- What is node JS?
- Architecture
- Web UI
- Node JS
- Mongo DB
- Coding time
Node.js is an open-source, cross-platform JavaScript run-time environment that executes JavaScript code outside the browser. Historically, JavaScript was used primarily for client-side scripting, in which scripts written in JavaScript are embedded in a webpage's HTML and run client-side by a JavaScript engine in the user's web browser. Consequently, Node.js represents a "JavaScript everywhere" paradigm, unifying web application development around a single programming language, rather than different languages for server side and client side scripts.
Nodejs is a platform that uses javascript to execute server-side code. Node is particularly used in RTA (Real Time Application) or SPA (Single Page Application) like with React, Angular or Vue.js. Node is not limited to web development and is also used to make applications like with Electron.
In browsers like Chrome, FireFox and others, there is always a Javascript engine. It is this engine that allows the browser to understand the JS code we write. You all know it, we use it every day.
One day, a gentleman named Ryan Dahl had the brilliant idea to take the JS engine from Chrome (the V8 version) and use it outside the browser. The nodejs platform was born.
Let's imagine that we want all users (clients) of a chat to be notified when a new user logs in.
The new client will send a "newConnection" event to the server. The server will send him an event to all other users triggering a message that will appear on the screen of the other users. This is more or less the same as the addEventlistener() we use in js on the browser side.
Not-blocking includes Asynchronous. That is, the instructions will run in the order you wrote them, but if an operation takes a long time to execute, the following operations will still run. With synchronous code, this will not be the case. The code will freeze until the operation is executed.
Let's imagine that we have to create three operations.
In synchronous - With a blocking code.
The operations will therefore be carried out one by one. They will wait until the previous operation is finished. This can be long in some cases.
<Task 1 ... >
-------------<Task 2 ... >
--------------------------<Task 3 ...>
Asynchronous - With a not-blocking code.
While an operation is being executed, the following operations are also executed. They do not wait for the end of task 1.
Task 1 ... >
-----Task 2 ... >
-----------Task 3 ... >
Or to better illustrate:
Its execution will be faster. But then, asynchronous can bring some errors if we start thinking like in PHP (or any other synchronous programming language).
EXAMPLE Look at the code below and copy and paste it into the console.
console.log('first line')
setTimeout(() => { console.log('2nd asynchronous line executed')}, 0);
console.log('3rd line')The result will give
first line
3rd line
2nd asynchronous line executedAs you can see, the 3rd log console is executed before the second one. An encoder used to synchronous coding may be confused when he comes across a case like this one (very often in JS)
**Caution, do not confuse synchronous, asynchronous, mono-thread and multi-thread.
Node is a relatively low level language. That is to say that it is a very light platform and you have to add the modules you want to use one by one. To make our task easier, we have created a manager for these famous modules, which is called npm.
Remember that nodeJS is a run-time environment that enables javascript frameworks/libraries. As a metaphor, imagine that nodeJS is the one that makes it possible to create a web of different nodes, those nodes can be any javascript-code you want to link to your app.
NodeJS’s most popular used framework is ExpressJS (imagine Express JS being one of NodeJS nodes for your app).
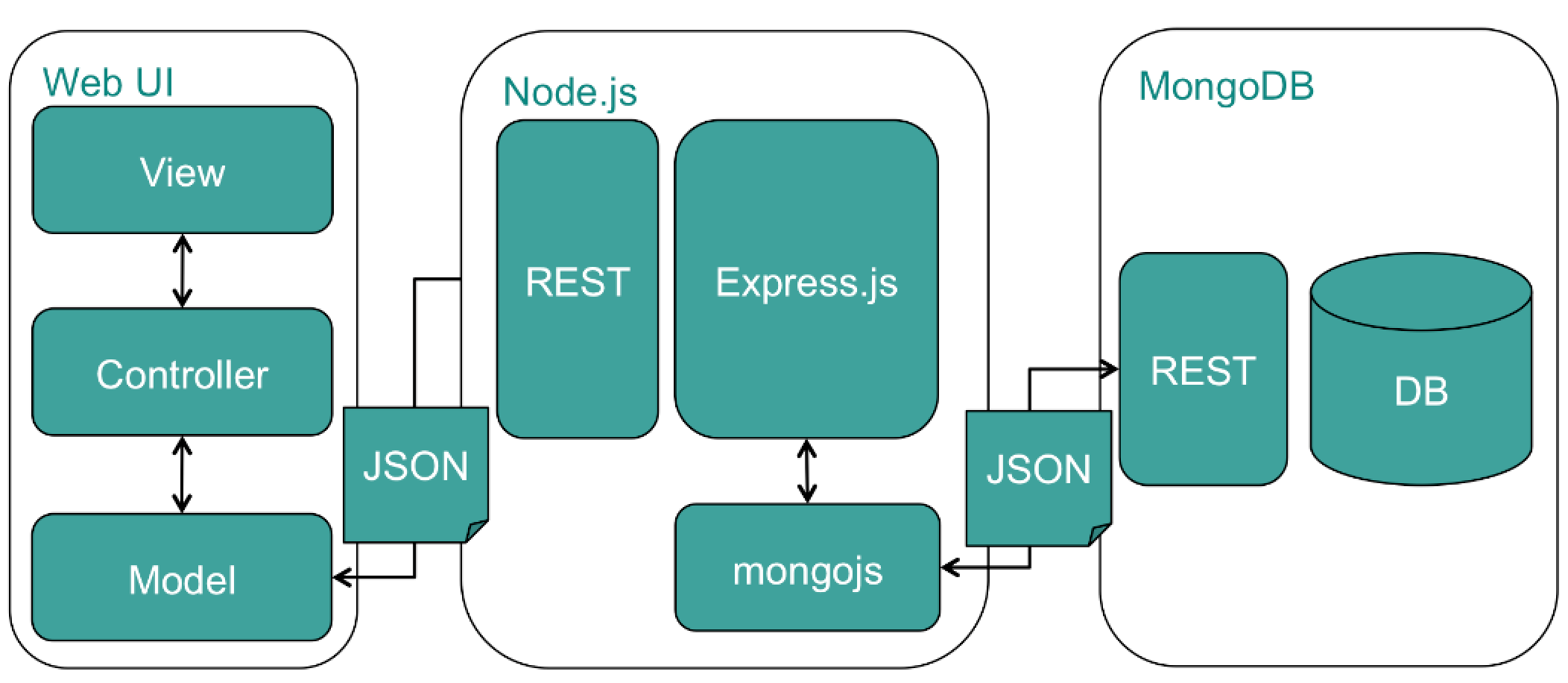
An app's client, user interface, front-end, the web UI. Maybe you are familliar with HTML being rendered from the back-end, as does for example PHP or Rails, in the image above the client is a seperate tier. Why? Because today there is a lot of optimization potential doing it this way, MVC clients. The web UI communicated with node JS (the back-end) in JSON format and the different kinds of data requests represent the M (model) in MVC. A web UI's client also has a structure to orchestrate incoming data, more than just displaying it, that's the C (controller) in MVC. The web UI's rendering of HTML (+ data) is what we call the V (view) in MVC.
Client <-> Server communication does so through API endpoints. In the chart's example the API is designed RESTfully. This makes routes in your app rather predictable structure and better dev-team synergy. REST is the most common used API design. The importance of using node for Javascript projects equals needing solid earth before building a house. We take the earth beneath us for granted, don't do the same for node. Like most tech-stacks MERN (Mongo, Express, React, Node), MEAN (Mongo, Express, Angular, Node) and other tech-stacks. Node JS is the industry standard and it's not going anywhere, worth learning!
The DB of choice is Mongo (no-sql). Though any kind of Database can communicate with Express, choose the right parser/sequalizer for when you decide to go SQL. A data-entry in NO-SQL is a document, i.e. a user, a car, etc. Grouping this documents is a collection. An app's Database in no-sql has many collections, and those collections contain documents.
ok, ready to be jS pro ?