MorseTranlator
A bit of history
Morse code is a character encoding scheme used in telecommunication that encodes text characters as standardized sequences of two different signal durations called dots and dashes or dits and dahs. Morse code is named for Samuel F. B. Morse, an inventor of the telegraph. Link
Before the invention of the telegraph, most messages that had to be sent over long distances were carried by messengers who memorized them or carried them in writing. These messages could be delivered no faster than the fastest horse. Messages could also be sent visually, using flags and later, mechanical systems called semaphore telegraphs, but these systems required the receiver to be close enough to see the sender, and could not be used at night.
The telegraph allowed messages to be sent very fast over long distances using electricity. The first commercial telegraph was developed by William Forthergill Cooke and Charles Wheatstone in 1837. They developed a device which could send messages using electrical signals to line up compass needles on a grid containing letters of the alphabet. Then, in 1838, Samuel Morse and his assistant, Alfred Vail, demonstrated an even more successful telegraph device which sent messages using a special code - Morse code. Link
How does it work
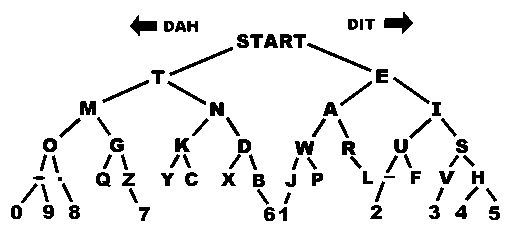
Different people have different styles of learning. Amateur Radio Operator KB3BYT in Jim Thorpe, Pennsylvania, suggests that this code listening tool may be very helpful to some beginners just getting started on learning the International Morse Code. If it looks like it might be helpful to you, give it a try. Here are his steps for using the Decoding Tree chart below to learn Morse Code:
- Print the chart on your printer.
- Place your pencil on START and listen to Morse Code.
- Move down and to the right every time you hear a DIT (a dot).
- Move down and to the left every time you hear a DAH (a dash). Link
Examples:
- e -> Right -> DIT -> .
- 3 -> Right, right, right, left, left -> DIT, DIT, DIT, DAH, DAH -> ...--
- 0 -> Left, left, left, left, left -> DAH, DAH, DAH, DAH, DAH -> -----
How to use
Project version 0.2
This project is compatible with both python2 and python3. Only compatible with English for the moment, compatibility with non-english extension will be added later. (Such as: à, æ, ź ...)
Translate English:
from MorseTranlator import MorseTranlator
mt = MorseTranlator()
english = "Test"
mt.translate(english) # Will return "- . ... -"Translate Morse code:
from MorseTranlator import MorseTranlator
mt = MorseTranlator()
morse = "- . ... -"
mt.translate(morse) # Will return "test"Requirement English sentence:
- Not special requirements, upper or lower letters, use of punctuations
Requirement Morse code:
- Every morse code must be separated by a space " ", words must be separated by "/"
- Example: ".-.. . / --. .-. .- ... / -.-. .----. . ... - / .-.. .- / ...- .. ." = "le gras c'est la vie"
As Morse code does not support capital letters, the output of a Morse code will always be in lower case. Up to you to add an capital letter on the first letter of the sentence and after a dot.
TODO
- Fix bug when found
- Add option to play morse sounds
- Add compatibility with special extension (might not be compatible with python2)