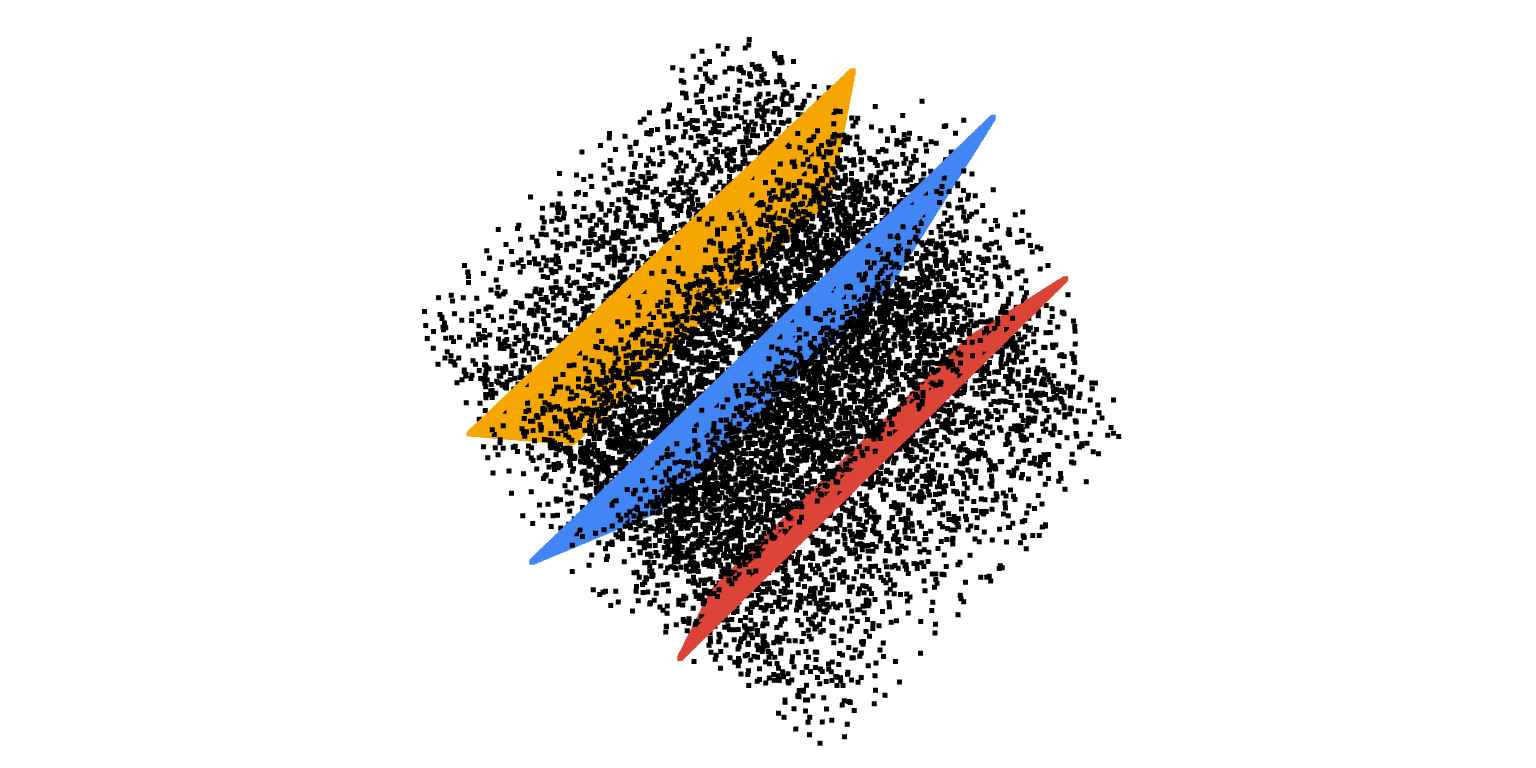This project relies on OpenCV using C++ 11 as the programming language, a multi-plane detection algorithm of point cloud is realized. At the same time, a relatively effective algorithm optimization is proposed. It has a good performance in the accuracy and speed of multi-plane detection.
Author: Yechun Ruan, Wanli Zhong, Changzhen Zhang
- OpenCV 4.5.1
- g++ 5.4
- Python 3.6 + Open3D Python version (optional,used for visualization)
Installation Tutorial: OpenCV, Open3D
The interface of 3D point cloud plane detection is:
/**
*
* @param labels The label that the point belongs to a certain plane, n × 1 matrix, n is equal to the size of the input point cloud (output)
* @param planes Holds the vector of plane equations, the equation is expressed as ax + by + cz + d = 0 (output)
* @param points3d Input point cloud data
* @param thr Threshold
* @param max_iterations Maximum number of iterations
* @param desired_num_planes Number of target planes
* @param grid_size Downsampling grid size, if less than or equal to 0, it means no downsampling
* @param normal Normal vector constraint, nullptr means no constraint is used, otherwise the detected plane normal vector satisfies the constraint
*/
void get_planes(cv::Mat &labels, std::vector<cv::Vec4f> &planes, cv::InputArray &points3d,
float thr, int max_iterations, int desired_num_planes, float grid_size, cv::Vec3f *normal);Explain in Detail:
- labels: The parameter type is
cv::Mat, n × 1 matrix, single channel, int type data, used to save the label of the point, 0 means not belonging to any plane, positive integer k means belonging to the number k plane - planes: The parameter type is
std::vector<cv::Vec4f>, which is used to save the equations of the plane. [a, b, c, d] quaternion corresponds to ax + by + cz + d = 0 - points3d: The parameter type is
cv::Mat, n × 3 matrix, single channel, float type data, used to store point cloud data - thr: The parameter type is
float, if the distance from the point to the plane is less than this value, the point is considered to belong to the inner point of the plane - max_iterations: The parameter type is
int, the iteration will stop when the number of iterations reaches this value, and the plane equation with the most interior points will be output - desired_num_planes: The parameter type is
int, this value represents the number of planes that you want to find from the point cloud - grid_size: The parameter type is
float, the side length of the voxel filtering down-sampling grid, if it is less than or equal to 0, it means no down-sampling processing - normal: The parameter type is
cv::Vec3f*, the normal vector of the plane in the three-dimensional space, nullptr means no constraint is used, otherwise the detected plane normal vector satisfies the constraint
- Clone
git clone https://github.com/No-Plane-Cannot-Be-Detected/Plane_Detection- Compile
cd Plane_Detection
cmake .
makeNote: The above are the compilation steps for Linux operating system. If it is windows operating system, please modify the ninth line of the CMakeLists.txt file and set the OpenCV directory to the corresponding installation directory.
- Run
- DEMO 1
./Point-Cloud-Plane-Detection 3 0.2 0.2 1000 ./data/check.ply 0 0 0- DEMO 2
./Point-Cloud-Plane-Detection 3 0.5 0.22 1000 ./data/Cassette_GT_.ply-sampling-0.2.ply 0 0 0The incoming parameters are the number of target planes, the threshold, the grid size, the maximum number of iterations, the path of the point cloud file, and the normal vector constraint (0, 0, 0 means not using the normal vector constraint).
Point cloud visualization can be achieved through Open3D (APP version, C++ version, Python version), PCL (C++ version, Python version), etc.
The Python version of the Open3D visualized point cloud sample code is in ./viz/Pointcloud-Visualization-With-Open3D.py
- DEMO
python ./Pointcloud-Visualization-With-Open3D.py -cloud "../data/check.ply" -label "../data/check_label.txt".
├── data (Data input and output directory)
│ ├── Cassette_GT_.ply-sampling-0.2.ply
│ └── check.ply
│ └── check_label.txt
├── images (Document picture directory)
├── include (Header file directory)
│ ├── ransac.h
│ └── utils.h
├── source (Source file directory)
│ ├── main.cpp
│ ├── ransac.cpp
│ └── utils.cpp
└── viz (Visual sample code directory)
└── Pointcloud-Visualization-With-Open3D.py
Some datasets are from: IQmulus & TerraMobilita Contest. Download links: Zones 0-4, Cassette_idclass.zip.
Another part of the dataset is generated by standard plane equation with noise points.
Technical Background and Scheme Design
Radar real-time demonstration video of ZhiRen activity room in SUSTech
- R. Adams and L. Bischof. Seeded region growing. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 16(6):641-647, 19 94.
- Dorit Borrmann, Jan Elseberg, Kai Lingemann, and Andreas Nuchter. The 3d hough transform for plane detection in point clouds: A review and a new accumulator design. 3D Research, 0202, 06 2011.
- Onduřej Chum, Jiří Matas, and Josef Kittler. Locally optimized ransac. In Bernd Michaelis and Gerald Krell, editors, Pattern Recognition, pages 236-243, Berlin, Heidelberg, 2003. Springer Berlin Heidelberg.
- M. Fischler and R. Bolles. Random sample consensus: A paradigm for model fitting with applications to image analysis and automated cartography. Communications of the ACM, 24(6):381-395, 1981.
- Fork this warehouse
- Create new Feat_xxx branch
- Submit the code
- New Pull Request