Have questions or want the latest news?
Join the PoolTogether Discord or follow us on Twitter:
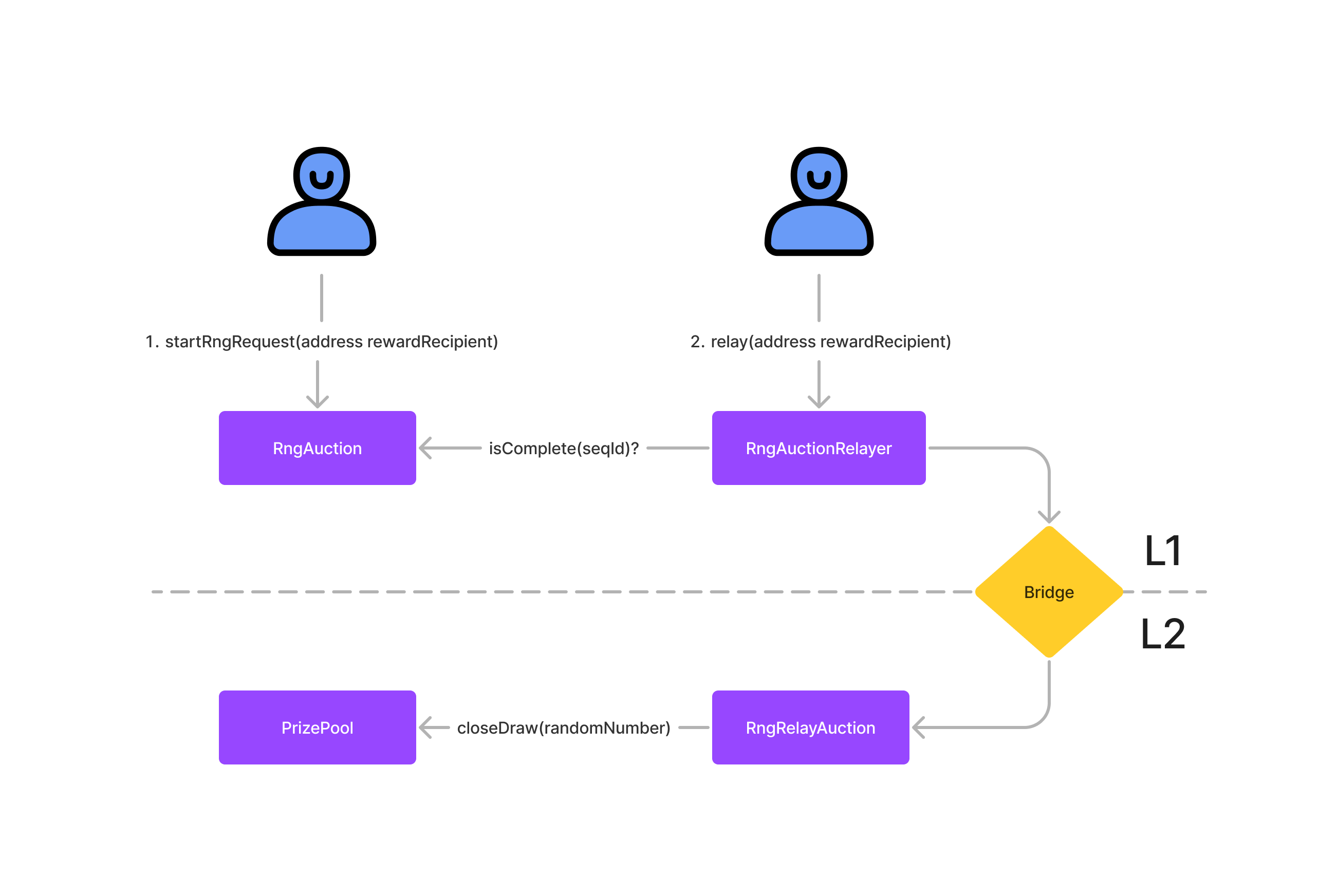
The Draw Auction is a suite of contracts that auctions off the transactions required to push a new random number to the Prize Pool.
PoolTogether V5 Prize Pools have periodic Draws. A "Draw" is when a random number is used to distribute the next batch of prizes to the users. This means that an external contract must source a random number and push the random number to the Prize Pool.
To incentivize new draws, each Prize Pool holds a reserve of tokens. A privileged "draw manager" is allowed to push random numbers to the Prize Pool and withdraw from the reserve.
The Draw Auction serves as the draw manager for all Prize Pools.
Random numbers come from an RNG service on Ethereum, and Prize Pools live on L2s. This means that we need to incentivize a sequence of transactions to generate a new random number on Ethereum, then bridge it to the Prize Pool on L2.
Each sequence includes two auctions:
- Starting the RNG request. This is when the RNG request kicks-off, and may require funds (the Chainlink VRF 2.0 needs LINK tokens).
- Relaying the RNG results to L2 via a bridge.
Starting the RNG request occurs on L1, and receiving the bridge RNG result occurs on L2. The auctions don't have pricing data, so they compute the reward as a fraction of the available Prize Pool reserve. This means that the auction on L1 does not need to know how much reserve is available in a Prize Pool on L2.
There are three key contracts:
- RngAuction: auctions off the initial RNG request
- RngAuctionRelayer: relays the RNG results to the RngRelayAuction
- RngRelayAuction: incentivizes the relay with an auction and triggers close draw on the Prize Pool
For more information, see the detailed PoolTogether V5 Draw Auction documentation
You may have to install the following tools to use this repository:
- Foundry to compile and test contracts
- direnv to handle environment variables
- lcov to generate the code coverage report
Install dependencies:
npm i
Copy .envrc.example and write down the env variables needed to run this project.
cp .envrc.example .envrc
Once your env variables are setup, load them with:
direnv allow
Run the following command to compile the contracts:
npm run compile
Forge is used for coverage, run it with:
npm run coverage
You can then consult the report by opening coverage/index.html:
open coverage/index.html
Husky is used to run lint-staged and tests when committing.
Prettier is used to format TypeScript and Solidity code. Use it by running:
npm run format
Solhint is used to lint Solidity files. Run it with:
npm run hint
A default Github Actions workflow is setup to execute on push and pull request.
It will build the contracts and run the test coverage.
You can modify it here: .github/workflows/coverage.yml
For the coverage to work, you will need to setup the MAINNET_RPC_URL repository secret in the settings of your Github repository.