- 本项目是 NVIDIA TensorRT Hackathon 2023 的参赛题目,我们将Qwen-7B模型转换到TensorRT-LLM并部署到NVIDIA A10 GPU上。其原始模型的相关链接如下:
-
模型复现结果(由于在测试环境中,所选模型FP32精度下显存不足,只测试了FP16和int8结果):
- Huggingface和TensorRT-LLM模型FP16时加速比在1.42左右,int8时加速比在2.06
- Huggingface和TensorRT-LLM模型FP16时绝对误差在0.002左右,相对误差0.005左右
- Huggingface和TensorRT-LLM模型int8时绝对误差在0.05左右,相对误差0.1左右
-
以下是本项目运行所需的环境,项目结构和运行方式说明:
🎉 1.项目所需环境
点我查看所需环境
-
主机硬件环境:
Linux version 5.15.0-73-generic (buildd@bos03-amd64-060) (gcc (Ubuntu 11.3.0-1ubuntu1~22.04.1)), NVIDIA显卡:NVIDIA A10 (24G) -
主机软件环境:
Driver Version: 525.105.17,CUDA 12.1/cuDNN8.9/TensorRT-9.0.0.2,Docker和NVIDIA-Docker
# 拉取镜像
docker pull registry.cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com/trt-hackathon/trt-hackathon:final_v1
# 启动容器
docker run --gpus all --name trt2023 -it --rm --ipc=host --ulimit memlock=-1 --ulimit stack=67108864 registry.cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com/trt-hackathon/trt-hackathon:final_v1
# 如果容器已经存在并停止
docker start trt2023
# 使用docker ps -s查看运行容器,如果正在运行,使用如下命令进入容器操作
docker exec -it trt2023 bash🎉 2.代码结构
点我查看代码结构
# model
tensorrt_llm_july-release-v4/tensorrt_llm/models/qwen7b/model.py
# QWenMLP
tensorrt_llm_july-release-v4/tensorrt_llm/layers/mlp.py
# example
./tensorrt_llm_july-release-v1/examples/qwen7b/
├── README.md
├── benchmarks # benchmark文件
├── build.py # trt模型build
├── configuration_qwen.py # 修改的HF配置文件
├── convert.py #
├── hf_qwen_convert.py # int8 kv cache scale转换文件
├── model # Huggingface 模型相关文件
├── profile.py # Huggingface模型profile文件
├── run.py # TRT-LLM模型运行文件
├── smoothquant.py # int8相关量化文件
├── summarize.py # Rouge 来对比模型优化前后的精度差距
├── test_qwen.py # 测试TRT-LLM模型的精度
├── test_qwen_int8_kv_cache.py # 测试TRT-LLM int8 kv cache模型的精度
├── test_qwen_weight_only.py # 测试TRT-LLM iweight-only int8模型的精度
├── test_rms_norm.py # 测试rmsnorm plugin的精度
├── test_swiglu.py # 测试swiglu plugin的精度
└── weight.py # HF模型权重转换相关文件
# rmsnorm plugin
tensorrt_llm_july-release-v1/cpp/tensorrt_llm/kernels/rmsnormKernels.cu
tensorrt_llm_july-release-v1/cpp/tensorrt_llm/kernels/rmsnormKernels.h
tensorrt_llm_july-release-v1/cpp/tensorrt_llm/plugins/rmsnormPlugin/rmsnormPlugin.cpp
tensorrt_llm_july-release-v1/cpp/tensorrt_llm/plugins/rmsnormPlugin/rmsnormPlugin.h
# swiglu plugin
tensorrt_llm_july-release-v1/cpp/tensorrt_llm/kernels/swigluKernels.cu
tensorrt_llm_july-release-v1/cpp/tensorrt_llm/kernels/swigluKernels.h
tensorrt_llm_july-release-v1/cpp/tensorrt_llm/plugins/swigluPlugin/swigluPlugin.cpp
tensorrt_llm_july-release-v1/cpp/tensorrt_llm/plugins/swigluPlugin/swigluPlugin.h🎉 3.运行方式说明
点我查看运行方式
- 1.重新编译tensorrt_llm
# 官方的docker中TensorRT位于/usr/local/TensorRT-9.0.0.2/
cd /root/workspace/tensorrt_llm_july-release-v1/
# 按照/root/workspace/tensorrt_llm_july-release-v1/README.md中说明进行安装和编译
# 如果需要重新编译所有tensorrt_llm代码
./scripts/build_wheel.py --clean --trt_root /usr/local/TensorRT-9.0.0.2/
# 编译完成之后安装tensorrt_llm
pip3 install ./build/tensorrt_llm-0.1.3-py3-none-any.whl
- 2.运行example中的代码
cd /root/workspace/tensorrt_llm_july-release-v1/examples/qwen7b/
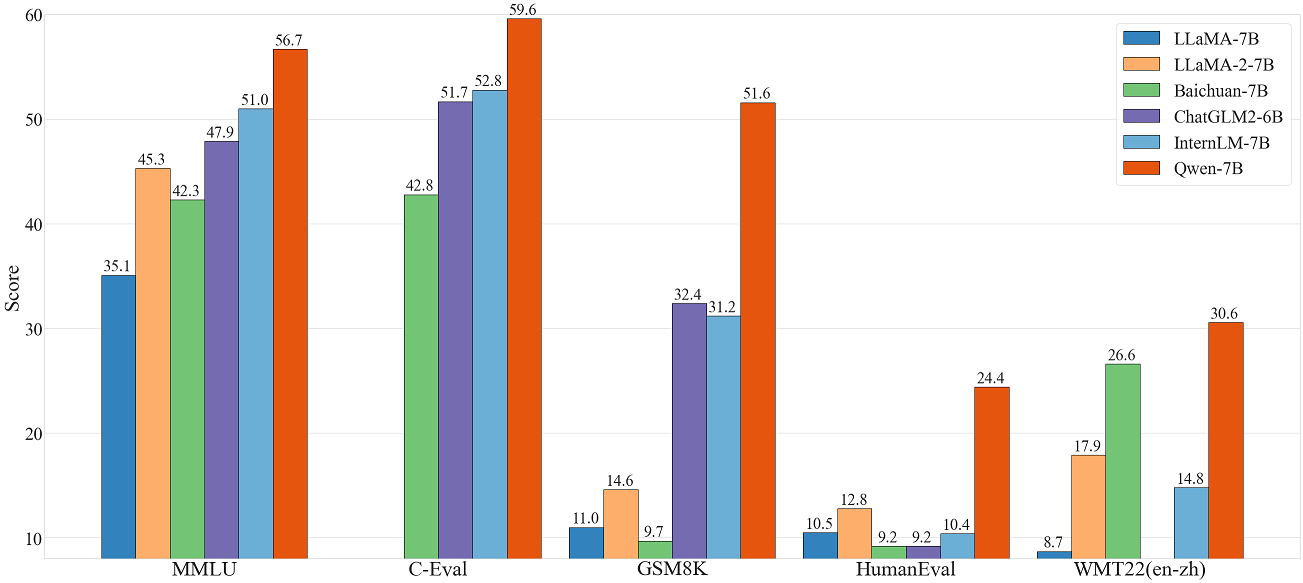
# 按照examples/qwen7b/README.md中的说明运行build.py, run.py, summarize.py等.通义千问-7B(Qwen-7B) 是阿里云研发的通义千问大模型系列的70亿参数规模的模型。Qwen-7B是基于Transformer的大语言模型, 在超大规模的预训练数据上进行训练得到。预训练数据类型多样,覆盖广泛,包括大量网络文本、专业书籍、代码等。 Qwen-7B结构与LLaMA相似的架构。使用来自公开的超过 2.2 万亿个tokens的数据和 2048 个上下文长度进行预训练,训练数据覆盖一般和专业领域,在语言方面重点关注英语和中文。 与标准transformer的主要区别如下:
- 使用untied embedding嵌入;
- 使用旋转位置嵌入-即RoPE相对位置编码;
- normalization实现--即RMSNorm代替LayerNorm;
- FFN激活函数-即SwiGLU代替 ReLU。
我们仿照examples的代码组织形式,完成了模型搭建,并可顺利输出文本(实现weight.py/build.py/run.py),用Nsight对模型进行Profiling,并最终确定了有针对性的优化方案,包括:
- QWenMLP 冗余结构耗时
- RMSNorm 冗余结构耗时
- dynamic ntk和logn attn实现
- int8 kv cache实现
- weight-only int8实现
- rmsnorm plugin和模型精度对齐
针对于上述问题我们通过修改TRT-LLM相关源码,开发了相关的plugin和脚本.
- 模型搭建中在mlp.py中增加了QWenMLP实现(融合fc和gate为一个linear)
- 在现有的gpt attention plugin代码中添加了dynamic ntk和logn attn实现
- 实现了Rmsnorm plugin
- 实现了Swiglu plugin(速度太慢弃之)
- 仿照example中的代码实现了int8 kv cache和weight-only int8
- 实现了test_qwen.py,test_swiglu.py,test_rms_norm.py
- 1. QWenMLP
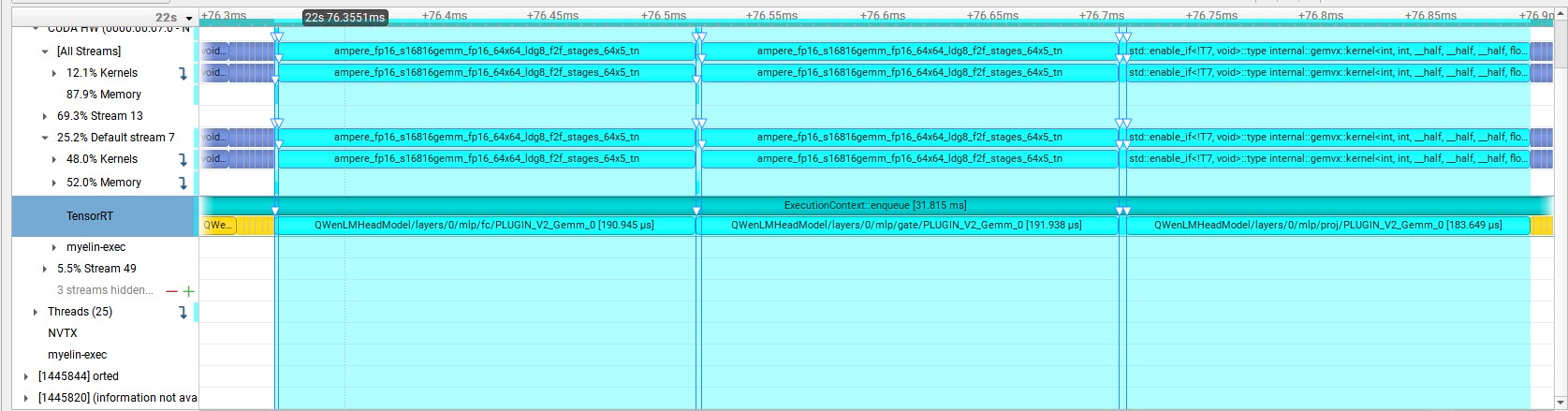
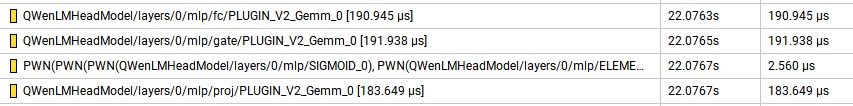
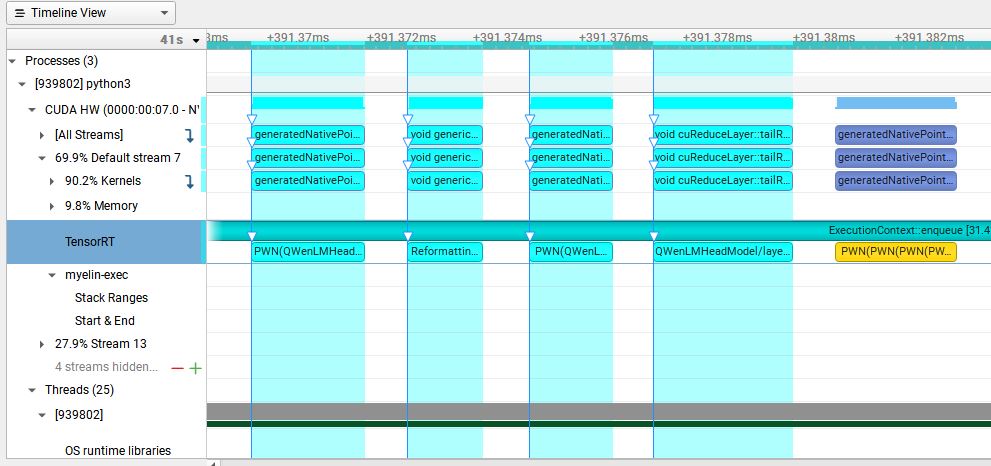
原TensorRT-LLM中的GatedMLP中对输入数据进行了self.fc和self.gate两个linear运算,然后使用了silu激活函数。整个网络包含32个此结构, 运行以下代码生成Nsight Profiling文件:
nsys profile -o qwen python3 run.py --max_output_len=8 --tokenizer_dir ./model --engine_dir=./trt_engines/qwen/7B/trt_engines/fp16/1-gpu/
在Nsight下发现GatedMLP的耗时情况如下图所示:
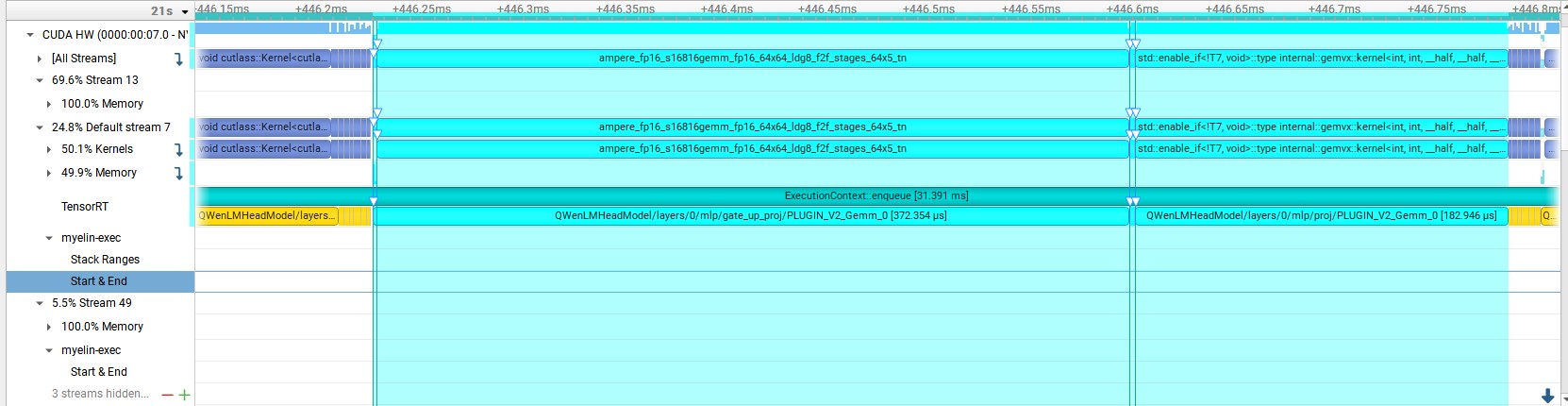
其在一个block中的一个GatedMLP的耗时为569.092us,因此我们对GatedMLP进行了优化,把self.fc和self.gate两个linear融合为一个linear,
然后使用swiglu激活函数。优化后的耗时为557.795us,较优化前缩短了11.297us,相同位置的QWenMLP结构的Nsight如下:
此外还实现了Swiglu Plugin,但是速度比TensorRT中的原生算法融合慢很多,因此弃用之。
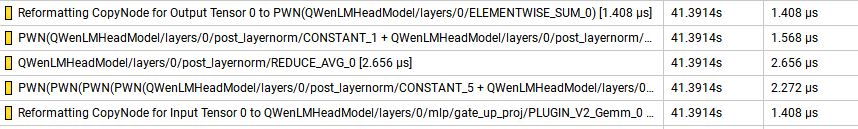
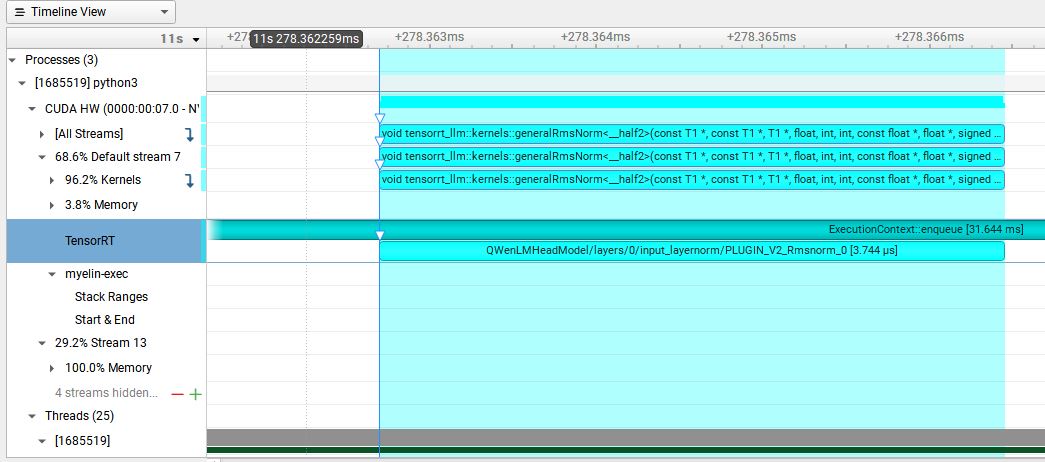
- 2. RMSNorm
每个QWenBlock包含2个RMSNorm,整个网络包含64个此结构,在Nsight下发现RMSNorm的耗时情况如下图所示:
其在一个QWenBlock中的一个RMSNorm的耗时为9.312us,因此我们对RMSNorm进行了优化,实现了Rmsnorm Plugin。优化后的耗时为3.776us,较优化前缩短了5.536us,相同位置的QWenMLP结构的Nsight如下:
- 3. int8 kv cache and int8 weight-only
我们仿照examples中的代码实现了int8 kv cache和int8 weight-only,我们通过benchmark统计了FP16、FP16+int8 kv cache及int8 weight-only的显存使用情况。运行examples/qwen7b/benchmarks中的benchmark程序可以得到运行结果
# 以batch_size=1为例
# Run benchmark using the Qwen 7B TRT-LLM model in FP16.
python ./benchmarks/benchmark.py \
-m qwen \
--mode plugin \
--batch_size "1" \
--input_output_len "10,512" \
--engine_dir ./trt_engines/qwen/7B/trt_engines/fp16/1-gpu/
# Run benchmark using the Qwen 7B TRT-LLM model quantized to INT8.
python ./benchmarks/benchmark.py \
-m qwen \
--mode plugin \
--batch_size "1" \
--input_output_len "10,512" \
--use_weight_only \
--engine_dir ./trt_engines/qwen/7B/trt_engines/weight_only/1-gpu/| batch_size | FP16 memory(GB) | int8 memory(GB) | diff(GB) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 16.43 | 10.39 | -6.04 |
| batch_size | FP16 memory(GB) | int8 kv cache(GB) | diff(GB) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 16.43 | 16.27 | -0.16 |
-
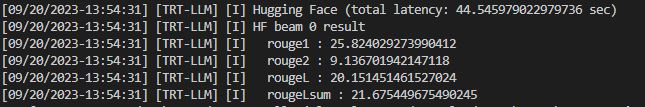
性能测试
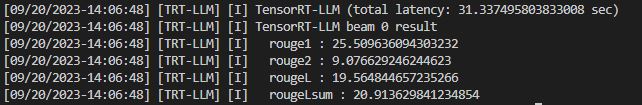
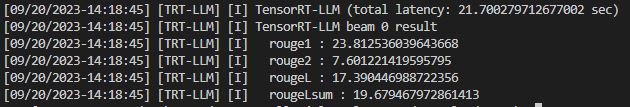
我们通过summarize统计了Huggingface FP16、TRT FP16、TRT int8 weight-only的加速情况。运行examples/qwen7b/summarize.py程序可以得到运行结果
# Run summarization using the Qwen 7B HF model in FP16.
python summarize.py --test_hf \
--batch_size 1 \
--hf_model_location ./model \
--data_type fp16 \
--check_accuracy \
--tensorrt_llm_rouge1_threshold=14 \
--engine_dir ./trt_engines/qwen/7B/trt_engines/fp16/1-gpu/
# Run summarization using the Qwen 7B TRT-LLM model in FP16.
python summarize.py --test_trt_llm \
--batch_size 1 \
--hf_model_location ./model \
--data_type fp16 \
--check_accuracy \
--tensorrt_llm_rouge1_threshold=14 \
--engine_dir ./trt_engines/qwen/7B/trt_engines/fp16/1-gpu/
# Run summarization using the Qwen 7B TRT-LLM model weight quantized to INT8.
python summarize.py --test_trt_llm \
--batch_size 1 \
--hf_model_location ./model \
--data_type fp16 \
--check_accuracy \
--tensorrt_llm_rouge1_threshold=14 \
--engine_dir ./trt_engines/qwen/7B/trt_engines/weight_only/1-gpu/- sumarize统计时间(second)
| batch_size | Huggingface | FP16 | int8 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 44.6 | 31.3 | 21.7 |
- 加速比
| batch_size | Huggingface | FP16 | int8 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1.0 | 1.42 | 2.06 |
- 精度测试
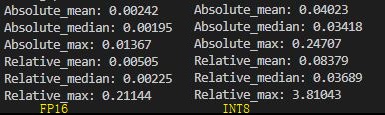
关于精度测试的验证仿照tests中的代码,采取的方式是绝对误差和相对误差的均值,中位数和最大值。运行examples/qwen7b/test_qwen.py和examples/qwen7b/test_qwen_weight_only.py程序可以得到运行结果
# 评估HF输出和TRT-LLM输出的FP16模型精度是否对齐
python test_qwen.py
# 评估HF输出和TRT-LLM输出的INT8模型精度是否对齐
python test_qwen_weight_only.py
| DataType | max abs | median abs | mean abs | max rel | median rel | mean rel |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| fp16 | 0.0137 | 0.00195 | 0.00242 | 0.21144 | 0.00225 | 0.00505 |
| int8 | 0.2919 | 0.0359 | 0.0426 | 3.659 | 0.0389 | 0.0893 |
- FP16精度损失主要在gpt attention plugin中,该plugin输出结果和Huggingface输出结果有一定的误差
- INT8由于只是对weight进行了对称量化,没有经过SmoothQuant等量化策略,因此输出结果和Huggingface输出结果有较大的误差
- python3 run.py --max_output_len=8
Input: Born in north-east France, Soyer trained as a
Output: chef before moving to London in the late
- python3 summarize.py --engine_dirtrt_engine/gpt2/fp16/1-gpu --test_hf --batch_size1 --test_trt_llm --hf_model_location=gpt2 --check_accuracy --tensorrt_llm_rouge1_threshold=14
[09/06/2023-00:46:00] [TRT-LLM] [I] TensorRT-LLM beam 0 result
[09/06/2023-00:46:00] [TRT-LLM] [I] rouge1 : 21.869322054781037
[09/06/2023-00:46:00] [TRT-LLM] [I] rouge2 : 6.258925475911645
[09/06/2023-00:46:00] [TRT-LLM] [I] rougeL : 16.755771650012953
[09/06/2023-00:46:00] [TRT-LLM] [I] rougeLsum : 18.68034777724496
[09/06/2023-00:46:00] [TRT-LLM] [I] HF beam 0 result
[09/06/2023-00:46:01] [TRT-LLM] [I] rouge1 : 18.182978950152904
[09/06/2023-00:46:01] [TRT-LLM] [I] rouge2 : 5.166241888544473
[09/06/2023-00:46:01] [TRT-LLM] [I] rougeL : 14.851620358520162
[09/06/2023-00:46:01] [TRT-LLM] [I] rougeLsum : 16.95757748412272
基于TensorRT-LLM和Plugin我们已经搭建了Qwen-7B模型并做了一定的优化,由于时间关系并未进行SmoothQuant等量化,真的非常遗憾,未来希望持续进一步的优化,未来工作:
- 整体精度还存在优化空间,未来将进一步优化。
- pipeline的速度存在一定优化空间,替换更加高效的sample采样方案。
- rmsnorm plugin和swiglu plugin速度存在优化空间,未来将进一步优化。
- 尝试SmoothQuant或GPTQ等int8量化方案。