This is a personal project that I created to get some hands on on some cool algorithms I've been learning about recently. This project contains both pathfinding and maze generation algorithms, and I'll keep updating them as I go.
The app contains a settings panel on the left and a grid where the visualization will occur. As of now, this grid and the algorithms, only support 4 directions (north, south, east, west).
A quick introduction to pathfinding algorithms. All of these algorithms introduce a distinct way to traverse the grid (in this case) and to path find from root to the target. Not all of the following algorithms will always return the shortest path nor necessarily work with weights. The following table should clarify this.
| Algorithm | Supports Weights | Shortest Path Guarantee |
|---|---|---|
| Dijkstra | True | True |
| A* | True | False |
| A* Optimal | True | True |
| WavePropagation | False | True |
Also keep in mind that this table is specific to my implementations. Some of these could be reworked to do more or less than they do as implemented in this project.
Dijkstra's shortest path algorithm guarantees the shortest path between two nodes, if it exists.
 Dijkstra algorithm running without weighted nodes. Because it is weightless, it behaves like a generic breath-first search.
Dijkstra algorithm running without weighted nodes. Because it is weightless, it behaves like a generic breath-first search.
 Dijkstra algorithm running with weighted nodes.
Dijkstra algorithm running with weighted nodes.
The A* algorithm is known for it's optimal efficiency. It works based on a heuristic that tries to estimate the distance between the root and the target node (no heuristic should ever overshoot the actual distance). I've implemented the A* that stops immediately once it sees the target (which will not necessarily find the shortest path, as it did not visit all the possible nodes) and what I called A*Optimal, which searches all nodes in the grid and guarantees the shortest path.
- Heuristics: This algorithms requires heuristics to run efficiently. For this app (2 dimensional grid), the Manhattan distance is the optimal solution. See here for how do they work.
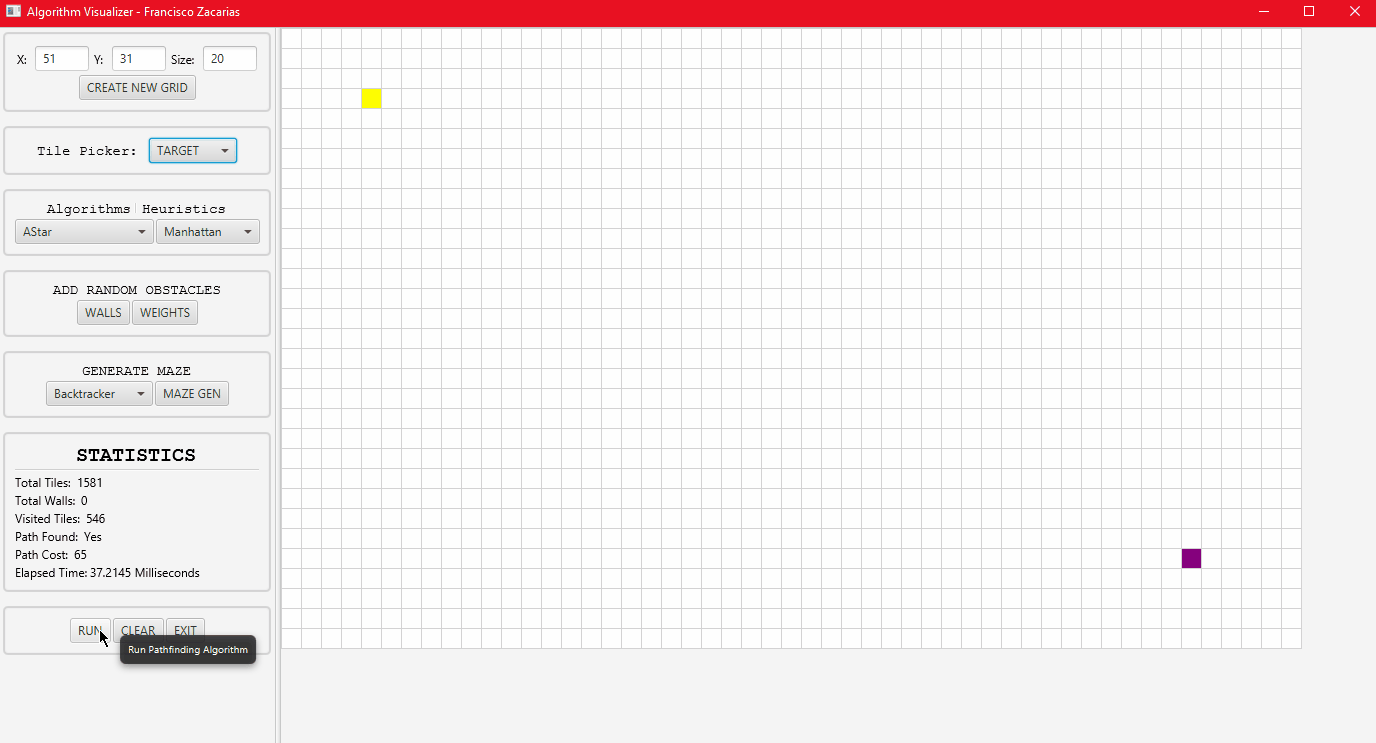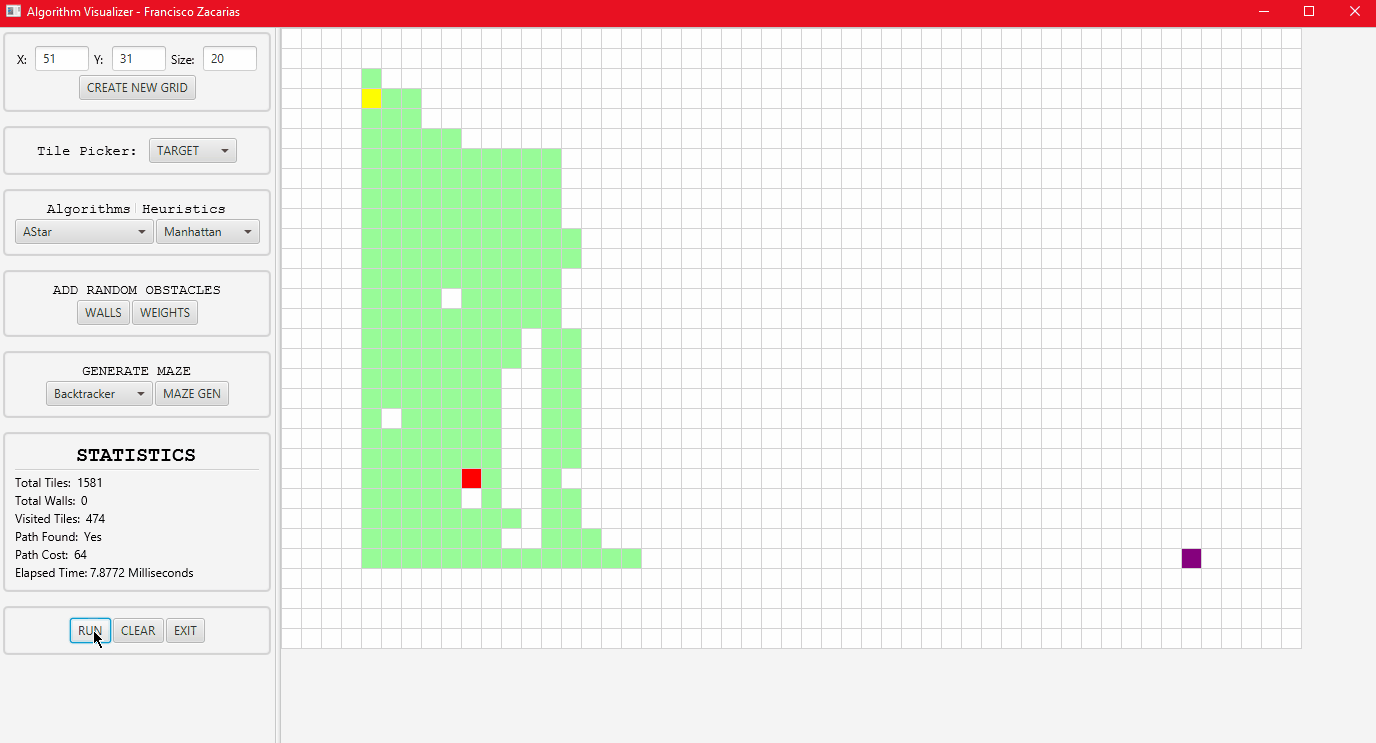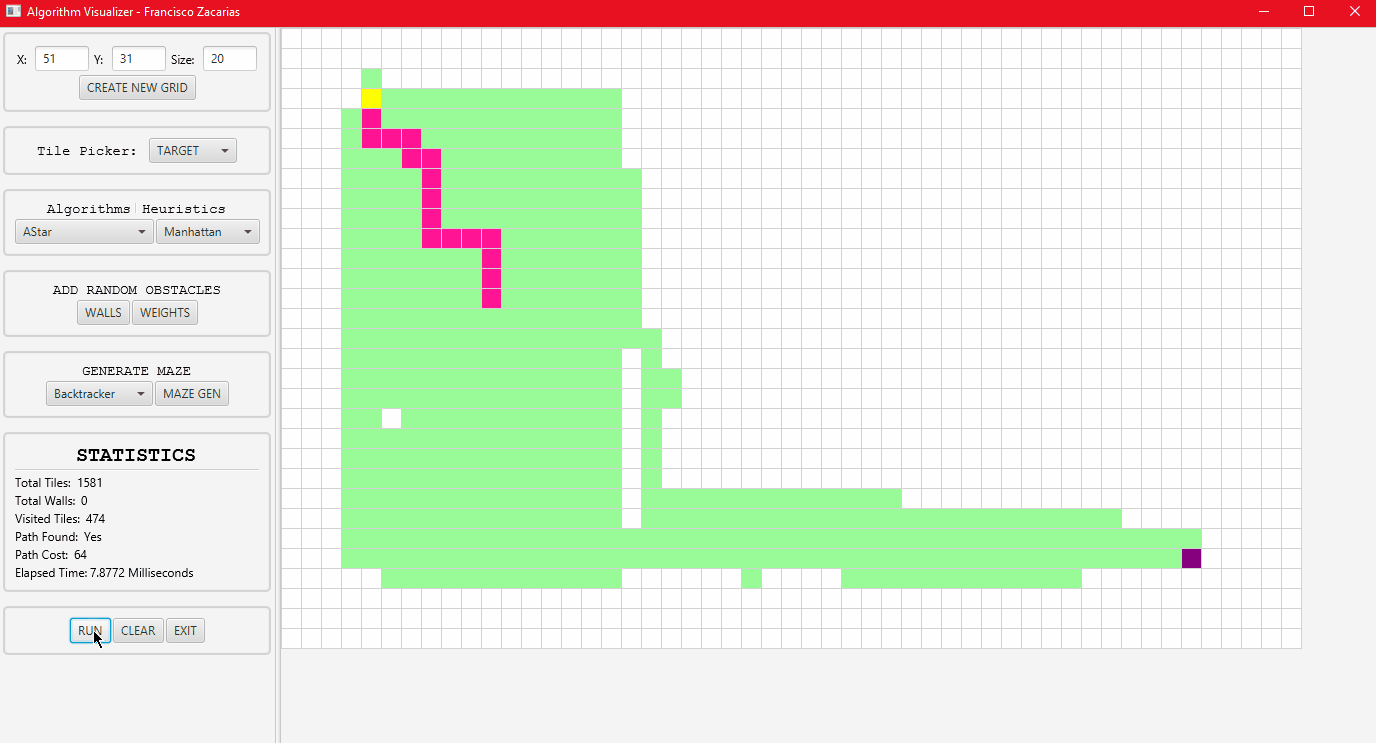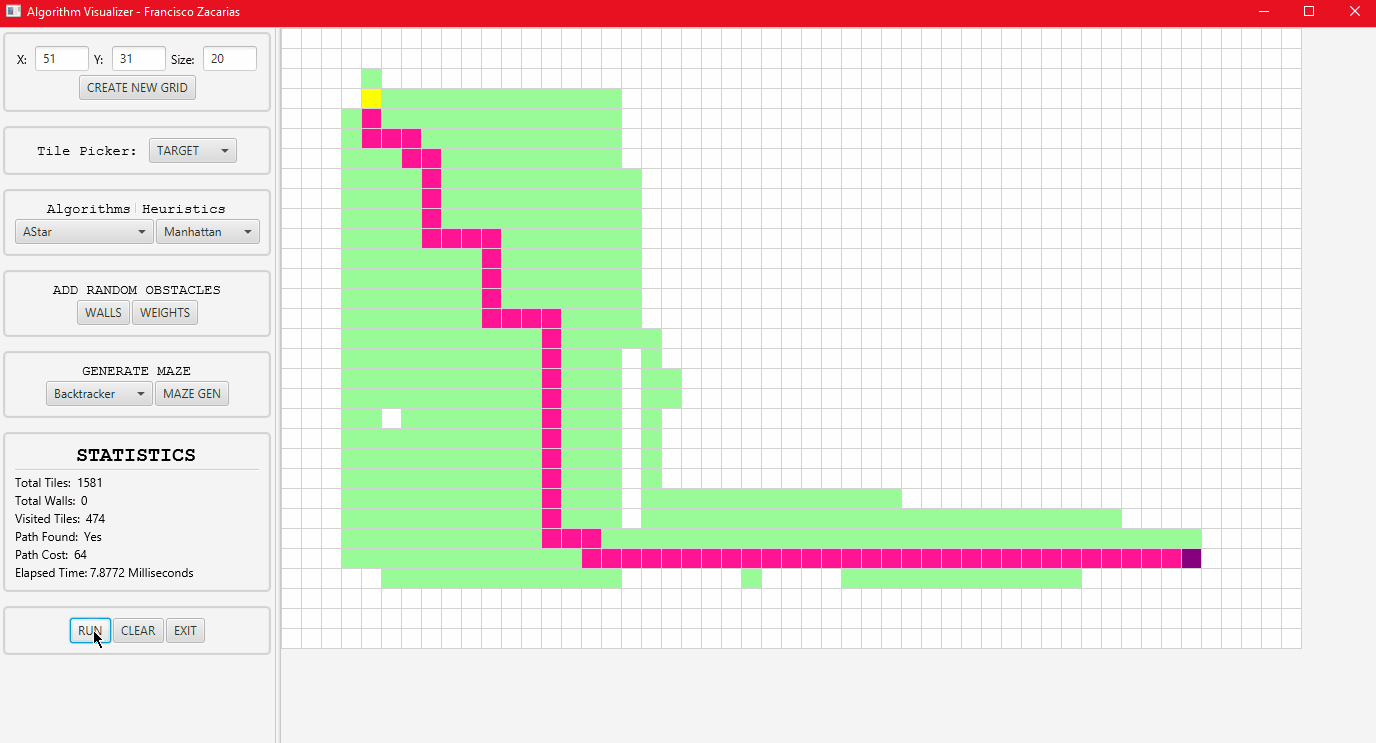 A* algorithm running with the Manhattan distance Heuristic.
A* algorithm running with the Manhattan distance Heuristic.
It's a much more simple pathfinding algorithm, and I would say not as useful (generally), as it is not the fastest, ignores weights and does not guarantee shortest path.
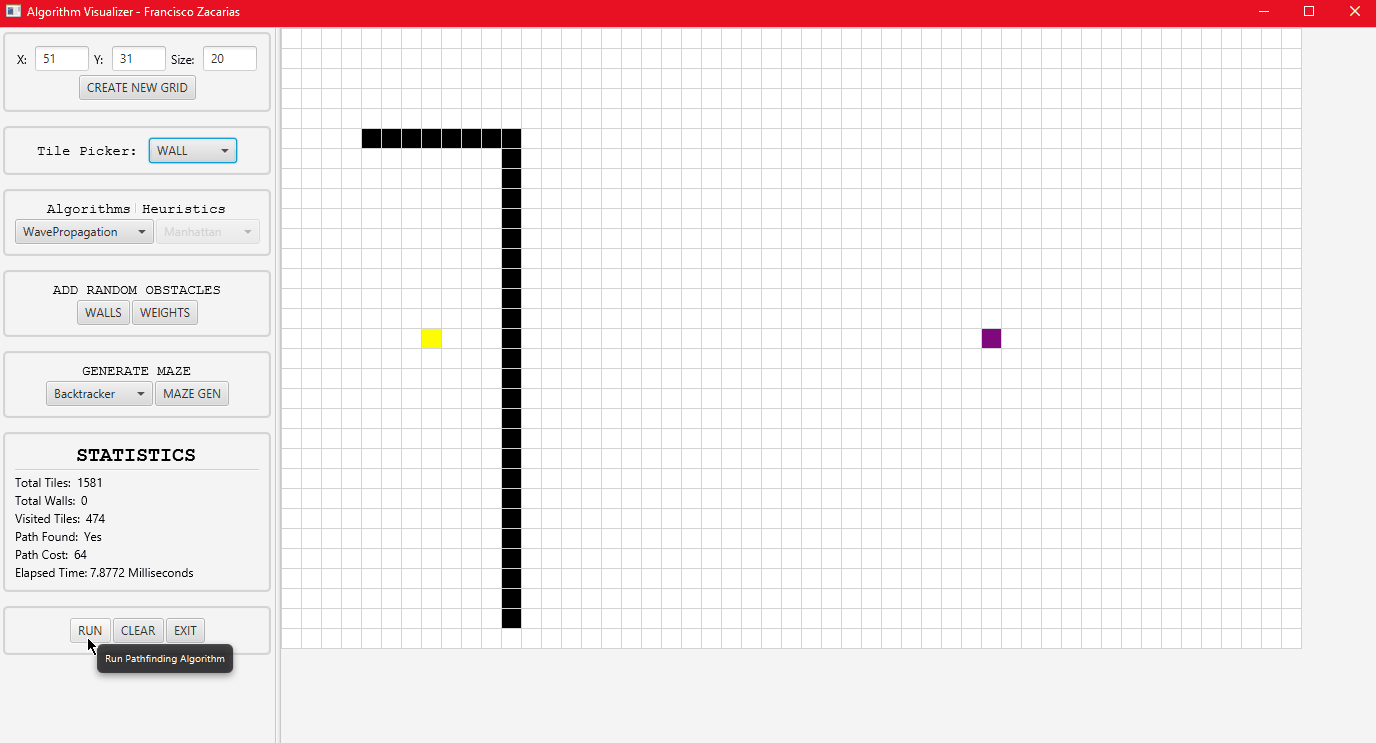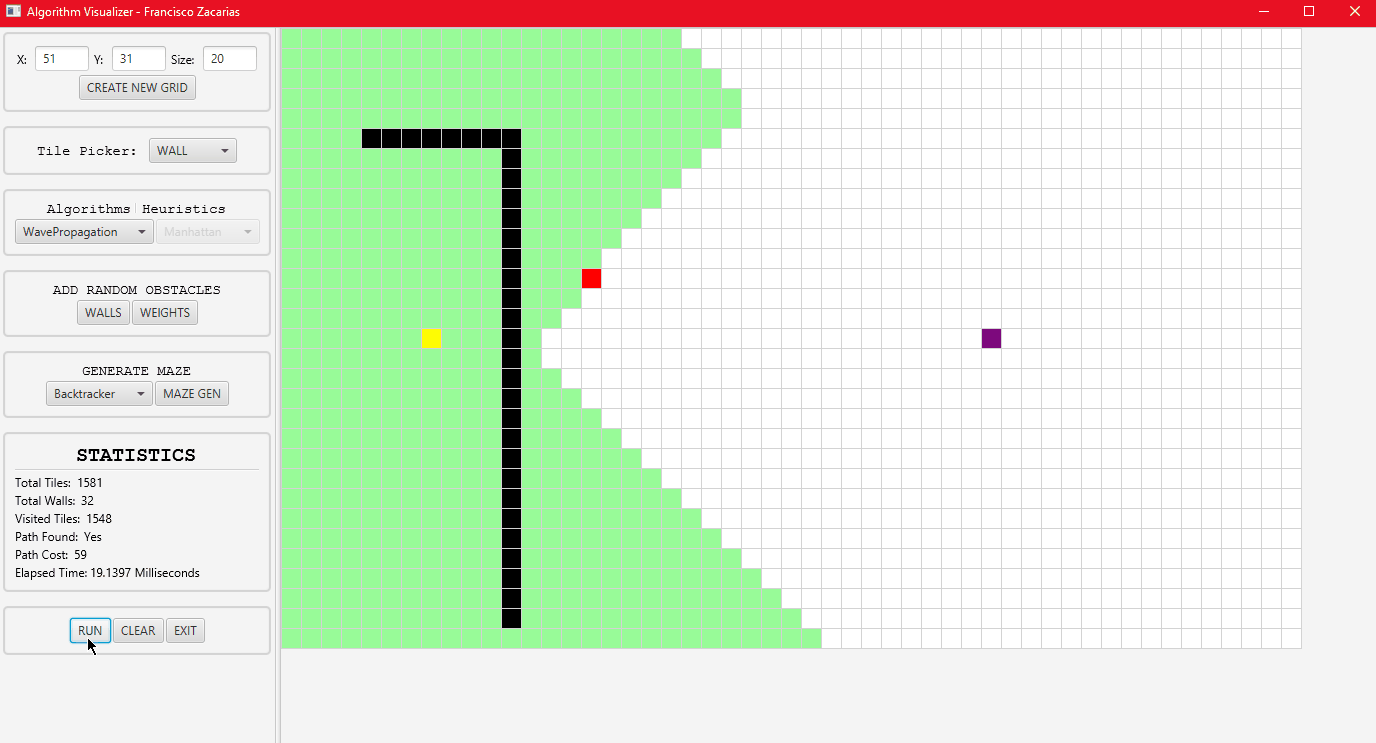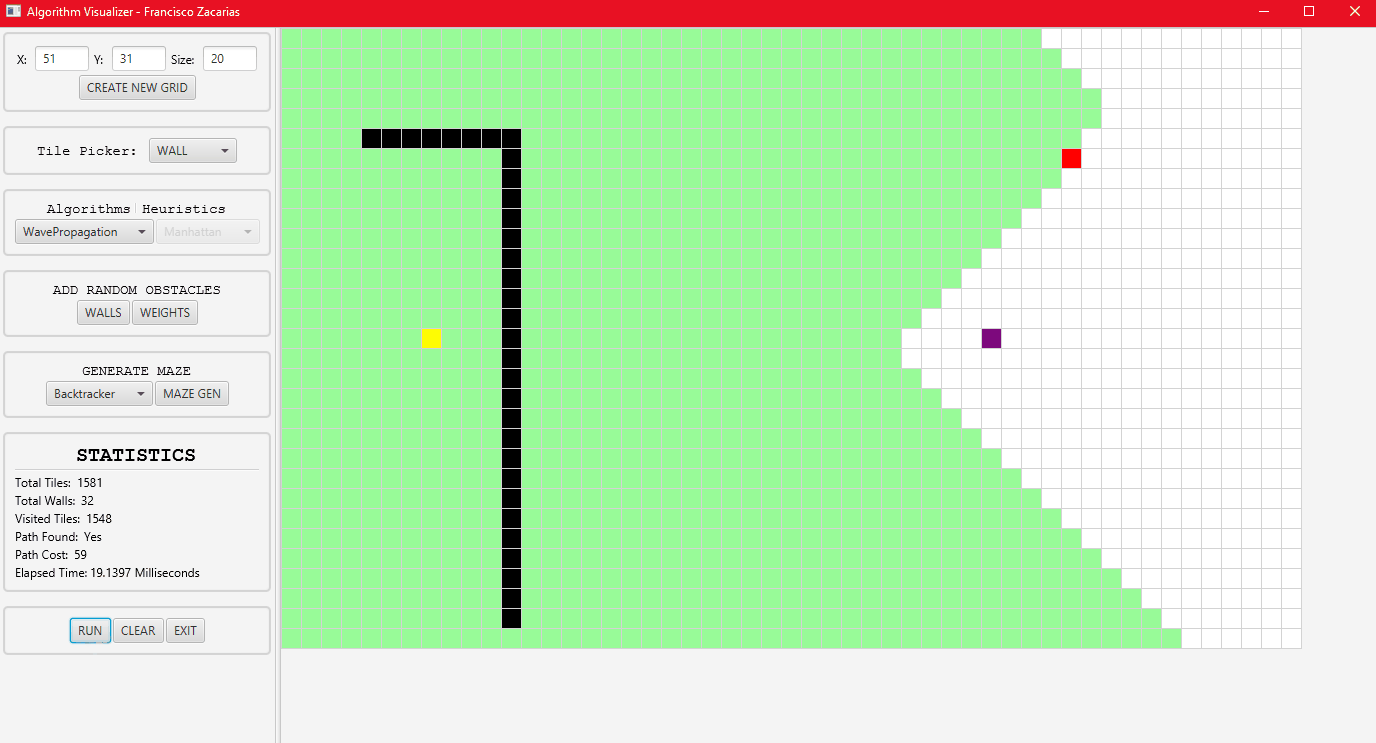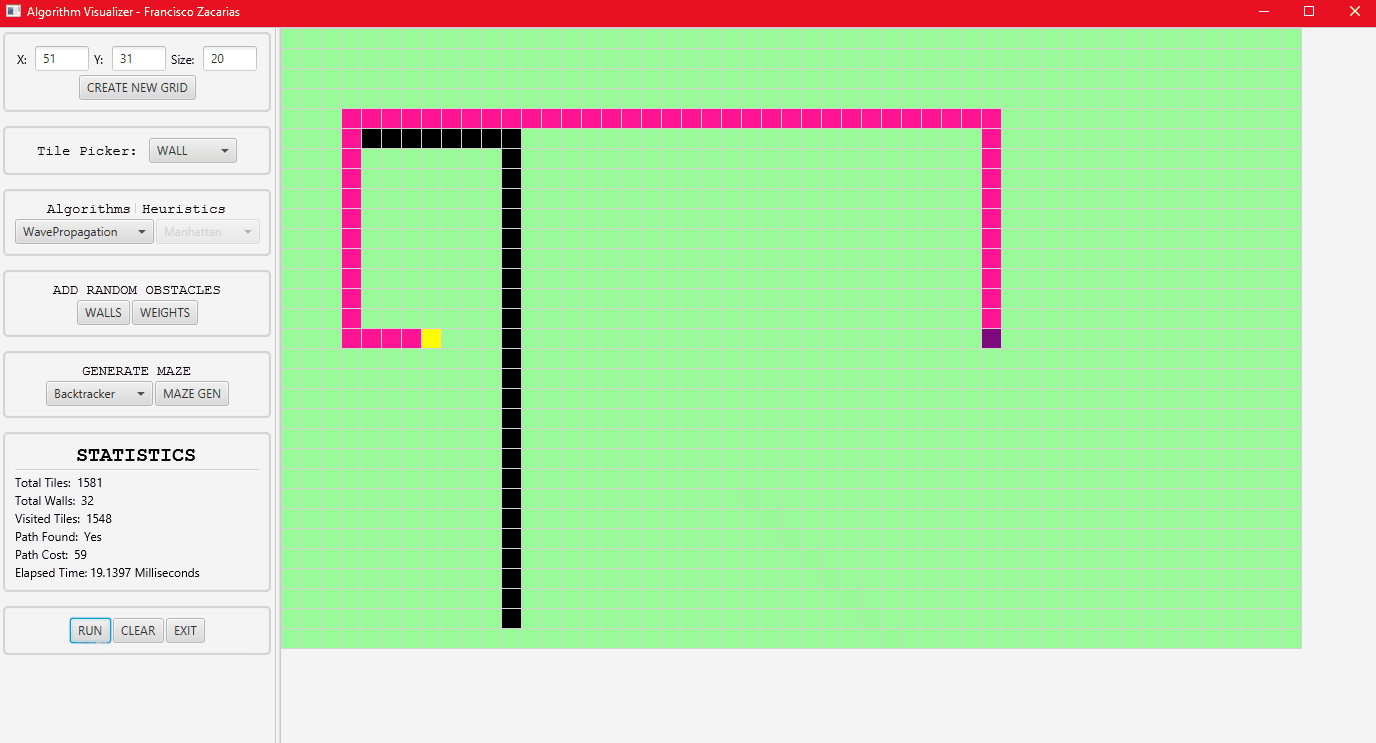 Wave propagation algorithm running.
Wave propagation algorithm running.
Before we take a look at the maze generation algorithms, I couldn't take another step without mentioning this great blog about it! Surely my job would be much harder had I not found it. Hats off to Jamis Buck.
This algorithm picks random directions in the grid to go to, as long as they have not been visited yet. If it sees itself stuck, it backtracks itself to the last node with an available neighbor. If no more are available, it backtracks back to the root node and the algorithm is complete.
![]() Recursive backtracker maze generation algorithm.
Recursive backtracker maze generation algorithm.
This algorithm is a twist on the Kruskal's algorithm for producing a minimal spanning tree from a weighted graph. Instead of pulling edges with the lowest weight, we pull random edges (or walls) and carve a path from there.
While it doesn't produce a particularly 'pretty' maze, the algorithm process does look cool!
 Kruskal's algorithm for maze generation
Kruskal's algorithm for maze generation
This algorithm, as well as the last one, has it's original purpose on producing minimal spanning trees. This approach differs from the previous by simply growing out of one point, instead of randomly growing throughout the grid.
 Prim's algorithm for maze generation.
Prim's algorithm for maze generation.
