´namp´ is a wildly use network scanning tool that has survived the test of time, is maintained and open source. You can perform host discovery, port scanning and guess operating system. We'll also look at how to manipulate and store the output.
- Disclaimer
- Pre requisists
- Installing namo
- Basic Usage
- Host Discovery, DNS, TCP, UDP
- OS detection, Fingerprinting, Throtling
Remember scanning a network is likely to trigger alarms with your thorough request. Create a simple local network or prob servers that have been setup for this purpose.
- namp
- network to scan
- Linux fundamentals
Linux system
$ sudo apt install nmapYou can also built from source or install distro/OS specific https://nmap.org/download.html
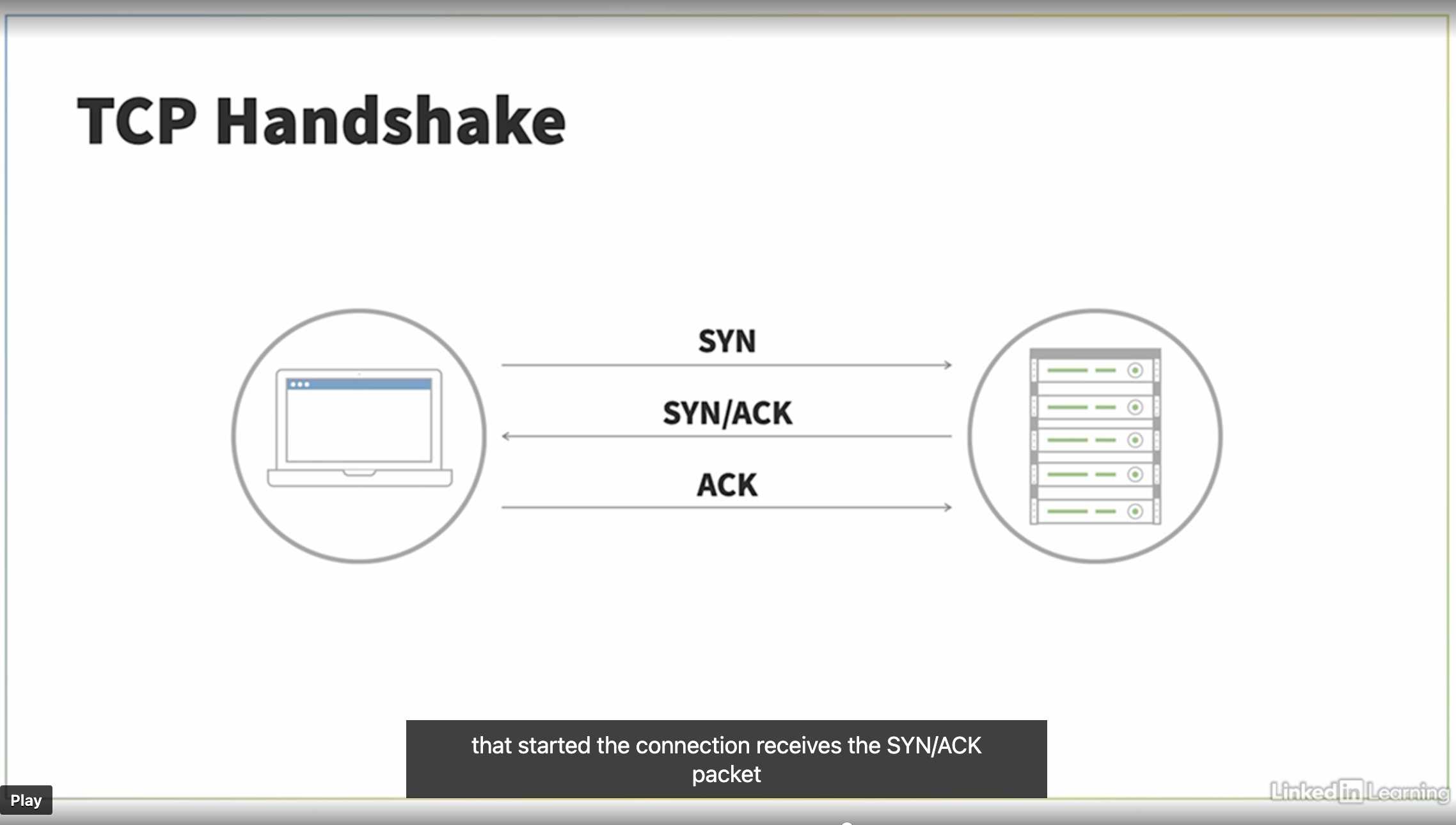
TCP Main way of transfering data is TPC. Transmission Control Protocol (TPC) acknologes delivery of packages and hence is a reliable protocol commonly used. It has these main requests whene establishing a or closing a connection:
- SYN - Opens a connection
- ACK - Acknologes a SYN or FIN
- FIN - Closes a connection
UDP UDP is also used for data tranfering, but does so blindly. It doesn not acknologe anything! It is there for less comonly used and harder to ensure that or anything was received as inteded.
OSI Model
Basics usage is the following
# Syntax
$ nmap -flags-opt <ip/submask>
# example scanning ip range using submask
$ nmap 192.168.1.0/29 Scanning with pre set default setting to actually find anything use the -A flag:
# Using -A flag for seraral severs
$ nmap -A 45.33.32.156
# Very Verbose, -A preset common settings, output to readable text, multiple target list
$ nmap -vv -A -oN certmikr_nampWEB_IP-A_general-read.txt -iL ~/code/nmap101/scans/scan_targets2.txtYou can scang a range of ips using a range, a submask and you can feed it a list of of targets.
# Using a range of ips
$ nmap 192.168.1.0-6
# Using a submask of ips
$ nmap 192.168.1.0/29
# Using a list of targets
$ nmap -iL ~/code/nmap101/scans/scan_targets.txt
scan_targets2.txt
nmap has specific tuning to all of these.
Specific to host discovery there are different ways to performe this that wield diferent resilts. You can send "SYN" connects but you can also ping or do some other methods to find the host. More reading needed on this area. Some also need Admin rights
Turning off host discovery when you know there is something there
# turning off host dicover
$ nmap -Pn scan2.certmike.com
# Verbose No host dicover + -A settings and storing the output in text file
$ nmap -v -Pn -A -oN certmikr_scan2_NoHostDisc_-A_general-read.txt scan2.certmike.comBy default nmap uses reverse DNS resolution. You can define a diferent one such as google's 8.8.8.8, the machine DNS or other. This will affect the performance of the scan. It is an area that can be fined tuned to make your scans more efficients.
Standard namp uses reverse DNS
# Standard reverse DNS look up
$ nmap 45.33.32.156
>(...)
> Nmap done: 1 IP address (1 host up) scanned in 59.03 seconds
# Disabling the reverse DNS lookup
$ nmap -n 45.33.32.156
>(...)
> Nmap done: 1 IP address (1 host up) scanned in 58.02 seconds
# System reverse DNS lookup
$ nmap --system-dns 45.33.32.156
>(...)
> Nmap done: 1 IP address (1 host up) scanned in 56.55 seconds
# System specifc external DNS lookup
$ nmap --dns-servers 8.8.8.8 45.33.32.156
>(...)
> Nmap done: 1 IP address (1 host up) scanned in 55.21 secondsYou can fine tune these areas. More reading needed
There are over 65,0000 ports. 65,535 to be exact. It would be very time consuming to test all. By default Nmap test the most "1000" used ports. There are ways to specify a port
# Specify a port using -p
nmap -p 80 45.33.32.156
# Specify multiple ports
nmap -p 80,443 45.33.32.156
nmap -p http,https 45.33.32.156
# Specify range
nmap -p 80-1000 45.33.32.156
# Fast 100 most used ports
nmap -F 45.33.32.156# -sV flag
$ namp -sV scan3.certmike.com
# Very Verbose, Service discovery, write plain text to file, seach scan2.certmike.com
$ nmap -vv -sV -oN certmikr-scan2-os_discovery-read.txt scan2.certmike.comEasiest way is using timing templates
| Template | Description |
|---|---|
| -T5 | Insane |
| -T4 | Aggressive |
| -T3 | Normal |
| -T2 | Polite |
| -T1 | Sneaky |
| -T0 | Paranoid (mostly useless) |
# Using insane timing template
$ nmap -T5 192.168.1.0/29