Repository to store all my solutions and notes for the book JavaScript for Kids by Nick Morgan.
Each folder contains the solutions to the challenges of that chapter. I'm more used to Back-End development, so I wrote .js scripts and ran all of them in terminal with the following command:
node *path/to/script.js* # just change the path to the one in your computerp.s.: to run scripts that way, your machine needs to attend all requirements detailed in Requirements subsection.
That's probably not the best way to do this (lol), so feel free to call them in a .html file (as shown below) and see them in action in your favourite browser, or just copy and paste its code directly into your browser's console (just press the F12 key to open it :).
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<script src="path/to/script.js"> </script>
</html>To run the scripts on terminal (as I did), you'll need to have NodeJS installed in your machine. As I'm writing this README, I'm using Ubuntu 20.04 as operational system on my machine and present the steps I followed to install NodeJS and its dependencies. You may want to follow one of these tutorials if you're using a different OS:
Okay, if you're a Ubuntu user for a while (or any other Debian-based linux distro), you may think that installing NodeJS and its package manager NPM is as easy as this:
sudo apt install nodejs npmI did this and, surprisingly, it didn't work 'Out of the Box'. The problem was that the NPM and NodeJSversions available on the official PPAs didn't get along very well.
So, after reading lots of tutorials and testing many different forms of installing these two things, I find out that the best solution was to install them via NVM, which stands for Node Version Manager (it's useful to have NVM installed in your machine for plenty other reasons).
To get to the nitty-gritty, installing NVM can be done by just running one the following commands in your terminal:
curl -o- https://raw.githubusercontent.com/nvm-sh/nvm/v0.35.3/install.sh | bashor
wget -qO- https://raw.githubusercontent.com/nvm-sh/nvm/v0.35.3/install.sh | bashp.s.1: if you don't have curlor wget in your system yet, just run
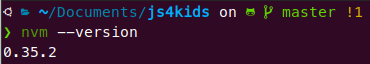
sudo apt install *package_name* # just change *package_name* to your desired choice (curl or wget)If all went well, the output of nvm --version should look like the following:
Now that NVM was successfully installed, we can install NodeJS and NPM by simply executing:
nvm install node # this will install the latest version of NodeJSPersonally, I recommend installing the LTS (Long Term Support) version by running
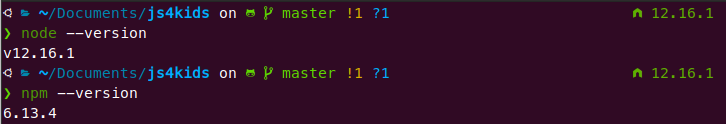
nvm install --lts # Currently, the LTS version corresponds to 12.16.1And voilà. NodeJS and NPM were successfully installed with this simple command. If you want to check, the output of node --version and npm --version both should look like the following:
Finally, you're all set. To run a .js file in terminal, just use
node *path/to/script.js* # just change the path to the one in your computerThe Node Version Manager proves to be really useful specially if you're working on different projects and need to use different versions of Node. To alternate between different versions, just do
nvm use --version # just change --version to the one you want to use, e.g., 10.10.0For example, to use the latest version of NodeJS, it would be as simple as
nvm use --latestTo install a specific node version, just run
nvm install --version # just change --version to the one you want to use, e.g., 8.9.1To list all installed versions in your system:
nvm lsFinally, to list all available versions on the remote repository:
nvm ls-remoteThis way, you can choose your desired version and install it in case you don't have it yet on your machine. :)
On the official NVM GitHub Repo there are lots of other useful commands and usage examples.