distributed-algorithms-graphs-simulation
Info:
Simulation of synchronic distributed algorithms over weighted directed networks implemented in Python
Watching Graphs
python3 Graph.py N f b
where N is the number of nodes, f the Erdos Renyi probability, and b can be 0 or 1 to determine if it is undirected (1) or not (0).
To make the following picture the command was
python3 Graph.py 8 0.3 1.
Leader Election (FloodMax)
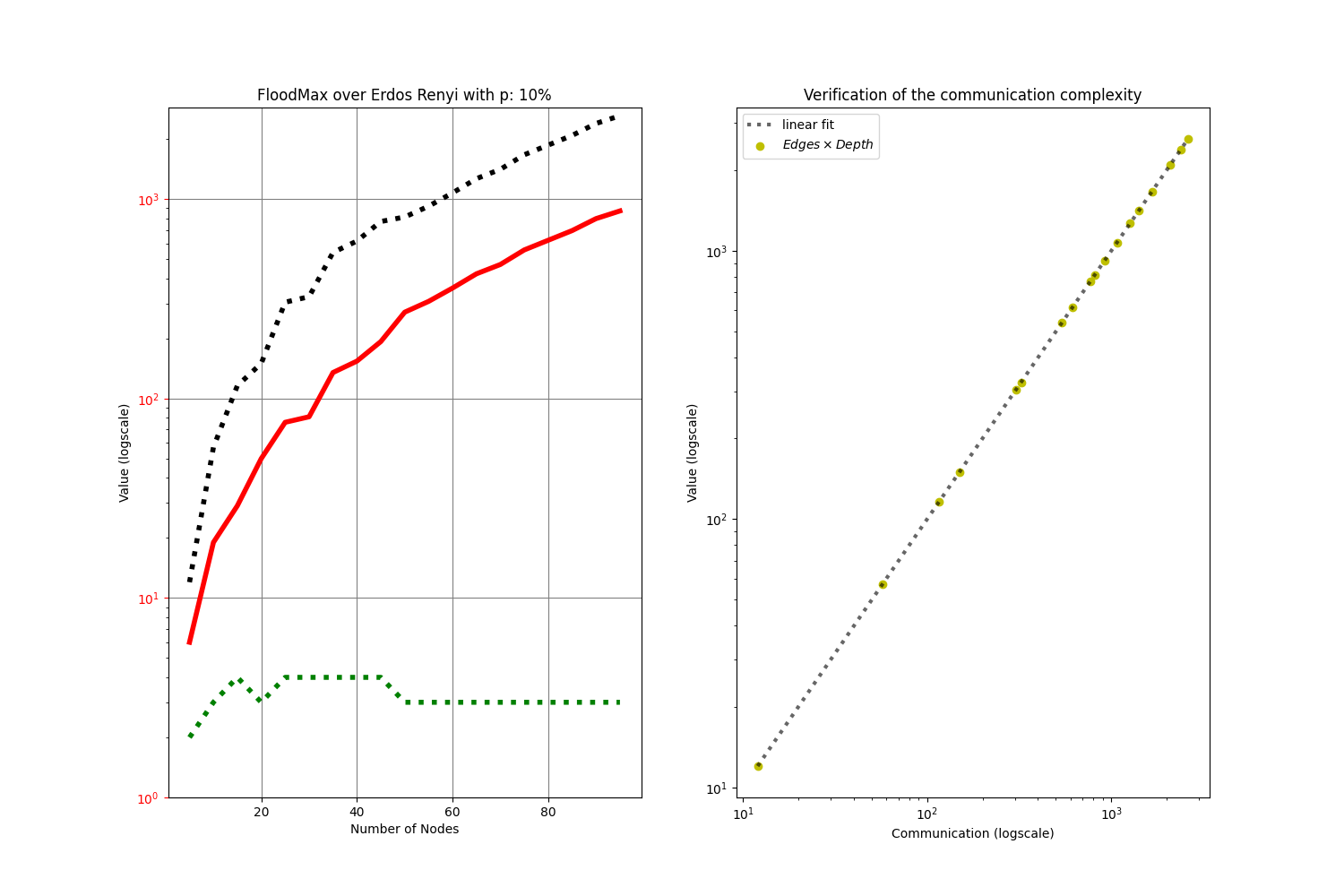
The distributed algorithm called FloodMax is able to elect a leader.
From the raw simulation results (left), it can be noted (right) that the communication complexity is O(|Edges|Depth) (p.54 Distributed Algorithms, Nancy Lynch)
To produce the simulation run ./FloodMax.sh
Tree Building (SynchBFS)
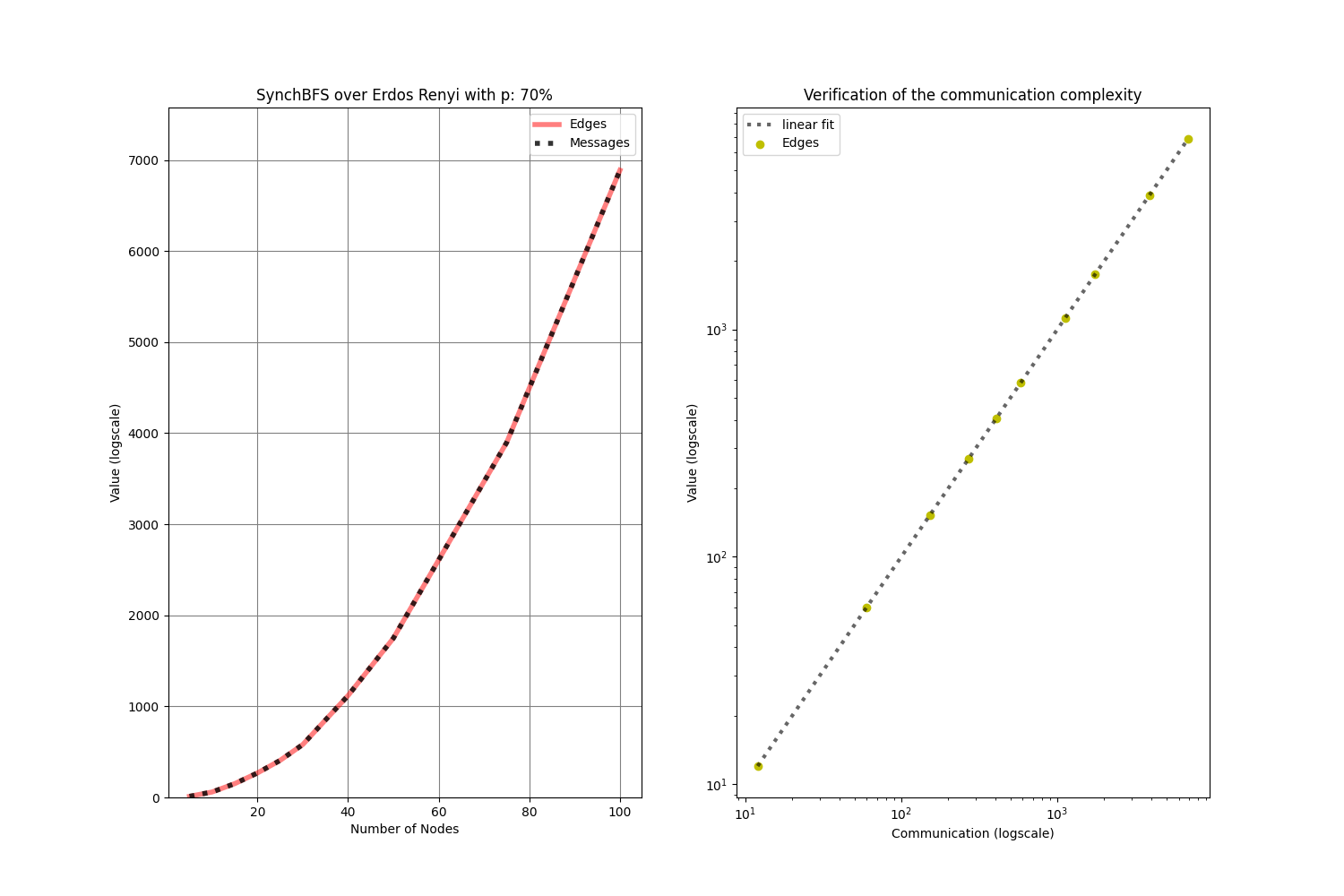
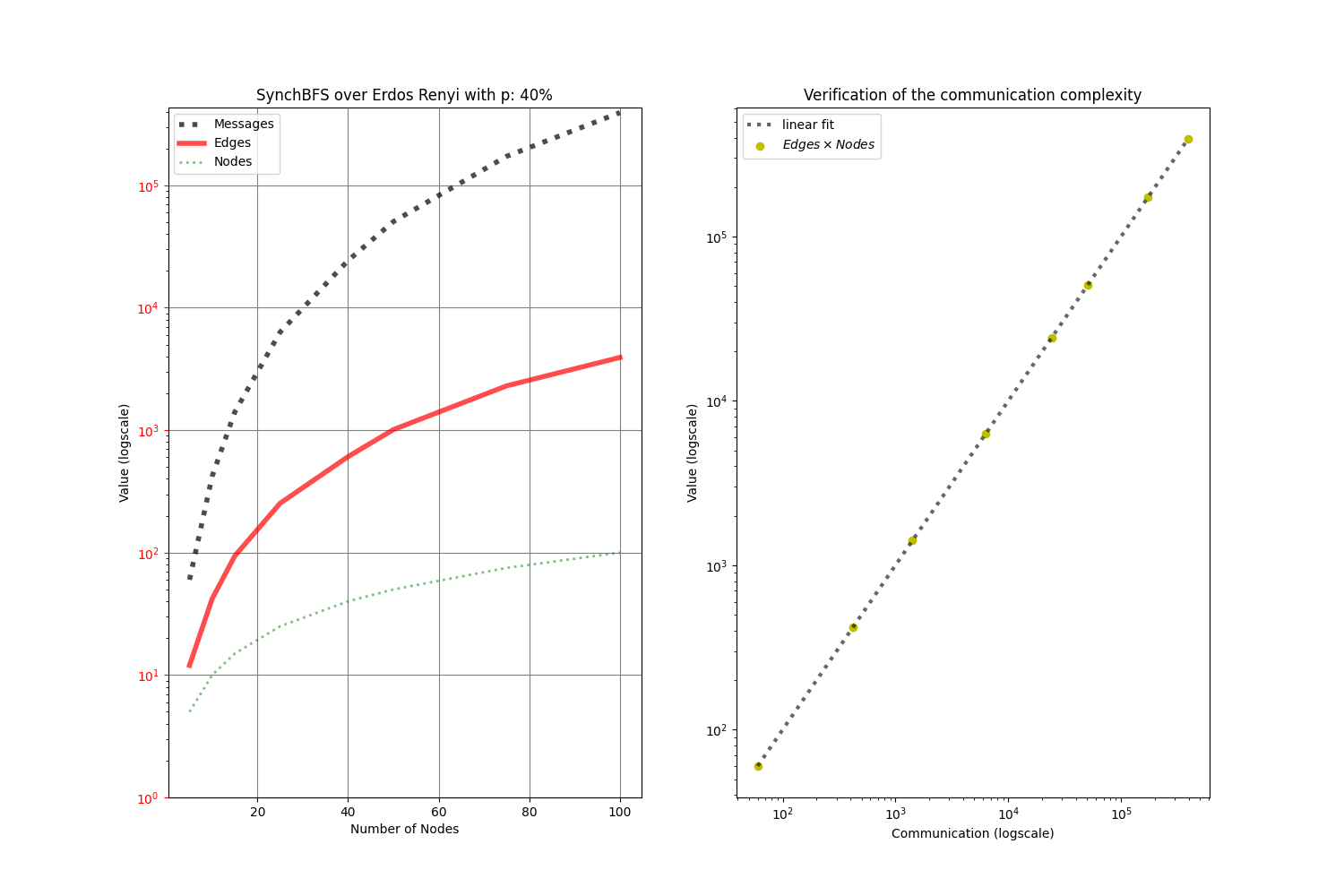
In synchronous networks, as those here simulated, the distributed algorithm called SynchBFS is able to build the breadth-first tree.
From the raw simulation results (left), it can be noted (right) that the communication complexity is O(|Edges|) (p.58 Distributed Algorithms, Nancy Lynch)
To produce the simulation run ./SynchBFS.sh
Routing (BellmanFord)
The distributed algorithm called BellmanFord is able to build the optimal path for routing.
From the raw simulation results (left), it can be noted (right) that the communication complexity is O(Nodes|Edges|) (p.62 Distributed Algorithms, Nancy Lynch)
To produce the simulation run ./BellmanFord.sh
Configuration
The probability of the Erdos Renyi graph p and the exact sequence of number of nodes [N1,...,Nm] can be configured at each simulation's main file.