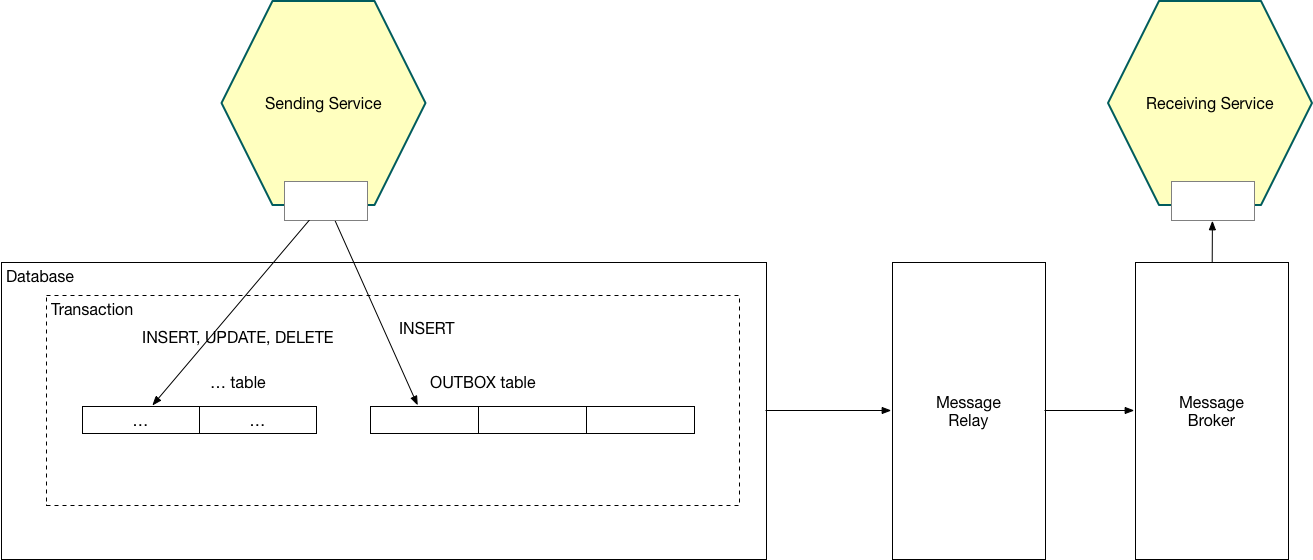
The Eventuate Tram framework enables a Java/Spring application to send messages as part of an database transaction. This enables an application atomically update state and send a message or a domain event. It is a foundation of ensuring data consistency within a microservice architecture.
Eventuate Tram (which was formerly known as Tarr) is described in more detail in my book Microservice Patterns. It provides several messaging abstractions:
-
messaging - send and receive messages over named channels
-
events - publish domain events and subscribe to domain events
-
commands - asynchronously send a command to a service and receive a reply
Eventuate Tram messaging implements the Application events pattern.
An message producer inserts events into an OUTBOX table as part of the ACID transaction that updates data, such as JPA entities.
A separate message relay (a.k.a. CDC service) publishes messages to the message broker.
The message relay works in one of two ways:
-
Transaction log tailing - currently implemented for MySQL
-
Polling - for other databases
There are the following examples applications:
-
Todo list - a Java/JPA/Spring Boot Todo list application, which publishes domain event using Eventuate Tram
-
Customers and Orders, which is built using the Eventuate Tram Sagas framework
Don’t hesitate to create an issue or see
-
[Mailing list](https://groups.google.com/d/forum/eventuate-users)
-
[Slack](https://eventuate-users.slack.com). [Get invite](https://eventuateusersslack.herokuapp.com/)
-
[Contact us](http://eventuate.io/contact.html).
Send a message using MessageProducer:
public interface MessageProducer {
void send(String destination, Message message);
}Receive messages using:
public interface MessageConsumer {
void subscribe(String subscriberId, Set<String> channels, MessageHandler handler);
}See this example of transactional messaging.
The domain event package builds on the core APIs.
Publish domain events using the DomainEventPublisher interface:
public interface DomainEventPublisher {
void publish(String aggregateType, Object aggregateId, List<DomainEvent> domainEvents);
...Subscribe to domain events using a DomainEventDispatcher:
public class DomainEventDispatcher {
public DomainEventDispatcher(String eventDispatcherId,
DomainEventHandlers eventHandlers,
...) {
...
}Handle the events using DomainEventHandlers:
public class RestaurantOrderEventConsumer {
public DomainEventHandlers domainEventHandlers() {
return DomainEventHandlersBuilder
.forAggregateType("net.chrisrichardson.ftgo.restaurantservice.Restaurant")
.onEvent(RestaurantMenuRevised.class, this::reviseMenu)
.build();
}
public void reviseMenu(DomainEventEnvelope<RestaurantMenuRevised> de) {See this example of transaction events.
Transaction commands are implemented using transactional messaging.
Send a command using a CommandProducer:
public interface CommandProducer {
String send(String channel, Command command, String replyTo, Map<String, String> headers);
...
}Subscribe to commands using a CommandDispatcher:
public class CommandDispatcher {
public CommandDispatcher(String commandDispatcherId,
CommandHandlers commandHandlers) {
...
}Handle commands and send a reply using CommandHandlers:
public class OrderCommandHandlers {
public CommandHandlers commandHandlers() {
return CommandHandlersBuilder
.fromChannel("orderService")
.onMessage(ApproveOrderCommand.class, this::approveOrder)
...
.build();
}
public Message approveOrder(CommandMessage<ApproveOrderCommand> cm) {
ApproveOrderCommand command = cm.getCommand();
...
}See this example of transactional commands.
The artifacts are in JCenter. The latest version is:
There are the following API artifacts:
-
io.eventuate.tram.core:eventuate-tram-messaging:$eventuateTramVersion- core messaging APIs -
io.eventuate.tram.core:eventuate-tram-events:$eventuateTramVersion- domain event API -
io.eventuate.tram.core:eventuate-tram-commands:$eventuateTramVersion- commands/reply API
There are the following 'implementation' artifacts:
-
io.eventuate.tram.core:eventuate-tram-jdbc-kafka:$eventuateTramVersion- JDBC database and Apache Kafka message broker -
io.eventuate.tram.core:eventuate-tram-in-memory:$eventuateTramVersion- In-memory JDBC database and in-memory messaging for testing
In addition to a database and message broker, you will need to run the Eventuate Tram CDC service. It reads events inserted into the database and publishes them to Apache Kafka. It is written using Spring Boot. The easiest way to run this service during development is to use Docker Compose. The Eventuate Tram Code Basic examples project has an example docker-compose.yml file.