This material is based upon work supported by the Defense Advanced
Research Project Agency (DARPA) under Contract No. HR0011-18-C-0013.
Any opinions, findings, conclusions or recommendations expressed in
this material are those of the author(s) and do not necessarily
reflect the views of DARPA.
Distribution Statement "A" (Approved for Public Release, Distribution
Unlimited)
npm install
cd ./back-end && npm install- Follow instructions in the back-end README
cd ./front-end && npm installnpm run startfrom the front-end directory- Follow isntructions in front-end README
In the back-end, serverless is pinned to 1.44.1 this should be updated periodically
On both the front-end and the back-end there are pre-commit hooks installed which will only allow a commit to happen if all of the files pass the linter.
NOTE: The following process outlines the general build process for production when there are changes to make to the FETT Portal codebase and for updates to AMI's. If there are changes to just the AMIs then only the Updating AMI's section is necessary. For triggering a build on another branch follow the same process but replace the target branch receiving the pull request where webhooks have been setup.
- Make sure
developbranch on github has the changes needed for the new build. - Create pull request (PR) from
developbranch tomaster. - PR requires a reviewer and approval.
- Merge PR
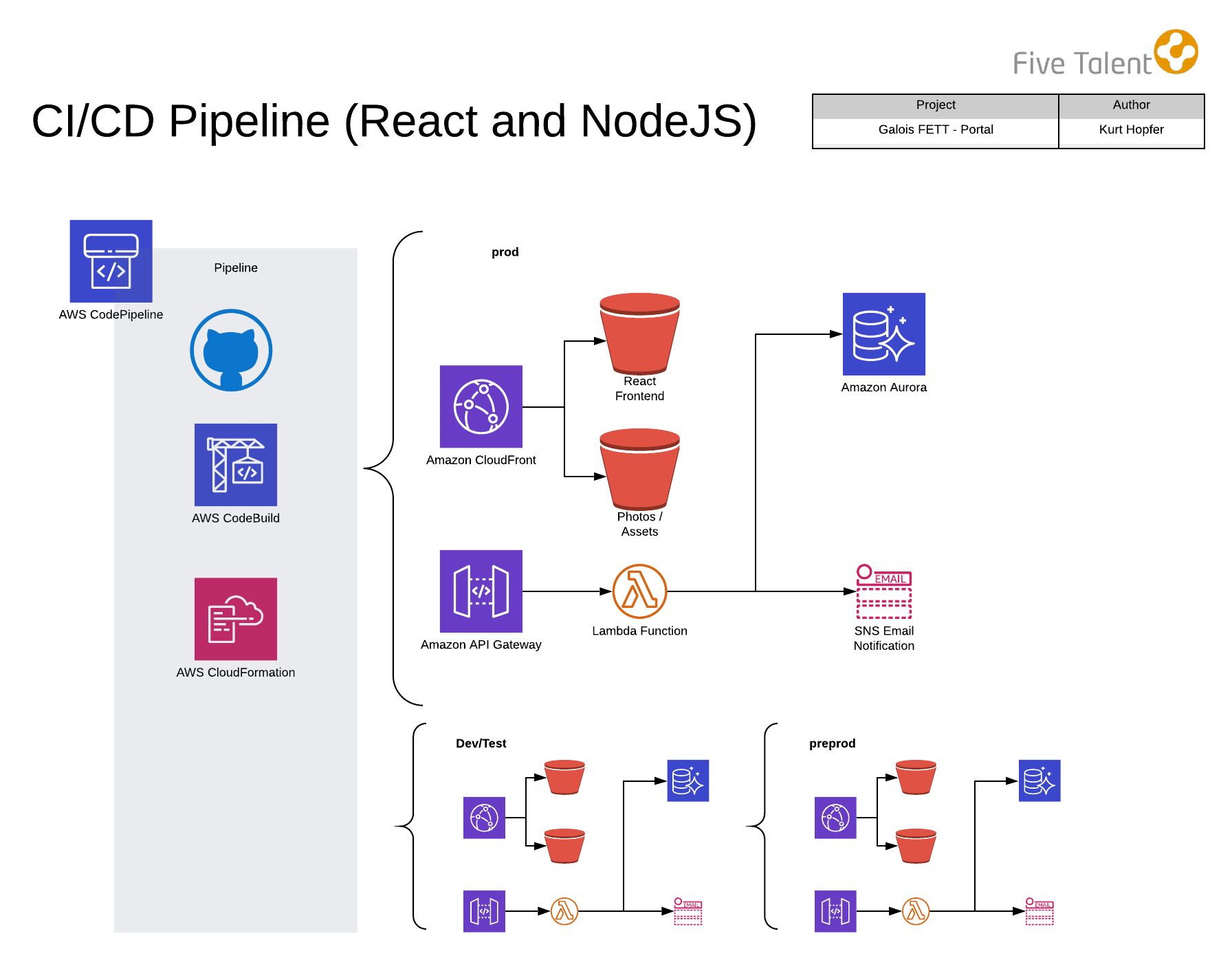
With proper setup, the CICD process should be automated. After approval an authorized github user can merge the PR to master triggering the Amazon Web Services (AWS) CodePipeline for CICD. The CICD process will start with the backend setting up the Node environment, deploying with Serverless Framework, updating Cloudformation stacks, and then running migrations. The frontend build then sets up it's environment, environment variables and syncs static front-end content with the AWS S3 hosting bucket. This is followed by log files being synced with S3 buckets for learning documents and CICD artifacts.
In the AWS Console CodePipeline section there is a live logging tool for the CICD process that can be used to monitor progress. The console should say in progress after the github hook as been triggered. After clicking on the pipeline the user should see a link to the build logs in order to see the near-live log outputs of the process.
-
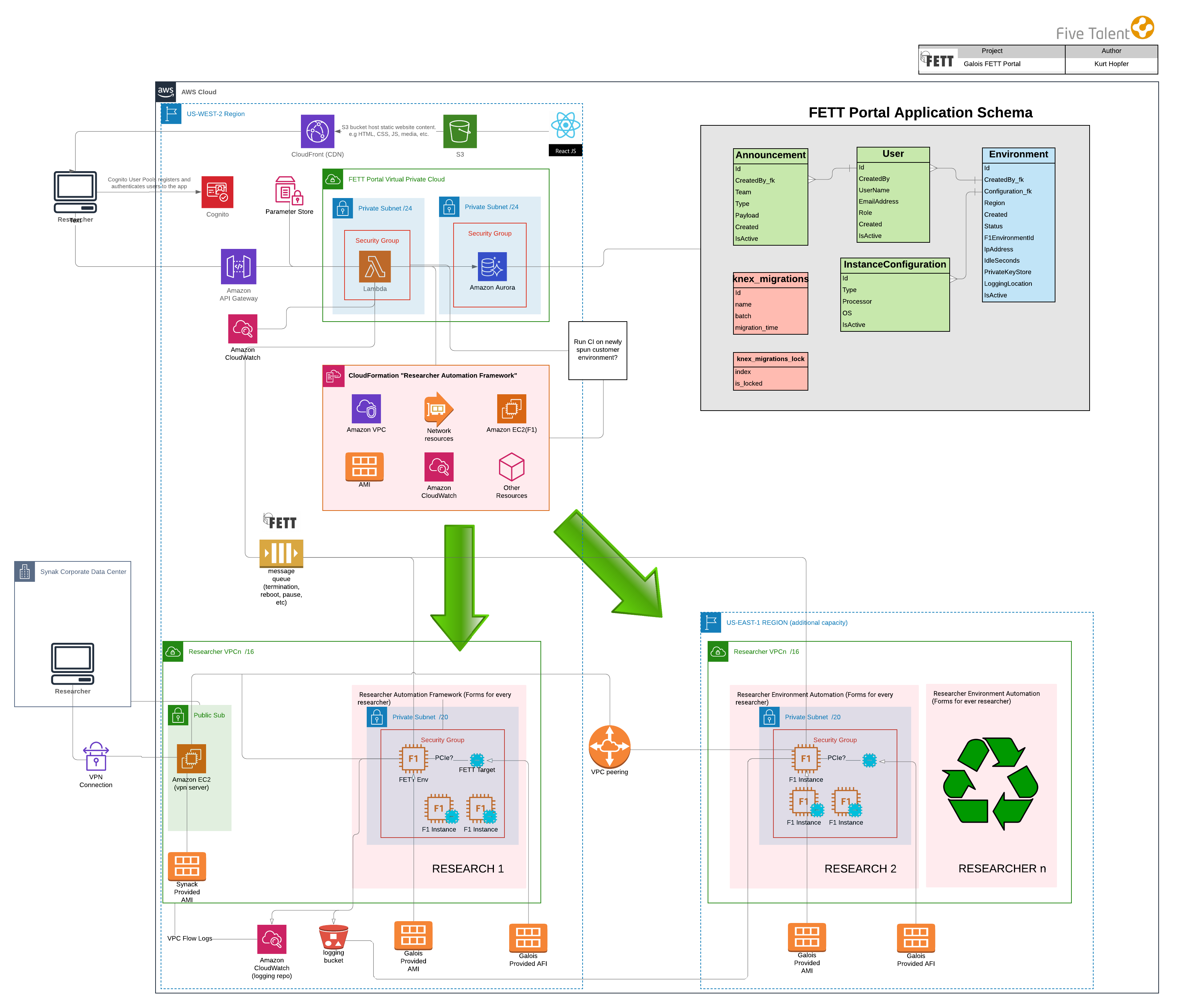
After the build process is complete, it is necessary to update database references to the correct AMIs for each region (i.e., us-west-2 and us-east-1). The AWS Aurora DB cluster is housed behind a security group which limits its possible connections. The easiest way to communicate with the DB outside of the serverless functions is to use AWS Query Editor which can be accessed in the AWS Console RDS Section. A link in the sidebar will take the user to Query Editor.
-
In the query editor modal select the DB from the dropdown followed by the Username/Password which should be pulled in from AWS Secrets Manager. Finally, enter the schema name
FettPortaland press enter. -
There are two AMI Ids which are the same for each each instance configuration differing only for region. Add an SQL statement in the text box to update the AMIs, e.g.,
UPDATE InstanceConfiguration SET AMIId_West = "ami-04675bd812151965d", AMIId_East = "ami-0e618934f4e7a2f00";NOTE: The AMIs will br provided by the FETT Target Team upon updating them. -
Test that each of the instance configurations is working properly by logging in to the portal with ftsresearcher login and launch an instance of each type. After spinning up instances of each test that each can also be terminated.
-
Repeat step 4. Then going back to the query editor change the region for the ftsresearcher,
UPDATE User SET Region = "us-west-2" WHERE Id = 2, and test step 4 twice more. Change the ftsresearcher back to region = 'us-east-1'.
Logs for CICD Process are captured in the AWS Console under CodePipeline. If there is trouble with completing the build process this is the best place to look for hints to where issues may have arisen. If the new configuration of the portal and associated AMIs are causing errors while launching instances from the portal, logs are created during several steps. AWS Cloudwatch is used to handle logging of the initiation functions and internal FETT Target logs. The startup serverless functions ( createEnvironmentRecord and createResearcherInstance ) first sync the launch with the db and handle spinning up an AWS EC2 Instance with a script to begin the FETT Target spinup process. User-Logs will tell the user what was included in the initiation script. Fett-Logs will show logs from the Fett Target spinning up and handling termination requests. The serverless function for handling termination and spinup successes that sync with the db and if needed stop an EC2 is sent a message from the FETT Target with AWS SQS. The logs for this function are under receiveStatusSignal.