In this repository I'll store some personal study notes about D3.js and some example charts and projects I'm going to make in order to apply the new concepts and techniques I've just learned.
- 1-svg_basics: in this folder you are going to find some basic review notes about the
svgelement and how to use D3 to create and modify it on an HTML page. - 2-scales-and-axes: study notes and examples about how axes and scales work in D3 and how to add them to an
svggroup. - 3-dynamic: some examples and notes about
D3 updatepattern and transitions. - 4-interactive: gapminder example revisited to add some interactive elements, like event listeners and handlers, tooltips and selection boxes to make it change as a response to user's selection.
To visualize all D3 files appropriately, you need to set up a basic HTTP server in your local machine. Next, I present two easy ways to do this: one using Python 3 and a slightly more advanced one using Node JS and NPM (Node Package Manager).
p.s.: for the sole purpose of seeing the content in this folder, I personally recommend the Python alternative as it is easier to install and implement in any operating system. But if you already use Node JS or simply don't want to install Python for any reason, I also present a way to do this using Node JS.
First, for obvious reasons, you need to make sure that the Python 3 interpreter is installed in your system. To do this, just go to this web page, download the installation file according to your OS and follow the instalation steps.
If you are on linux, install Python can be as easy as running the following command (on Ubuntu):
sudo apt install python3 # this will install the latest Python 3 version available for your systemIf you're using other linux distribution, you need to replace apt for your distro's package manager.
p.s.: chances are that you already have Python 3 pre-installed. you may want to verify it first by running the commands in the following section.
Just open your terminal (or Windows command prompt) and type this:
python --version # this may call the Python 2 interpreter if you have it in your systemor
python3 --versionp.s.: On windows you may need to follow some more steps to add Python to your system's PATH. Here is a good reference to do this .
Once you have the Python 3 interpreter set up and running in your machine, to set up a http server is as simple as
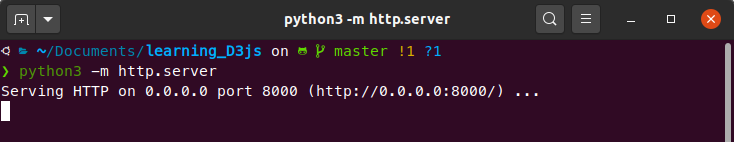
python3 -m http.serverYou'll see something like this in your terminal (or Windows cmd):
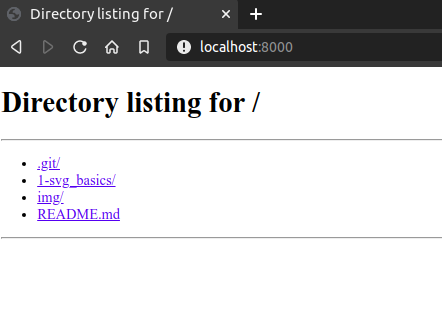
This means that the server is up and running at http://localhost:8000/. If you go to your favourite browser and navigate to this address, you should see this repo's structure like this:
To change the port, just execute
python3 -m http.server *port_number* # you can add any port number you likeAssuming you already have NodeJS and NPM installed (if you don't, see the following section for useful references), all you need to do is install the http-server package from NPM:
npm install -g http-server # this install it globally. To install locally, remove -g Finally, to start the server, just navigate to this directory in terminal and execute:
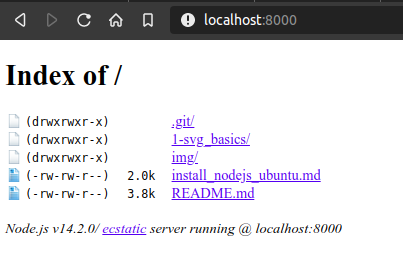
http-server -p 8000This will start the server at port 8000 and the result is similar to
Further options for the http-server library can be found here.
If you need instructions to install NodeJS and NPM, here are some references you can look up for:
Additionally, I added the steps I followed to install if on linux Ubuntu 20.04 on file install_nodejs_ubuntu. If you are using another linux distribution, you may want to try the same steps replacing apt for your distro's package manager (like dnf for Fedora and pacman for Manjaro).