Article link : https://doi.org/10.1017/jfm.2019.814
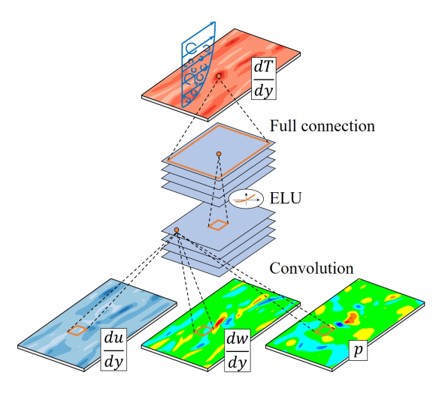
As shown in figure, we applied convolutional neural network(CNN) to the prediction of turbulent heat transfer in wall-bounded turbulence. CNN is constructed to predict the wall-normal heat flux based on the nearby other wall information including wall-shear stresses and pressure. As training results, very high prediction accuracy could be achieved even at a higher Reynolds number than the trained one. It stands for the existence of nonlinear relationship between the heat transfer and other wall information. We tried to figure out the spatial relationship between input and the heat transfer. The deep neural network is well-known as a black box method, however, through observation of a gradient map with statistical sense, we found that the trained CNN contains meaningful patterns that reveal underlying physics. In future work, our framework could be extended to other problems including turbulence reconstruction, turbulence control, and especially other turbulence physics analysis.
Code related to our article is given in 'Sample code.py'. Our code is written in tensorflow library with version 1.4.X If you use tensorflow version 2.0, see https://www.tensorflow.org/guide/migrate. In our code, minor things are omitted for simplicity. The example network is composed of three 3x3 convolution layers and one 11x11 convolution layer.
Some data (fortran binary data), 250 instantaneous flow fields, are compressed into ten zip files, and given in 'DLdata' folder. For reading fortran binary data, library scipy.io.FortranFile is used in code 'LoadData.py'. The file number gap, 4, is corresponded to 36 in wall time unit. Each file is composed of 2D flow fields including du/dy, dw/dy, p, and dT/dy. Grid size of field is 192 x 192, and domain size of that is 4pi x 2pi. In the given data, the mean values of input data are subtracted, and they are 180 (of du/dy), 0 (of dw/dy), and 0 (of p), respectively, while the mean value of dT/dy is not subtracted. Root-mean-square values of given data are approximately 66.3 (of du/dy), 37.0 (of dw/dy), and 1.58 (of p), respectively.
If you have any questions about the article and the code, please email junhyuk6@yonsei.ac.kr.