English | 中文
| OS (Compiler Version) | Status |
|---|---|
| Ubuntu 22.04 (clang 14.0.0) | |
| Ubuntu 22.04 (gcc 11.2.0) | |
| macOS Monterey 12 (AppleClang 14.0.0.14000029) | |
| Windows Server 2022 (MSVC 19.33.31630.0) |
cinatra是一个高性能易用的http框架,它是用modern c++(c++20)开发的,它的目标是提供一个快速开发的c++ http框架。它的主要特点如下:
- 统一而简单的接口
- header-only
- 跨平台
- 高效
- 支持面向切面编程
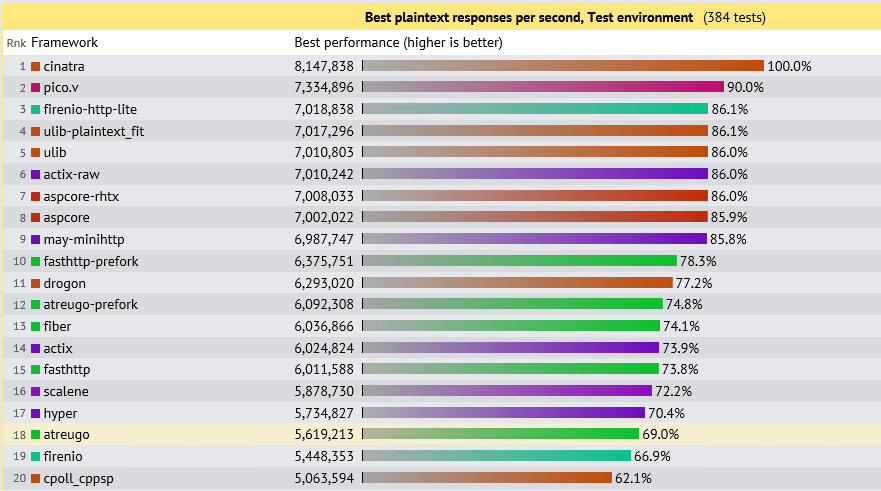
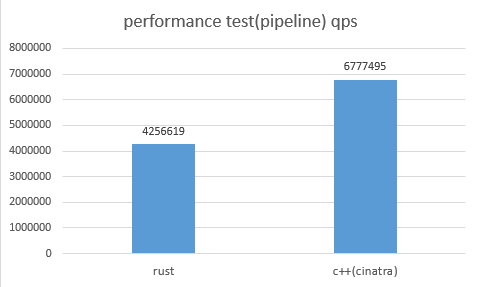
cinatra目前支持了http1.1/1.0, ssl和websocket, 你可以用它轻易地开发一个http服务器,比如常见的数据库访问服务器、文件上传下载服务器、实时消息推送服务器,你也可以基于cinatra开发一个mqtt服务器。 cinatra是世界上性能最好的http服务器之一,性能测试详见性能测试
除此之外,cinatra 还提供了一个基于C++20 协程的http(https) client,包括普通get/post请求、文件上传下载和web socket、redirect、proxy等功能。
cinatra目前被很多公司在使用,在这里可以看到谁在用cinatra.
- C++20 编译器 (gcc 10.2, clang 13, Visual Studio 2022,或者更高的版本)
cinatra是header-only的,引用include头文件目录,并设置如下编译选项:
如果 linux, 设置:
set(CMAKE_CXX_FLAGS "${CMAKE_CXX_FLAGS} -pthread -std=c++20")
如果 g++ 编译,再设置:
set(CMAKE_CXX_FLAGS "${CMAKE_CXX_FLAGS} -fcoroutines")
set(CMAKE_CXX_FLAGS_RELEASE "${CMAKE_CXX_FLAGS_RELEASE} -fno-tree-slp-vectorize")
cinatra支持通过指令集优化其内部逻辑,其通过宏来控制是否使用指令集。使用之前请确保cpu支持。
使用如下命令即可编译带simd优化的cinatra。注意只能开启一种simd指令集优化,开启多个会导致编译失败。
cmake -DENABLE_SIMD=SSE42 .. # 启用sse4.2指令集
cmake -DENABLE_SIMD=AVX2 .. # 启用avx2指令集
cmake -DENABLE_SIMD=AARCH64 .. # arm环境下,启用neon指令集 #include "include/cinatra.hpp"
using namespace cinatra;
int main() {
int max_thread_num = std::thread::hardware_concurrency();
coro_http_server server(max_thread_num, 8080);
server.set_http_handler<GET, POST>("/", [](coro_http_request& req, coro_http_response& res) {
res.set_status_and_content(status_type::ok, "hello world");
});
server.sync_start();
return 0;
}5行代码就可以实现一个简单http服务器了,用户不需要关注多少细节,直接写业务逻辑就行了。
#include "cinatra.hpp"
struct person_t {
void foo(coro_http_request &, coro_http_response &res) {
res.set_status_and_content(status_type::ok, "ok");
}
};
async_simple::coro::Lazy<void> basic_usage() {
coro_http_server server(1, 9001);
server.set_http_handler<GET>(
"/get", [](coro_http_request &req, coro_http_response &resp) {
resp.set_status_and_content(status_type::ok, "ok");
});
server.set_http_handler<GET>(
"/coro",
[](coro_http_request &req,
coro_http_response &resp) -> async_simple::coro::Lazy<void> {
resp.set_status_and_content(status_type::ok, "ok");
co_return;
});
server.set_http_handler<GET>(
"/in_thread_pool",
[](coro_http_request &req,
coro_http_response &resp) -> async_simple::coro::Lazy<void> {
// will respose in another thread.
co_await coro_io::post([&] {
// do your heavy work here when finished work, response.
resp.set_status_and_content(status_type::ok, "ok");
});
});
server.set_http_handler<POST, PUT>(
"/post", [](coro_http_request &req, coro_http_response &resp) {
auto req_body = req.get_body();
resp.set_status_and_content(status_type::ok, std::string{req_body});
});
server.set_http_handler<GET>(
"/headers", [](coro_http_request &req, coro_http_response &resp) {
auto name = req.get_header_value("name");
auto age = req.get_header_value("age");
assert(name == "tom");
assert(age == "20");
resp.set_status_and_content(status_type::ok, "ok");
});
server.set_http_handler<GET>(
"/query", [](coro_http_request &req, coro_http_response &resp) {
auto name = req.get_query_value("name");
auto age = req.get_query_value("age");
assert(name == "tom");
assert(age == "20");
resp.set_status_and_content(status_type::ok, "ok");
});
server.set_http_handler<cinatra::GET, cinatra::POST>(
"/users/:userid/subscriptions/:subid",
[](coro_http_request &req, coro_http_response &response) {
assert(req.params_["userid"] == "ultramarines");
assert(req.params_["subid"] == "guilliman");
response.set_status_and_content(status_type::ok, "ok");
});
person_t person{};
server.set_http_handler<GET>("/person", &person_t::foo, person);
server.async_start();
std::this_thread::sleep_for(300ms); // wait for server start
coro_http_client client{};
auto result = co_await client.async_get("http://127.0.0.1:9001/get");
assert(result.status == 200);
assert(result.resp_body == "ok");
for (auto [key, val] : result.resp_headers) {
std::cout << key << ": " << val << "\n";
}
result = co_await client.async_get("/coro");
assert(result.status == 200);
result = co_await client.async_get("/in_thread_pool");
assert(result.status == 200);
result = co_await client.async_post("/post", "post string",
req_content_type::string);
assert(result.status == 200);
assert(result.resp_body == "post string");
client.add_header("name", "tom");
client.add_header("age", "20");
result = co_await client.async_get("/headers");
assert(result.status == 200);
result = co_await client.async_get("/query?name=tom&age=20");
assert(result.status == 200);
result = co_await client.async_get(
"http://127.0.0.1:9001/users/ultramarines/subscriptions/guilliman");
assert(result.status == 200);
// make sure you have installed openssl and enable CINATRA_ENABLE_SSL
#ifdef CINATRA_ENABLE_SSL
coro_http_client client2{};
result = co_await client2.async_get("https://baidu.com");
assert(result.status == 200);
#endif
}
int main() {
async_simple::coro::syncAwait(basic_usage());
} #include "cinatra.hpp"
using namespace cinatra;
//日志切面
struct log_t
{
bool before(coro_http_request& req, coro_http_response& res) {
std::cout << "before log" << std::endl;
return true;
}
bool after(coro_http_request& req, coro_http_response& res) {
std::cout << "after log" << std::endl;
return true;
}
};
//校验的切面
struct check {
bool before(coro_http_request& req, coro_http_response& res) {
std::cout << "before check" << std::endl;
if (req.get_header_value("name").empty()) {
res.set_status_and_content(status_type::bad_request);
return false;
}
return true;
}
bool after(coro_http_request& req, coro_http_response& res) {
std::cout << "after check" << std::endl;
return true;
}
};
//将信息从中间件传输到处理程序
struct get_data {
bool before(coro_http_request& req, coro_http_response& res) {
req.set_aspect_data("hello world");
return true;
}
}
int main() {
coro_http_server server(std::thread::hardware_concurrency(), 8080);
server.set_http_handler<GET, POST>("/aspect", [](coro_http_request& req, coro_http_response& res) {
res.set_status_and_content(status_type::ok, "hello world");
}, check{}, log_t{});
server.set_http_handler<GET,POST>("/aspect/data", [](coro_http_request& req, coro_http_response& res) {
auto& val = req.get_aspect_data();
res.set_status_and_content(status_type::ok, std::move(val[0]));
}, get_data{});
server.sync_start();
return 0;
}本例中有两个切面,一个校验http请求的切面,一个是日志切面,这个切面用户可以根据需求任意增加。本例会先检查http请求的合法性,如果不合法就会返回bad request,合法就会进入下一个切面,即日志切面,日志切面会打印出一个before表示进入业务逻辑之前的处理,业务逻辑完成之后会打印after表示业务逻辑结束之后的处理。
本代码演示如何使用RESTful路径参数。下面设置了两个RESTful API。第一个API当访问,比如访问这样的urlhttp://127.0.0.1:8080/numbers/1234/test/5678时服务器可以获取到1234和5678这两个参数,第一个RESTful API的参数是(\d+)是一个正则表达式表明只能参数只能为数字。获取第一个参数的代码是req.matches_[1]。因为每一个req不同所以每一个匹配到的参数都放在request结构体中。
同时还支持任意字符的RESTful API,即示例的第二种RESTful API"/string/:id/test/:name",要获取到对应的参数使用req.get_query_value函数即可,其参数只能为注册的变量(如果不为依然运行但是有报错),例子中参数名是id和name,要获取id参数调用req.get_query_value("id")即可。示例代码运行后,当访问http://127.0.0.1:8080/string/params_1/test/api_test时,浏览器会返回api_test字符串。
#include "cinatra.hpp"
using namespace cinatra;
int main() {
int max_thread_num = std::thread::hardware_concurrency();
coro_http_server server(max_thread_num, 8080);
server.set_http_handler<GET, POST>(
R"(/numbers/(\d+)/test/(\d+))", [](request &req, response &res) {
std::cout << " matches[1] is : " << req.matches_[1]
<< " matches[2] is: " << req.matches_[2] << std::endl;
res.set_status_and_content(status_type::ok, "hello world");
});
server.set_http_handler<GET, POST>(
"/string/:id/test/:name", [](request &req, response &res) {
std::string id = req.get_query_value("id");
std::cout << "id value is: " << id << std::endl;
std::cout << "name value is: " << std::string(req.get_query_value("name")) << std::endl;
res.set_status_and_content(status_type::ok, std::string(req.get_query_value("name")));
});
server.sync_start();
return 0;
}
cinatra 支持反向代理也很简单,3步5行代码就可以了。 先看一个简单的例子:
reverse_proxy proxy_rr(10, 8091);
proxy_rr.add_dest_host("127.0.0.1:9001");
proxy_rr.add_dest_host("127.0.0.1:9002");
proxy_rr.add_dest_host("127.0.0.1:9003");
proxy_rr.start_reverse_proxy<GET, POST>("/rr", true,
coro_io::load_blance_algorithm::RR);第一步创建一个代理服务器,设置其线程数和端口; 第二步添加需要访问的服务器列表; 第三步启动代理服务,设置loadbalance 策略,这里选择的是round robin 策略。
在浏览器或者client里访问http://127.0.0.1:8091/rr 就会根据RR 策略选择三个服务器中的一个。
如果要选择random 策略就设置为coro_io::load_blance_algorithm::random。
如果要选择weight round robin 策略,就需要设置服务器权重。
reverse_proxy proxy_wrr(10, 8090);
proxy_wrr.add_dest_host("127.0.0.1:9001", 10);
proxy_wrr.add_dest_host("127.0.0.1:9002", 5);
proxy_wrr.add_dest_host("127.0.0.1:9003", 5);
proxy_wrr.start_reverse_proxy<GET, POST>("/wrr", true,
coro_io::load_blance_algorithm::WRR);在浏览器或者client里访问http://127.0.0.1:8090/wrr ,第一次和第二次会返回9001服务器的结果,第三次返回9002服务器的结果,第四次返回9003服务器的结果,第五次又重新返回9001服务器的结果,这就是WRR的策略。
void test_sync_client() {
{
std::string uri = "http://www.baidu.com";
coro_http_client client{};
auto result = client.get(uri);
assert(!result.net_err);
print(result.resp_body);
result = client.post(uri, "hello", req_content_type::json);
print(result.resp_body);
}
{
coro_http_client client{};
std::string uri = "http://cn.bing.com";
auto result = client.get(uri);
assert(!result.net_err);
print(result.resp_body);
result = client.post(uri, "hello", req_content_type::json);
print(result.resp_body);
}
}
#ifdef CINATRA_ENABLE_SSL
void test_coro_http_client() {
using namespace cinatra;
coro_http_client client{};
client.init_ssl("../../include/cinatra", "server.crt"); // optinal 一般情况下可以不调用这一行
auto data = client.get("https://www.bing.com");
std::cout << data.resp_body << "\n";
data = client.get("https://www.bing.com");
std::cout << data.resp_body << "\n";
}
#endif
async_simple::coro::Lazy<void> test_async_client() {
std::string uri = "http://www.baidu.com";
{
coro_http_client client{};
auto data = co_await client.async_get(uri);
print(data.status);
data = co_await client.async_get(uri);
print(data.status);
data = co_await client.async_post(uri, "hello", req_content_type::string);
print(data.status);
}
#ifdef CINATRA_ENABLE_SSL
std::string uri2 = "https://www.baidu.com";
std::string uri3 = "https://cn.bing.com";
coro_http_client client{};
client.init_ssl("../../include/cinatra", "server.crt");
data = co_await client.async_get(uri2);
print(data.status);
data = co_await client.async_get(uri3);
print(data.status);
#endif
}
void start_server() {
coro_http_server server(1, 9001);
server.set_http_handler<POST>(
"/form_data",
[](coro_http_request &req,
coro_http_response &resp) -> async_simple::coro::Lazy<void> {
assert(req.get_content_type() == content_type::multipart);
auto boundary = req.get_boundary();
multipart_reader_t multipart(req.get_conn());
while (true) {
auto part_head = co_await multipart.read_part_head(boundary);
if (part_head.ec) {
co_return;
}
std::cout << part_head.name << "\n";
std::cout << part_head.filename << "\n";// if form data, no filename
auto part_body = co_await multipart.read_part_body(boundary);
if (part_body.ec) {
co_return;
}
std::cout << part_body.data << "\n";
if (part_body.eof) {
break;
}
}
resp.set_status_and_content(status_type::ok, "multipart finished");
});
server.start();
}async_simple::coro::Lazy<void> test_upload() {
std::string uri = "http://127.0.0.1:9001/form_data";
coro_http_client client{};
client.add_str_part("hello", "coro_http_client");
client.add_file_part("test", "yourfile.jpg");
result = co_await client.async_upload_multipart(uri);
print(result.status);
std::cout << "upload finished\n";
}
async_simple::coro::Lazy<void> test_download() {
coro_http_client client{};
std::string uri =
"http://www.httpwatch.com/httpgallery/chunked/chunkedimage.aspx";
std::string filename = "test.jpg";
std::error_code ec{};
std::filesystem::remove(filename, ec);
auto r = co_await client.async_download(uri, filename);
assert(!r.net_err);
assert(r.status == 200);
std::cout << "download finished\n";
}
async_simple::coro::Lazy<void> test_websocket() {
coro_http_client client{};
auto r = co_await client.connect("ws://localhost:8090/ws");
if (r.net_err) {
co_return;
}
co_await client.write_websocket("hello websocket");
auto data = co_await client.read_websocket();
CHECK(data.resp_body == "hello websocket");
co_await client.write_websocket("test again");
data = co_await client.read_websocket();
CHECK(data.resp_body == "test again");
co_await client.write_websocket("ws close");
data = co_await client.read_websocket();
CHECK(data.net_err == asio::error::eof);
CHECK(data.resp_body == "ws close");
}cinatra提供了一个高性能的http1.1 压测工具, 它是基于coro_http_client 实现的,内部通过多线程和协程实现了高效的压测,能够在单核或多核cpu上发送大量请求以此来测试服务器性能。
./cinatra_press_tool -t 4 -c 40 -d 30s http://127.0.0.1上面的命令代表使用4个线程并且保持40个连接打开(协程)对网址http://127.0.0.1进行30s的基准测试。
输出如下:
Running 30s test @ http://127.0.0.1
4 threads and 40 connections
Thread Status Avg Max Variation Stdev
Latency 4.12ms 8.15ms 3.367ms 1.835ms
462716 requests in 30.001s, 592.198250MB read, total: 462716, errors: 0
Requests/sec: 15423.86666667
Transfer/sec: 19.739390MB
-c, --connections total number of HTTP connections to keep open with
each thread handling N = connections/threads (int)
-d, --duration duration of the test, e.g. 2s, 2m, 2h (string [=15s])
-t, --threads total number of threads to use (int [=1])
-H, --headers HTTP headers to add to request, e.g. "User-Agent: coro_http_press"
add multiple http headers in a request need to be separated by ' && '
e.g. "User-Agent: coro_http_press && x-frame-options: SAMEORIGIN" (string [=])
-r, --readfix read fixed response (int [=0])
-?, --help print this message
这里有两个参数与wrk不同
-H参数,它表示添加http头到http请求中,该参数不止可以添加一个http头还可以以&&符号(4个字符)为分隔符来组装多个http头到http请求。
比如-H User-Agent: coro_http_press就是添加一个http头,而-H User-Agent: coro_http_press && x-frame-options: SAMEORIGIN则为添加User-Agent: coro_http_press和x-frame-options: SAMEORIGIN两个http头到http请求。添加三个以及多个http头的方法和上述方法相同。
-r参数,它表示是否读固定长度的response,这个参数可以避免频繁的解析response优化性能,有些服务器对于相同的请求返回的长度可能不同,这种情况下不设置这个参数或者将它设置为0。
websocket的业务函数是会多次进入的,因此写业务逻辑的时候需要注意,推荐按照示例中的方式去做。
cinatra depends on asio and async_simple.
press_tool depends on cinatra and cmdline.
A submodule of cinatra is iguana.
When you want to use this submodule, using the command git submodule init will pull the iguana library.
If you want to use the latest iguana, please use the command git submodule update --remote.
qq群:545605838