On startup the application associates with the compiled in wlan access point and registers on the SIP server.
Once a signal is detected on the selected GPIO, a call is initiated to a target number. On the phone, the custom string is displayed.
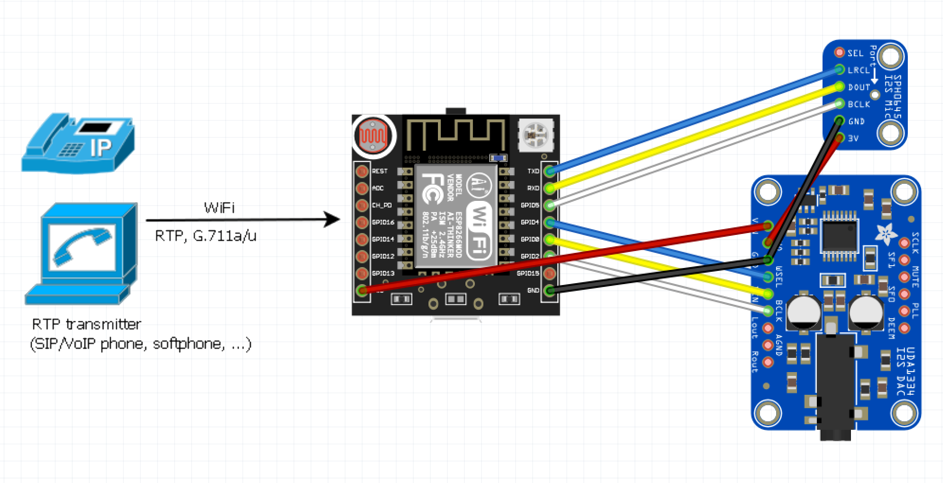
Adafruit components operating on the i2s bus have been selected for audio support.
The project aims to show the resources of the small and cheap ESP32 module and is based on the chrta's project.
The source code is mixed C and C++.
This application is to be used with `Espressif IoT Development Framework`_ (ESP-IDF).
Please check ESP-IDF docs for getting started instructions.
An ESP32 board can be used. Only one external GPIO (input is sufficient) must be available, to detect the call trigger.
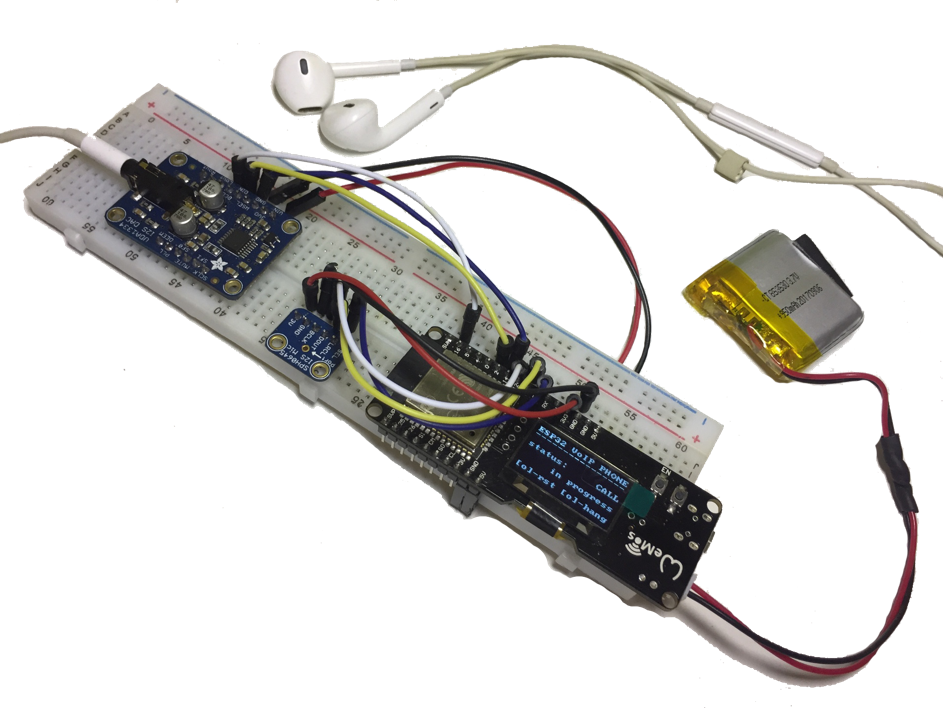
The software has been adapted for use on the WEMOS LOLIN32 development board with an integrated 0.96" monochrome OLED SSD1306 display, informing about the state of the device.
The audio output is dealt with by the DAC stereo decoder on the I2S bus, model UDA1334A from Adafruit, while the sound sampling system is the MEMS I2S microphone model SPH0645LM4H, also manufactured by Adafruit.
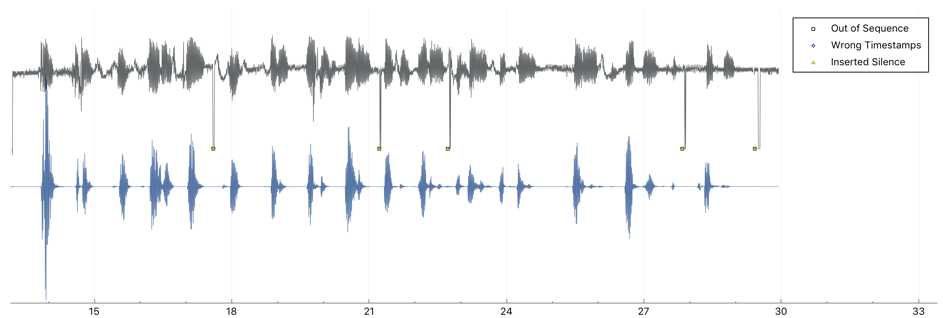
In order to verify the built-in VoIP client, the Asterisk VoIP server was launched in the test environment and the voice connection was successfully completed. RAM usage fluctuated around 319 kB from ESP32 512 kB available in ESP32.
The maximum jiiter in the stream from the built-in device was 5.1 ms, while the average was 4.14 ms - achieved value jitter is acceptable for a typical VoIP client.
If not otherwise specified, code in this repository is Copyright (C) 2017 Christian Taedcke <hacking@taedcke.com>, licensed under the Apache License 2.0 as described in the file LICENSE.