The GMBA Mountain Inventory v2.0 is an inventory of 8329 mountain ranges across the world, stored in a shapefile with a growing attribute table. Here, we provide a few R functions to explore the inventory and select mountain ranges based on user define criteria for subsequent analyses.
When using the inventory and/or gmbaR for your work, please cite the inventory publication as well as the inventory dataset as follows:
The GMBA Mountain Inventory v2.0 consists of two main files that are available on the EarthEnv project website:
The inventory shapefile GMBA_Inventory_v2.0.shp contains the spatial data of the GMBA Inventory v2.0.
The selection tool Selection file.xlsx is an Excel sheet providing the hierarchy data of the GMBA Inventory v2.0. When opening this in Excel, you have access to the full mountain inventory except the spatial data. You can manually select those mountain ranges you want to further use in your work in column AA ("Range_Selector") of the Excel sheet and then save the file for further use.
With gmba_ids_from_selectiontool you can read the selected IDs directly into R. Alternatively, you can use gmba_select() from gmbaR to filter and select mountain ranges from the inventory, or use one of the other functions listed below to get mountain range IDs based on different attributes.
If needed, use install.packages("devtools") to install the devtools package.
Then, use devtools::install_github("GMBA-biodiversity/gmbaR") to install gmbaR.
Before working with the GMBA Inventory v2.0, you need to read it to R. This can be done using gmba_read, which works for reading the inventory directly from the web or from your local drive. Note: gmba_read is to be used without an assignment operator (e.g. "<-"). For example, run gmba_read("web").
Thereafter, the inventory is stored in the function gmba_inv (similarly to the gmbaR functions starting with "gmba_"). This is because the inventory is used as reference/resource in the other gmbaR functions and therefore should not be renamed or edited. If you want to explore the inventory manually, you can do so with View(gmba_inv()). With objectname <- gmba_inv() you can turn the inventory into an object and further work with it as desired.
Next to reading the inventory, the main functionalities of gmbaR are to
- explore the GMBA Inventory v2.0 (gmba_search_names, gmba_names_from_ids),
- get mountain range IDs (gmba_ids_from_names, gmba_ids_from_points, gmba_ids_from_elevation, gmba_ids_from_area, gmba_ids_from_countries, gmba_lower_id_from_higher, gmba_ids_from_spi, gmba_ids_from_selectiontool), and
- subset the inventory based on mountain range IDs (gmba_subset).
The function gmba_select() can be used for all three functionalities.
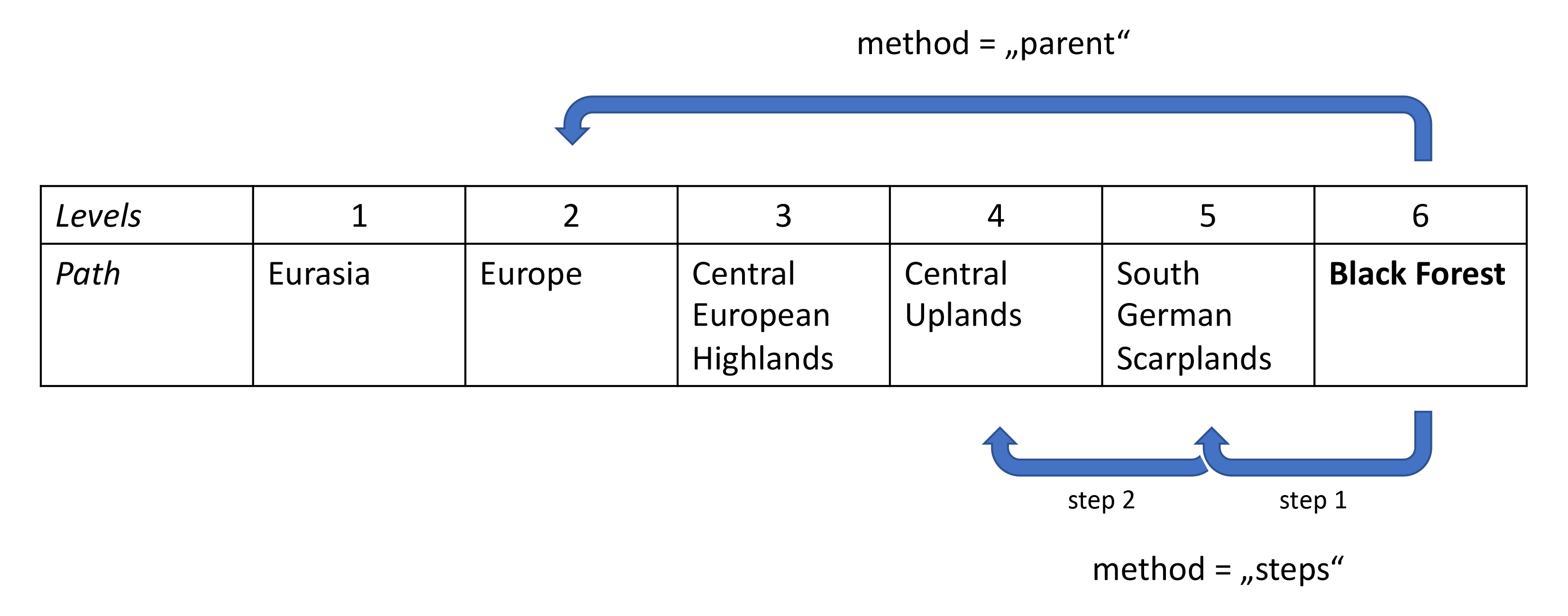
For analyses across scales, gmba_lower_id_from_higher() allows to take a certain mountain range, for example the Black Forest (ID = 11175) and get a certain lower level from its GMBA Inventory v2.0 hierarchy: With method = "parent", you can choose a specific lower level of the given input ID; with method = "steps", you can specify the number of lower levels you want to get from perspective of the given mountain range ID. See the figure for a visual explanation of the two methods, with lowerlevel_numeric = 2:
For more details and examples, see the help of the package or functions.