rabbit_chat is a command line tool that allows you to use a chat using RabbitMQ.
RabbitMQ is an open source message broker software written in Erlang that implements the Advanced Message Queuing Protocol (AMQP).
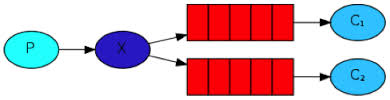
A message broker accepts messages from one or more endpoints ("Producers") and sends them to one or more endpoints ("Consumers"), but RabbitMQ is a bit more sophisticated than just that. It can also figure out what needs to do when, for instance:
- A consumer crashes -> store and re-deliver message.
- A consumer is slow -> queue messages.
- There are multiple consumers -> Load balancing.
RabbitMQ has a fundamental pieces:
-
Exchanges: exchanges are the entities where messages are sent. Exchanges takes a message and route it into zero or more queues. The routing algorithm used depends on the exchange type and rules called bindings. There are four exchanges types: direct, fanout, topic and headers.
-
Queues: they store messages that are consumed by applications.
-
Bindings: bindings are rules that exchanges use (among other things) to route messages to queues. To instruct an exchange E to route messages to a queue Q, Q has to be bound to E. Bindings may have an optional routing key attribute used by some exchange types. The porpuse of the routing key is to select certain messages published to an exchange to be routed to the bound queue. To be simple, the routing key acts like a filter.
-
Producers: sends messages to an exchange with "Routing key" indicating how to route the message.
-
Consumers: this entity subscribes to a queue to receive messages.
bash-3.2$ rabbit_chat
_ _ _ _ _ _ _
_ __ __ _| |__ | |__ (_) |_ ___| |__ __ _| |_| |
| '__/ _` | '_ \| '_ \| | __| / __| '_ \ / _` | __| |
| | | (_| | |_) | |_) | | |_| | (__| | | | (_| | |_|_|
|_| \__,_|_.__/|_.__/|_|\__| \___|_| |_|\__,_|\__(_)
Usage: rabbit_chat -option [parameter]
options:
-h: Help menu
-v: Get rabbit_chat version
-a: Add a new channel
-g: Get existing channels
You have to set the user with --u option.
-l: Listen on a existing channel.
You have to set the user with --u option.
-w: Write a message in a channel.Firstly, it is necessary to install some dependencies
$ cd /path/to/rabbit_chat
$ npm installTo start with rabbit_chat, you have to add your favourite channels with your username. That way, you can write or listen on this channel.
bash-3.2$ rabbit_chat -a
? Enter your username: John Nieve
? Enter channel name: WinterfellJohn Nieve will be able to write and listen on Winterfell now.
bash-3.2$ rabbit_chat -l -u "John Nieve"
? Select the channel name (Press <space> to select)
❯ ◯ "Winterfell"As it pointed before, John Nieve is only able to listen on his channels (Winterfell for now).
Like listening, John Nieve will be able to write into Winterfell.
bash-3.2$ rabbit_chat -w -u "John Nieve"
? Select destination channel (Press <space> to select)
❯ ◯ "Winterfell"bash-3.2$ rabbit_chat -w -u "John Nieve"
? Enter destination channel "Winterfell"
? Enter messageFor more information about RabbitMQ, please go to RabbitMQ Site and RabbitMQ tutorials.