Technical documentation
See User documentation: USER.md
Document Version: 1.2 (28.02.2020 - DD/MM/YYYY)
Author: Valentin Lebon (valentin.lebon@epitech.eu)
- Table of Contents
- Documentation
You need Docker installed with docker-compose.
See Docker official documentation.
See Docker Compose official documentation.
Services are describes in the docker-compose.yml file.
To build and launch the application, first check if the database/secrets.env file exist (see 6. Changing MongoDB's admin's password). Then, open a console/terminal and execute the following command in the root directory of this application.
docker-compose up --build -dAll commands in this part have to be executed in the root directory of this application.
When changing the docker configuration, you'll have to execute:
docker-compose up -d --buildTo change cerbot (SSL) configuration, you'll have to change the Dockerfile in cerbot directory, then take a look at Changing a Dockerfile file.
When changing the apache configuration (under apache/conf directory), you'll have to exectute:
docker-compose stop apache && docker-compose up --build -d apacheIf you want to update the website, you'll need to execute the command below, then wait for it to finish.
docker-compose up frontIf you want to update the API, you'll need to execute this command:
docker-compose stop api && docker-compose up api_builder && docker-compose up -d apiTo change the admin's password of the MongoDB database, you'll have to change the MONGO_INITDB_ROOT_PASSWORD value in database/secrets.env. If this file doesn't exit, create it.
To change the admin's username of the MongoDB database, you'll have to change the MONGO_INITDB_ROOT_USERNAME value in database/secrets.env. If this file doesn't exit, create it.
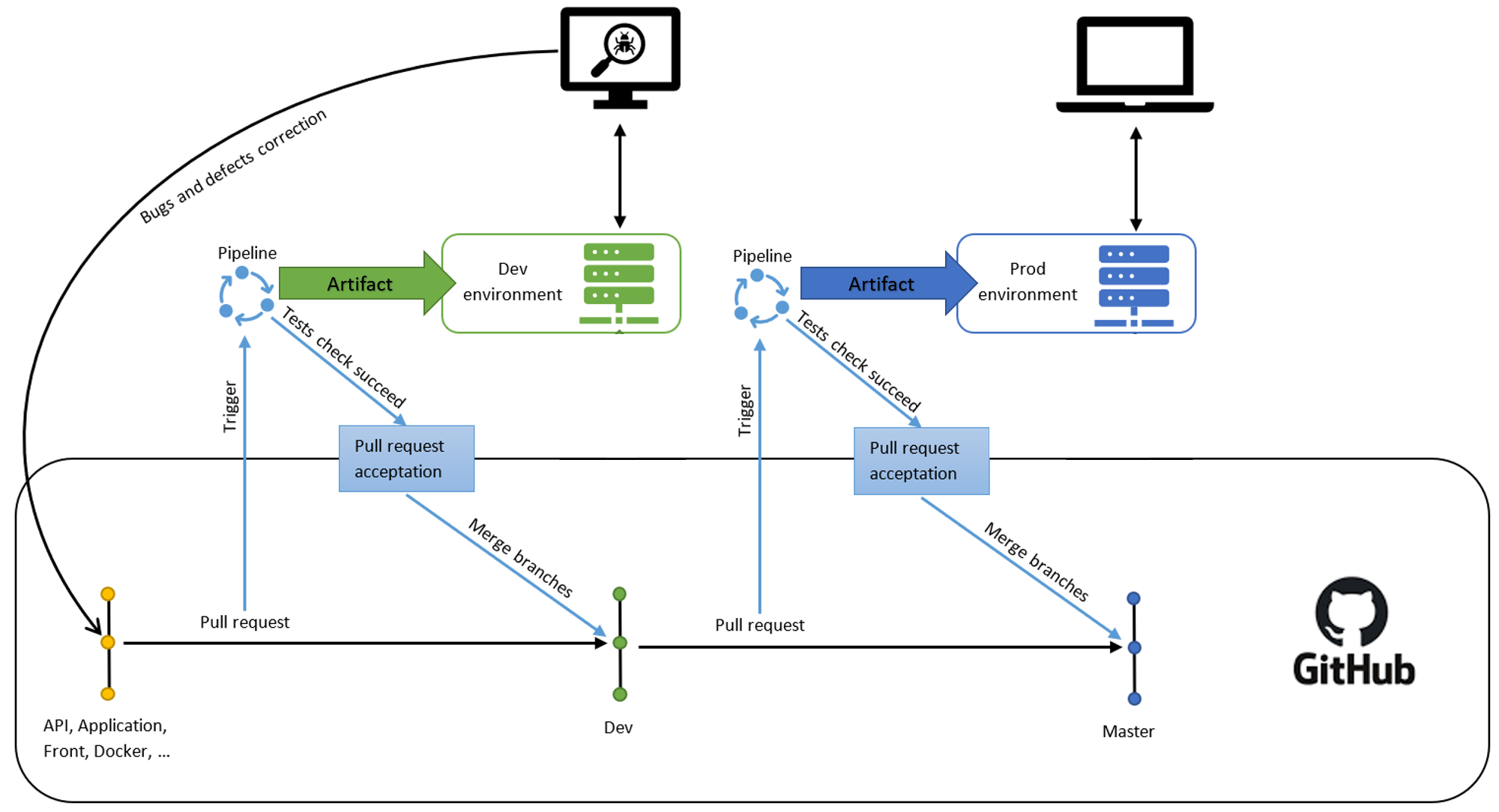
Gearstock's project's deployment's automation is taking place in two environments: Dev and Prod, each hosted on an Azure VM.
The Dev environment's purpose is to test together all the resources from the diferents branches to handle and correct (on those branches and NOT on dev branch) bugs and defects before uploading the resources to the Prod environment.
When a pull request is made to the dev branch, a pipeline is triggered. This pipeline will run tests on a separated environment, where the acceptance of the pull request is simulated.
If all the tests succeed, the pull request is accepted and the resulted resources are updated to the dev branch and then to the Dev environment.
The Prod environment's purpose is to provide the Gearstock's project to the final users.
When a pull request is made from the dev branch to the master branch, a pipeline is triggered. This pipeline will run tests on a separated environment, where the acceptance of the pull request is simulated.
If all the tests succeed, the pull request is accepted and the resulted resources are updated to the master branch and then to the Prod environment. The new version of the project is then available on Internet.