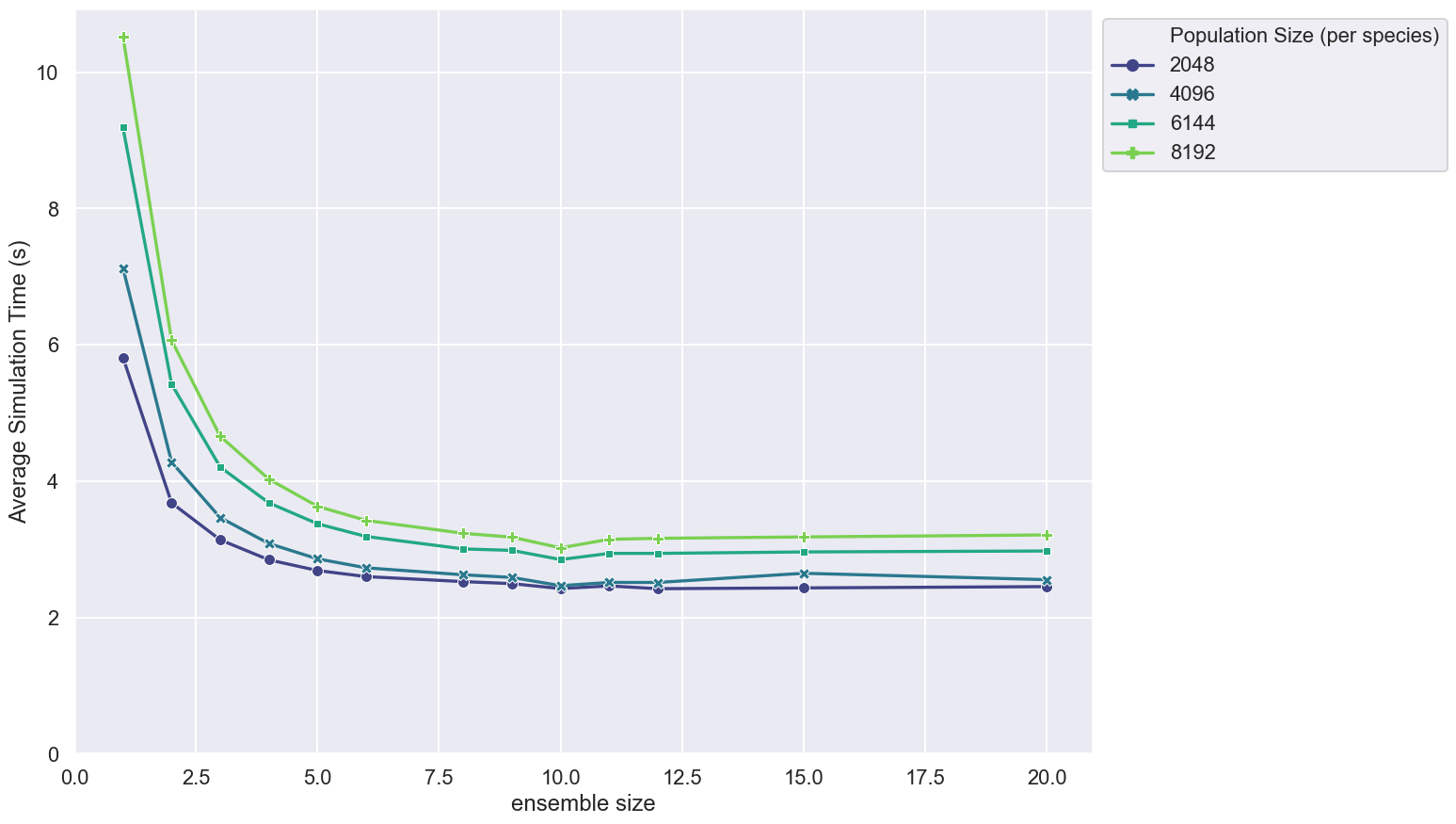
This figure shows how the average simulation time scales with ensemble size for different large population sizes of a brute force messaging Boids model.
- Population sizes are stepped between 2048 and 8192 at intervals of 2048
- Simulation timing is measured over 500 steps
This figure shows how the average simulation time scales with ensemble size for different large population sizes of a spatial messaging Boids model.
- Population sizes are stepped between 2048 and 8192 at intervals of 2048
- Simulation timing is measured over 500 steps
Detail of dependencies and the cmake build process are described in full in the FLAMEGPU2-example-template Repo and are not repeated here. The benchmark should be built with seatbelts off (e.g. -DFLAMEGPU_SEATBELTS=OFF passed to the cmake configuration step) to disable additional run-time checks. E.g. for Volta (SM_70) GPUs under Linux.
# Configure
cmake . -B build -DCMAKE_BUILD_TYPE=Release -DFLAMEGPU_SEATBELTS=OFF -DCMAKE_CUDA_ARCHITECTURES=70
# Build
cmake --build build -j`nproc` cd build
./bin/Release/ensemble-benchmark This will produce a number of .csv files in the build directory.
Note: The FLAMEGPU2_INC_DIR environment variable may need to be set to ./_deps/flamegpu2-src/include/ for run-time compilation (RTC) to succeed if the source directory is not automatically found.
Individual figures can be generated from data in CSV files via a python script plot.py. Alternatively a combined figure used for publication can be produced using plot_publication.py.
It is recommended to use python virtual environment or conda environment for plotting dependencies.
I.e. for Linux to install the dependencies into a python3 virtual environment and plot the results from all experiments output to the build directory.
# From the root of the repository
# Create the venv
python3 -m venv .venv
# Activate the venv
source .venv/bin/activate
# Install the dependencies via pip
python3 -m pip install -Ur requirements.txt
# Plot using csv files contained within the build directory
python3 plot.py build -o build/figures
# Use -h / --help for more information on optional plotting script parameters.The sample figures were generated from the root directory using
python3 plot.py sample/data/v100-515.65.01/2.0.0-rc-v100-11.0-beltsoff -o sample/figures/v100-515.65.01/2.0.0-rc-v100-11.0-beltsoffThe publication figure was generated using
python3 plot_publication.py -i sample/data/v100-515.65.01/2.0.0-rc-v100-11.0-beltsoff -o sample/figures/v100-515.65.01/2.0.0-rc-v100-11.0-beltsoff